Trying to quit social media addiction? Welcome to our digital detox series! This series focuses on how to stop digital and screen addictions. Findall our posts about digital addictions. Today, let’s talk about how to quit the social media addiction.

- What’s the social media addiction?
- Addiction to social media, a “real” addiction?
- What’s considered social media addiction?
- How much social media is too much?
- Some social media addiction facts & statistics
- Symptoms & Causes of the social media addiction
- Why is social media so addictive?
- Possible causes of social media dependency
- Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of social media addiction
- Problems, impacts & bad effects of social media
- Some benefits of social media
- Health problems
- Impact on brain & mental health
- Impact on relationships
- How to stop & quit your social media addiction
- Main steps and solutions to break the social media addiction
- Best social media blocker apps & functionalities
- Where to seek extra help?
- Conclusion
- To Go Further
- How to help someone with social media addiction
- Best books about social media addiction
- Research about social media addiction
What is the social media addiction?
About social media
Social media refers to digital platforms and applications that enable users to create, share, and interact with content and each other, fostering communication and community building globally. Examples include Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Addiction to social media, a “real” addiction?
Officially an addiction?
First, let’s have a look at the DSM-5,the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Does it include social media addiction?
As of the latest update, social media addiction is not officially listed as a distinct disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5.. The DSM-5, published by the American Psychiatric Association, is a widely used resource for diagnosing mental health conditions. While it does not specifically recognize social media addiction as a standalone disorder, it does acknowledge internet gaming disorder in its section on conditions that require further research.
Although social media addiction is not formally recognized, mental health professionals are increasingly aware of the potential negative impacts of excessive social media use. This includes issues such as anxiety, depression, and impaired social functioning. Researchers and clinicians may use criteria from related disorders, such as substance use disorders or behavioral addictions, to assess and address problematic social media use.
If you or someone you know is struggling with excessive social media use, it might be helpful to consult a mental health professional who can provide guidance and support tailored to individual needs.
So what does “social media addiction” mean?
What Is Social Media Addiction?
Social media addiction is when someone becomes overly dependent on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, or TikTok. This means they spend excessive amounts of time browsing, posting, and interacting online, often to the point where it interferes with their daily life. Here are a few key signs:
– Constant Checking: Feeling the need to check notifications or updates repeatedly throughout the day.
– Neglecting Responsibilities: Putting off work, school, or personal tasks to spend more time on social media.
– Mood Swings: Feeling anxious or upset when unable to access social media.
– Isolation: Choosing online interactions over face-to-face relationships, leading to loneliness.
Social media addiction can impact mental health, leading to issues like anxiety, depression, and decreased self-esteem. To overcome it, setting time limits, taking regular breaks, and engaging in offline activities can help create a healthier balance.
What is considered social media addiction?
Diagnosing social media addiction can be challenging, as it is not yet officially recognized as a distinct clinical disorder in major diagnostic manuals like the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) or the ICD-11 (International Classification of Diseases). However, researchers and mental health professionals have identified several criteria that can help in assessing whether an individual might be struggling with social media addiction. These criteria often draw parallels with other behavioral addictions. Here are some commonly considered factors:
- 1. Preoccupation with Social Media: Constantly thinking about social media or planning to use it. This includes feeling a strong urge to check social media accounts frequently.
- 2. Increased Use Over Time: Needing to spend more time on social media to achieve the same level of satisfaction or excitement.
- 3. Failed Attempts to Cut Back: Making unsuccessful efforts to reduce time spent on social media or to quit altogether.
- 4. Loss of Interest in Other Activities: Losing interest in hobbies, activities, or social interactions that were once enjoyable, in favor of spending time on social media.
- 5. Use Despite Negative Consequences: Continuing to use social media despite experiencing negative impacts on personal, professional, or academic life.
- 6. Withdrawal Symptoms: Experiencing feelings of anxiety, irritability, or sadness when unable to access social media.
- 7. Deception: Lying to family members, friends, or therapists about the extent of social media use.
- 8. Escapism: Using social media as a way to escape from personal problems or to relieve negative moods such as guilt, anxiety, or depression.
- 9. Jeopardizing Relationships or Opportunities: Sacrificing important relationships or career opportunities due to excessive social media use.
- 10. Neglecting Responsibilities: Failing to fulfill obligations at work, school, or home due to time spent on social media.
If someone exhibits several of these behaviors, it might indicate a problematic relationship with social media. However, a comprehensive assessment by a mental health professional is recommended for an accurate diagnosis and to explore potential underlying issues. Treatment approaches may include cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness practices, and developing healthier digital habits.
How much social media is too much?
Determining how much time spent on social media is “too much” can vary significantly depending on individual circumstances, goals, and mental health. However, there are some general guidelines and considerations that can help individuals assess their social media usage.
### General Guidelines
- 1. Average Usage: Studies suggest that the average person spends about 2 to 3 hours per day on social media. If your usage significantly exceeds this, it might be worth evaluating the impact on your life.
- 2. Purpose and Productivity: Consider the purpose of your social media use. If it’s primarily for work, networking, or staying informed, the time spent might be more justifiable. However, if it detracts from productivity or personal goals, it might be excessive.
- 3. Mental Health Impact: Pay attention to how social media affects your mental health. If you notice increased anxiety, depression, or feelings of inadequacy after using social media, it might be time to cut back.
- 4. Social and Personal Life: Evaluate if social media is interfering with your real-life relationships and responsibilities. If you find yourself choosing social media over personal interactions or important tasks, it might be a sign of overuse.
- 5. Sleep and Physical Health: Excessive social media use, especially before bed, can impact sleep quality.
Additionally, long periods of screen time can affect physical health, contributing to issues like eye strain or a sedentary lifestyle.
### Recommendations
– Set Limits: Use apps or built-in phone settings to monitor and limit your daily social media use.
– Scheduled Breaks: Implement regular breaks from social media, such as digital detox weekends or designated screen-free hours.
– Mindful Usage: Be intentional about your social media activities. Focus on meaningful interactions rather than mindless scrolling.
– Alternative Activities: Replace some of your social media time with other fulfilling activities, such as reading, exercise, or hobbies.
Ultimately, the key is balance. Social media can be a valuable tool for connection and information, but it’s important to ensure it doesn’t negatively impact your well-being or quality of life. Regularly assessing your usage and its effects can help maintain a healthy relationship with social media.
Some social media addiction facts & statistics

Social media addiction has become a growing concern as platforms continue to integrate into daily life. Here are some statistics and insights into the phenomenon:
- 1. Prevalence: Studies suggest that a significant portion of the global population exhibits signs of social media addiction. Estimates vary, but some research indicates that around 5-10% of social media users may meet the criteria for addiction.
- 2. Demographics: Younger individuals, particularly teenagers and young adults, are more susceptible to social media addiction. This demographic often reports higher usage rates and a stronger emotional attachment to their online presence.
- 3. Time Spent: On average, people spend about 2.5 hours per day on social media platforms. This figure can be much higher for those with addictive tendencies, sometimes reaching upwards of 5-6 hours daily.
- 4. Psychological Impact: Social media addiction is linked to various mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. The constant need for validation and fear of missing out (FOMO) can exacerbate these conditions.
- 5. Behavioral Signs: Common indicators of social media addiction include neglecting personal or professional responsibilities, experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not online, and using social media as a primary means of coping with stress.
- 6. Platform Usage: Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, TikTok, and Snapchat are often cited in studies as being particularly addictive due to their design, which encourages continuous engagement through features like infinite scrolling and push notifications.
- 7. Economic Impact: The addictive nature of social media has significant economic implications. Companies invest heavily in advertising on these platforms, capitalizing on the high engagement rates. However, productivity losses due to excessive use can negatively impact workplaces.
- 8. Intervention and Treatment: Recognizing social media addiction as a legitimate concern, some mental health professionals offer treatment programs similar to those for substance abuse. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and digital detoxes are common approaches.
- 9. Parental Concerns: Parents are increasingly worried about their children’s social media habits. Many express concerns about cyberbullying, privacy, and the impact on academic performance.
- 10. Global Trends: While social media addiction is a worldwide issue, its prevalence and impact can vary by region due to cultural, economic, and technological factors. Developed countries with high internet penetration rates often report higher instances of addiction.
Addressing social media addiction requires a multifaceted approach, involving education, personal responsibility, and potentially regulatory measures to ensure that these platforms contribute positively to users’ lives.
Is the social media addiction widespread?
Yes, a significant number of people are considered to be addicted to social media. This phenomenon has been widely studied and discussed by psychologists, sociologists, and other experts. Several factors contribute to social media addiction, including the platforms’ design, which often encourages prolonged use through features like infinite scrolling, notifications, and algorithms that tailor content to individual preferences.
Research indicates that social media addiction can lead to various negative outcomes, such as decreased productivity, impaired social interactions, and mental health issues like anxiety and depression. The constant need for validation through likes, comments, and shares can also affect self-esteem and overall well-being.
It’s important to note that while many people use social media regularly, not everyone who spends a lot of time on these platforms is necessarily addicted. Addiction is characterized by compulsive behavior that negatively impacts one’s life and is difficult to control despite adverse consequences.
Efforts to combat social media addiction include increasing awareness, promoting digital literacy, and encouraging healthier online habits. Some individuals find success in setting boundaries, such as limiting screen time or taking regular breaks from social media.
Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of social media addiction
Why is social media so addictive?
Why Is Social Media So Addictive?
Social media has a knack for keeping us hooked, and here’s why:
- 1. Instant Feedback: Every like, comment, or share gives us a quick boost of happiness. This instant gratification makes us want to keep checking for more.
- 2. Dopamine Delight: Our brains release dopamine when we receive notifications. This “feel-good” chemical makes using social media feel rewarding and encourages us to come back for more.
- 3. Connection and Belonging: Social media helps us stay connected with friends and family, creating a sense of community and belonging that we all crave.
- 4. Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Seeing others’ posts can make us worry we’re missing out on fun events or important news, pushing us to stay constantly updated.
- 5. Personalized Content: Algorithms tailor what we see based on our interests, ensuring that the content is always engaging and hard to stop scrolling through.
- 6. Endless Variety: With endless posts, videos, and stories, there’s always something new to catch our eye, making it easy to lose track of time.
- 7. Self-Expression: Social media provides a platform to express ourselves, share our lives, and receive validation, which can be very satisfying.
Understanding these factors can help us use social media in a healthier, more balanced way. It’s all about finding that sweet spot where we enjoy the benefits without getting too carried away!
Possible causes of social media dependency
Social media addiction is a growing concern, and its causes are multifaceted, involving psychological, social, and technological factors. Here are some of the primary causes:
- 1. Dopamine Release: Social media platforms are designed to trigger the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. Every like, comment, or share can give users a dopamine hit, reinforcing the behavior and leading to habitual use.
- 2. Social Validation: Many people seek validation and approval from others, and social media provides a platform for receiving immediate feedback. This need for social validation can drive individuals to spend excessive time online, constantly checking for updates and responses.
- 3. Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Social media can create a perception that others are leading more exciting or fulfilling lives, prompting users to stay constantly connected to avoid missing out on experiences or information.
- 4. Escapism: For some, social media serves as an escape from reality, providing a distraction from personal issues, stress, or boredom. This can lead to excessive use as individuals seek to avoid confronting real-life problems.
- 5. Peer Pressure: Social media usage is often influenced by peer behavior. If a person’s social circle is highly active on social media, they may feel pressured to engage similarly to maintain social connections and relevance.
- 6. Algorithmic Design: Platforms use sophisticated algorithms to keep users engaged by showing content tailored to their interests. This personalized content can create a loop of continuous engagement, making it difficult for users to disconnect.
- 7. Availability and Accessibility: With smartphones and constant internet access, social media is always available, making it easy for users to check their accounts frequently throughout the day.
- 8. Lack of Awareness: Many users are not fully aware of the time they spend on social media or the impact it has on their mental health and productivity. This lack of awareness can contribute to unchecked usage.
- 9. Psychological Traits: Certain personality traits, such as high levels of narcissism, anxiety, or low self-esteem, can make individuals more susceptible to social media addiction as they may use these platforms to fulfill unmet psychological needs.
- 10. Habit Formation: Over time, frequent social media use can become a habit. Users may find themselves automatically reaching for their phones without conscious thought, reinforcing the cycle of addiction.
Understanding these causes is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate social media addiction, such as setting usage limits, increasing awareness, and promoting healthier online habits.
Signs & Symptoms of social media addiction
Now let’s see if you have the social media addiction problem.
Social media has become an integral part of our daily lives, offering a platform for connection, information, and entertainment. However, for some, the line between healthy use and addiction can blur. Here are seven signs that you might be a social media addict:
- 1. Constant Checking: One of the most telling signs of social media addiction is the compulsive need to check your accounts. If you find yourself reaching for your phone first thing in the morning, during meals, or even in the middle of the night, it may be time to evaluate your habits.
- 2. Neglecting Responsibilities: When social media starts interfering with your daily responsibilities, such as work, school, or household chores, it could indicate an addiction. If you find yourself procrastinating or avoiding tasks to scroll through your feeds, it may be a sign of a deeper issue.
- 3. Mood Swings: Your mood may become heavily influenced by your social media interactions. For instance, receiving likes or positive comments might boost your mood, while negative feedback or lack of engagement could lead to feelings of anxiety or depression.
- 4. Withdrawal Symptoms: Just like with any addiction, withdrawal symptoms can occur when you try to cut back on social media use. These symptoms might include irritability, restlessness, or a strong urge to log back in, even when you’ve decided to take a break.
- 5. Loss of Interest in Offline Activities: If you find yourself losing interest in hobbies, socializing with friends in person, or participating in activities you once enjoyed, it might be a sign that social media is taking precedence over real-world experiences.
- 6. Preoccupation with Online Image: Being overly concerned with curating the perfect online persona can be a sign of addiction. This includes obsessing over what to post, how you’re perceived by others, and constantly comparing yourself to others online.
- 7. Time Distortion: Losing track of time while on social media is a common sign of addiction. If you often intend to spend a few minutes online but end up scrolling for hours, it might be time to reassess your usage patterns.
Recognizing these signs is the first step toward addressing a potential social media addiction. Setting boundaries, such as designated times for checking social media, and seeking support from friends, family, or professionals can help regain control and foster a healthier relationship with technology.
Try our digital habit & screen addiction test:
Problems, impacts & bad effects of social media: should you quit?

What are some benefits of social media
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, offering a multitude of benefits that have transformed the way we communicate, access information, and interact with the world. Here are some of the key pros and advantages of social media:
- 1. Connectivity and Networking: Social media platforms allow people to connect with friends, family, and colleagues across the globe. They provide opportunities to network with like-minded individuals, join communities, and build relationships that transcend geographical boundaries.
- 2. Information and Awareness: Social media is a powerful tool for disseminating information quickly. It keeps users informed about global events, trends, and news. It also raises awareness about social issues, enabling users to engage in meaningful discussions and advocacy.
- 3. Marketing and Business Opportunities: For businesses, social media is an invaluable marketing tool. It allows companies to reach a broad audience, engage with customers, and promote products and services. Social media platforms also offer targeted advertising options, making it easier for businesses to reach their desired demographic.
- 4. Creativity and Self-Expression: Social media provides a platform for creativity and self-expression. Users can share their art, music, writing, and other creative endeavors with a wide audience. This exposure can lead to new opportunities and recognition.
- 5. Community Building: Social media fosters the creation of communities around shared interests and causes. These communities provide support, encouragement, and a sense of belonging, which can be particularly valuable for individuals who feel isolated in their offline lives.
- 6. Educational Resources: Many social media platforms offer educational content and resources. Users can access tutorials, webinars, and discussions that enhance their knowledge and skills in various fields.
- 7. Customer Feedback and Engagement: Businesses can use social media to engage directly with customers, gather feedback, and improve their products and services. This direct line of communication helps companies build trust and loyalty with their customer base.
- 8. Entertainment and Leisure: Social media offers a wide array of entertainment options, from videos and memes to live streams and games. It provides a source of leisure and relaxation for users looking to unwind.
- 9. Job Opportunities and Career Development: Platforms like LinkedIn have revolutionized job searching and professional networking. Users can showcase their skills, connect with industry leaders, and discover job opportunities that align with their career goals.
- 10. Real-Time Communication: Social media enables real-time communication, allowing users to share experiences and updates instantly. This immediacy is particularly beneficial during emergencies or significant events when timely information is crucial.
While social media has its challenges, including issues related to privacy, misinformation, and mental health, its advantages make it a valuable tool in today’s digital landscape. By leveraging social media responsibly, individuals and businesses can harness its potential to foster connections, drive innovation, and create positive change.But on the other hand, what are some social media addiction problems that addicts suffer from?
General health problems
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, offering numerous benefits but also posing potential risks to our health. Understanding these effects can help individuals make informed decisions about their social media use. Here are some key ways social media can impact health:
### Positive Effects
- 1. Increased Connectivity and Support:
Social media platforms enable people to stay connected with friends and family, regardless of geographical distances. This connectivity can provide emotional support, reduce feelings of loneliness, and foster a sense of community.
- 2. Access to Information and Resources:
Social media serves as a powerful tool for disseminating information. Users can access educational content, health tips, and support groups that can empower them to make healthier lifestyle choices.
- 3. Opportunities for Self-Expression:
Platforms like Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok offer users a space to express themselves creatively. This can boost self-esteem and provide a sense of accomplishment and identity.
- 4. Professional Networking and Opportunities:
LinkedIn and similar platforms facilitate professional networking, which can lead to career advancement and personal growth.
### Negative Effects
- 1. Mental Health Issues:
Excessive use of social media has been linked to anxiety, depression, and stress. The constant comparison with others, cyberbullying, and the pressure to maintain a perfect online persona can negatively impact mental well-being.
- 2. Sleep Disruption:
The use of electronic devices, particularly before bedtime, can interfere with sleep patterns. The blue light emitted by screens can disrupt the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
- 3. Addiction and Reduced Productivity:
Social media can be addictive, leading to excessive use that detracts from real-life interactions and responsibilities. This can reduce productivity and impact personal and professional life.
- 4. Body Image Concerns:
Exposure to idealized images and content on social media can lead to body dissatisfaction and unhealthy body image issues, particularly among young people.
- 5. Information Overload and Misinformation:
The vast amount of information available on social media can be overwhelming.
Additionally, the spread of misinformation can lead to confusion and poor decision-making, particularly regarding health-related issues.
### Strategies for Healthy Social Media Use
- 1. Set Boundaries:
Limit the time spent on social media and establish specific times for checking updates to prevent excessive use.
- 2. Curate Your Feed:
Follow accounts that promote positivity and unfollow those that contribute to negative feelings or misinformation.
- 3. Engage Mindfully:
Be conscious of your interactions on social media. Focus on meaningful connections and avoid engaging in negative or toxic discussions.
- 4. Take Breaks:
Regular digital detoxes can help reset your relationship with social media and improve mental health.
- 5. Seek Professional Help:
If social media use is negatively impacting your mental health, consider seeking support from a mental health professional.
In conclusion, while social media offers numerous advantages, it is crucial to be mindful of its potential negative effects on health. By adopting healthy habits and setting boundaries, individuals can enjoy the benefits of social media while minimizing its risks.
social media and sleep disorders
Social media has become an integral part of daily life for many people around the world. While it offers numerous benefits, such as staying connected with friends and family, accessing information, and entertainment, there is growing concern about its impact on sleep. Research suggests that social media can indeed contribute to sleep disorders and problems. Here are several ways in which social media use can affect sleep:
- 1. Increased Screen Time: The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep-wake cycles. Prolonged exposure to screens, especially before bedtime, can delay the onset of sleep and reduce overall sleep quality.
- 2. Mental Stimulation: Engaging with social media content can be mentally stimulating, making it difficult for the brain to wind down. Scrolling through feeds, reading news, or engaging in online discussions can increase alertness and delay the transition to a restful state.
- 3. Emotional Impact: Social media can evoke a range of emotions, from excitement and joy to anxiety and stress. Negative interactions or exposure to distressing content can lead to heightened emotional arousal, making it harder to relax and fall asleep.
- 4. Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): The desire to stay updated with social media can lead to compulsive checking behaviors, even late at night. This fear of missing out on important updates or conversations can result in disrupted sleep patterns.
- 5. Sleep Displacement: Time spent on social media can encroach on time that would otherwise be allocated to sleep. This displacement can lead to insufficient sleep duration, which can have cumulative negative effects on health and well-being.
- 6. Anxiety and Depression: Excessive social media use has been linked to increased levels of anxiety and depression, both of which are known to contribute to sleep disturbances. The pressure to maintain a certain online persona or the comparison with others’ curated lives can exacerbate these feelings.
- 7. Disruption of Bedtime Routines: Consistent bedtime routines are crucial for good sleep hygiene. Social media use can disrupt these routines, leading to irregular sleep patterns and difficulty falling asleep.
To mitigate the impact of social media on sleep, individuals can adopt several strategies:
– Set Boundaries: Establish specific times for social media use and avoid it at least an hour before bedtime.
– Use Night Mode: Many devices offer a “night mode” feature that reduces blue light emission.
– Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading a book or practicing meditation.
– Limit Notifications: Turn off unnecessary notifications to reduce the temptation to check social media frequently.
– Prioritize Sleep: Recognize the importance of sleep for overall health and make it a priority over late-night social media use.
By being mindful of social media habits and their potential impact on sleep, individuals can take steps to ensure that their online activities do not interfere with their rest and well-being.
social media affecting your brain & mental health: bad for brain and mental health?
Some effects of social media on your brain
### The Not-So-Great Side of Social Media on Your Brain
Hey there! 🌟 we all love scrolling through our favorite social media platforms, sharing moments, and staying connected. But have you ever wondered how all that screen time affects your brain? Let’s dive into some of the not-so-great impacts social media might have on your noggin:
- 1. Boosts Anxiety and Stress Levels
Constant notifications and the pressure to keep up can make you feel anxious. Comparing your life to others’ highlight reels might lead to stress and worry.
- 2. Affects Attention Span
Scrolling through endless feeds can make it hard to focus on longer tasks. Your brain gets used to quick bites of information, making it challenging to concentrate on more extended activities.
- 3. Disrupts Sleep Patterns
Using your phone before bed exposes your eyes to blue light, which can interfere with your sleep. Poor sleep affects your mood, memory, and overall brain health.
- 4. Impacts Self-Esteem
Seeing others’ perfect photos and achievements can make you question your own worth. This comparison game might lower your self-esteem and confidence.
- 5. Encourages Addiction
Social media is designed to be engaging, sometimes leading to excessive use. This addiction can take time away from real-life interactions and activities you enjoy.
- 6. Creates Information Overload
Being bombarded with information nonstop can overwhelm your brain. It becomes harder to process and retain information, leading to mental fatigue.
- 7. Fosters Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
Always feeling like something exciting is happening elsewhere can make you anxious. FOMO can make you restless and less satisfied with your own life.
- 8. Reduces Face-to-Face Interactions
Spending too much time online might limit your in-person social skills. Building strong, personal relationships is crucial for mental well-being.
### Finding Balance is Key
While social media has its downsides, it’s all about how you use it. Setting boundaries, taking regular breaks, and being mindful of your usage can help mitigate these negative effects. Remember, your brain loves variety and real connections, so make sure to balance your online time with activities that nourish your mind and soul!
Stay happy and healthy! 😊✨
Some effects of social media on your mental health
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, offering numerous benefits such as connectivity, information sharing, and entertainment. However, its pervasive presence also poses significant challenges to mental health. Here are some of the negative effects social media can have on mental well-being:
- 1. Anxiety and Depression: Excessive use of social media can lead to increased feelings of anxiety and depression. Constant exposure to curated images and posts can create unrealistic expectations and feelings of inadequacy, leading to low self-esteem and depressive symptoms.
- 2. Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Social media platforms often highlight the exciting aspects of others’ lives, which can lead to FOMO. This fear can cause anxiety and a sense of exclusion, as individuals feel they are missing out on rewarding experiences.
- 3. Cyberbullying: The anonymity and reach of social media can facilitate cyberbullying, which can have devastating effects on mental health. Victims may experience increased stress, anxiety, and depression, sometimes leading to severe consequences like self-harm or suicidal thoughts.
- 4. Addiction: Social media can be addictive, with users spending excessive amounts of time online at the expense of real-world interactions and responsibilities. This addiction can lead to disrupted sleep patterns, decreased productivity, and increased stress.
- 5. Sleep Disturbances: The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with sleep cycles, and the habit of checking social media before bed can lead to insomnia or poor-quality sleep. Lack of sleep is closely linked to various mental health issues, including anxiety and depression.
- 6. Body Image Issues: Social media often promotes idealized body images, which can lead to body dissatisfaction and eating disorders. Constant comparison with these unrealistic standards can harm self-esteem and body image, particularly among young users.
- 7. Reduced Attention Span: The fast-paced nature of social media can contribute to reduced attention spans and decreased ability to concentrate. This can affect academic and professional performance, leading to stress and frustration.
- 8. Social Isolation: While social media is designed to connect people, excessive use can lead to social isolation. Users may prioritize online interactions over face-to-face communication, leading to weakened real-world relationships and increased feelings of loneliness.
- 9. Negative Impact on Self-Esteem: The feedback mechanisms inherent in social media, such as likes and comments, can significantly impact self-esteem. Negative comments or lack of engagement can lead to feelings of rejection and self-doubt.
- 10. Increased Stress Levels: Constant notifications and the pressure to stay updated can lead to increased stress levels. The need to respond promptly and maintain an online persona can be overwhelming and exhausting.
To mitigate these negative effects, it is crucial to cultivate a healthy relationship with social media. This can include setting time limits, curating a positive feed, engaging in digital detoxes, and prioritizing real-world interactions. Building awareness and promoting digital literacy can also empower individuals to navigate social media more mindfully, safeguarding their mental health.
Does social media cause stress and anxiety?
Yes, social media can indeed cause stress and anxiety for many individuals. While these platforms offer numerous benefits, such as staying connected with friends and accessing information, they also present several challenges that can contribute to mental health issues. Here are some ways in which social media can lead to stress and anxiety:
- 1. Comparison and Self-Esteem Issues: Social media often showcases curated and idealized versions of people’s lives. Constant exposure to these images and stories can lead users to compare themselves to others, resulting in feelings of inadequacy or low self-esteem.
- 2. Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Social media platforms are designed to keep users engaged, often highlighting events and experiences that others are having. This can lead to FOMO, where individuals feel anxious about not being included or missing out on important social interactions.
- 3. Cyberbullying and Harassment: Social media can be a breeding ground for negative interactions, including cyberbullying and harassment. Victims of online abuse may experience heightened stress, anxiety, and even depression.
- 4. Information Overload: The vast amount of information available on social media can be overwhelming. Constant exposure to news, opinions, and updates can lead to stress, especially when the content is negative or distressing.
- 5. Addiction and Time Management: The addictive nature of social media can lead to excessive use, which can interfere with daily activities and responsibilities. This can cause stress as individuals struggle to balance their online and offline lives.
- 6. Privacy Concerns: The sharing of personal information on social media can lead to anxiety about privacy and security. Users may worry about who can access their data and how it might be used.
- 7. Pressure to Maintain an Online Persona: Many users feel the need to present a perfect or idealized version of themselves online. This pressure to maintain a certain image can be stressful and contribute to anxiety.
- 8. Negative News and Content: Exposure to negative news, whether it’s related to global events or personal connections, can increase feelings of stress and anxiety, especially if users feel helpless to effect change.
To mitigate these effects, it’s important for individuals to set boundaries around their social media use, curate their feeds to include positive and supportive content, and take breaks when necessary.
Additionally, seeking support from mental health professionals can be beneficial for those experiencing significant stress or anxiety related to social media.
Can social media addiction lead to sadness and depression?

Social media has become an integral part of modern life, offering platforms for communication, entertainment, and information sharing. However, its pervasive presence has raised concerns about its potential impact on mental health, particularly regarding social media addiction and its possible link to sadness and depression.
### Understanding Social Media Addiction
Social media addiction is characterized by excessive use of social media platforms to the extent that it interferes with daily life. This compulsive behavior can manifest in various ways, such as spending an inordinate amount of time online, experiencing anxiety when unable to access social media, and neglecting personal, academic, or professional responsibilities.
### The Link to Sadness and Depression
1. Comparison and Self-Esteem: Social media often presents an idealized version of life, where users showcase their successes, happiness, and curated images. This can lead to unhealthy comparisons, where individuals measure their self-worth against the seemingly perfect lives of others. Such comparisons can diminish self-esteem and contribute to feelings of inadequacy and sadness.
2. Cyberbullying and Negative Interactions: The anonymity and distance provided by social media can sometimes lead to negative interactions, including cyberbullying. Victims of online harassment may experience increased feelings of isolation, sadness, and anxiety, which can contribute to depression.
3. Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Social media can amplify the fear of missing out, as users are constantly exposed to events and activities they are not part of. This can lead to feelings of exclusion and loneliness, which are risk factors for depression.
4. Disrupted Sleep Patterns: Excessive social media use, especially before bedtime, can disrupt sleep patterns. Poor sleep quality is closely linked to mood disorders, including depression.
5. Reduced Face-to-Face Interactions: While social media can connect people across distances, it can also reduce the frequency and quality of face-to-face interactions. This lack of real-world social engagement can lead to feelings of loneliness and depression.
### Research Findings
Several studies have explored the relationship between social media use and mental health. A 2018 study published in the journal *Computers in Human Behavior* found that individuals who spent more time on social media were more likely to report symptoms of depression. Another study published in *JAMA Psychiatry* in 2019 suggested that adolescents who used social media extensively were at a higher risk of developing depressive symptoms.
### Mitigating the Risks
To mitigate the potential negative effects of social media addiction on mental health, individuals can consider the following strategies:
– Set Boundaries: Limit the time spent on social media and establish specific periods during the day for checking updates.
– Practice Mindfulness: Be mindful of the content consumed and avoid engaging in negative comparisons.
– Prioritize Real-World Interactions: Make an effort to engage in face-to-face interactions and nurture offline relationships.
– Seek Professional Help: If social media use is significantly impacting mental health, consider seeking support from mental health professionals.
### Conclusion
While social media offers numerous benefits, its addictive nature can contribute to sadness and depression for some individuals. By understanding the potential risks and implementing strategies to manage social media use, individuals can enjoy its advantages while safeguarding their mental well-being.
Dopamine and social media
### The Dopamine Connection: How Social Media Hooks Users
In recent years, social media has become an integral part of daily life for millions around the globe. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok have revolutionized the way we communicate, share information, and entertain ourselves. However, beneath the surface of likes, shares, and endless scrolling lies a complex interplay of psychology and neurochemistry, with dopamine playing a central role.
#### Understanding Dopamine
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger in the brain, that plays a crucial role in how we experience pleasure and reward. It is involved in reinforcing behaviors by creating feelings of enjoyment and satisfaction, which encourages us to repeat those behaviors. This is part of what is known as the brain’s reward system.
#### The Social Media-Dopamine Loop
Social media platforms are designed to be engaging and rewarding, often using algorithms that prioritize content likely to captivate users. Here’s how dopamine fits into this equation:
- 1. Instant Gratification: Social media provides immediate rewards in the form of likes, comments, and shares. Each notification or positive interaction triggers a release of dopamine, giving users a sense of pleasure and validation.
- 2. Variable Rewards: Similar to slot machines, social media platforms employ variable reward schedules. Users don’t know when they will receive a like or a comment, which keeps them engaged and checking their devices frequently. This unpredictability enhances dopamine release and reinforces the habit of checking social media.
- 3. Social Validation: Humans are inherently social creatures, and social media taps into our desire for social validation. Positive interactions on these platforms can boost self-esteem, further increasing dopamine levels.
- 4. Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): The constant flow of information and updates can create anxiety about missing out on important events or news. This fear can drive compulsive checking behaviors, as users seek reassurance and connection, which again triggers dopamine release.
#### The Impact on Mental Health
While the dopamine-driven engagement with social media can be enjoyable, it also has potential downsides:
– Addiction: The cycle of reward and reinforcement can lead to addictive behaviors, where individuals feel compelled to check social media constantly, even to the detriment of other activities.
– Anxiety and Depression: Excessive use of social media has been linked to increased levels of anxiety and depression. The comparison with others, cyberbullying, and the pressure to maintain a certain online persona can negatively impact mental health.
– Reduced Attention Span: The constant barrage of information and the habit of quickly scrolling through content can diminish attention spans and reduce the ability to focus on longer tasks.
#### Finding Balance
Understanding the role of dopamine in social media use can help individuals develop healthier habits. Here are some strategies:
– Set Boundaries: Limit the time spent on social media and establish specific times for checking updates to prevent compulsive behavior.
– Mindful Use: Be conscious of the emotions and triggers associated with social media use. Focus on engaging with content that is genuinely enriching or informative.
– Digital Detox: Periodically disconnect from social media to reset and reduce dependency on digital validation.
– Seek Real-Life Connections: Prioritize face-to-face interactions and activities that provide fulfillment beyond the digital realm.
In conclusion, while social media platforms are designed to capture attention and stimulate dopamine release, being aware of these mechanisms can empower users to engage with them more mindfully. By finding a balance, individuals can enjoy the benefits of social media without falling into the traps of addiction and negative mental health outcomes.
social media effects on focus, productivity, attention span, academic performance…
### How Social Media Impacts Your Focus, Productivity, Attention Span, and Academic Performance
Hey there! 🌟 Social media is a big part of our daily lives, but have you ever wondered how it affects your focus, productivity, attention span, and even your academic performance? Let’s break it down in a simple way!
####
- 1. Focus
Social media can be a double-edged sword when it comes to focus. On one hand, it offers quick distractions that can pull your attention away from important tasks. Checking your phone for a quick scroll can interrupt your concentration, making it harder to stay on track. On the other hand, some platforms offer tools like task management and reminders that can help you stay organized. It’s all about how you use it!
####
- 2. Productivity
Your productivity can take a hit if social media becomes a time sink. Constant notifications and the urge to check updates can eat into your work time. Studies have shown that frequent social media use can reduce overall work efficiency. However, using social media strategically—for networking, learning new skills, or promoting your work—can actually boost productivity. It’s all about balance!
####
- 3. Attention Span
Short, bite-sized content on social media can train your brain to expect quick rewards, which might make it harder to engage in activities that require prolonged attention. This constant stream of information can fragment your focus, making it challenging to concentrate on one thing for an extended period. Taking regular breaks from social media can help improve your attention span over time.
####
- 4. Academic Performance
For students, social media can be both a help and a hindrance. It offers access to educational resources, study groups, and information sharing, which can enhance learning. However, excessive use can lead to procrastination, lower grades, and reduced academic performance. Setting specific times for social media and prioritizing study time can mitigate these negative effects.
### Tips to Manage Social Media Use Effectively
– Set Time Limits: Use apps or phone settings to limit how much time you spend on social media each day.
– Create a Schedule: Designate specific times for checking social media, so it doesn’t interfere with work or study.
– Stay Organized: Use social media tools that help you manage tasks and stay productive.
– Take Breaks: Regular breaks from social media can help improve your focus and attention span.
### Final Thoughts
Social media isn’t inherently bad, but like anything, moderation is key. By being mindful of how and when you use it, you can enjoy the benefits without letting it negatively impact your focus, productivity, attention span, or academic performance. Stay balanced and make social media work for you!
A word about ADHD and social media
Yes, people with ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) often interact with social media differently compared to those without the condition. Several factors contribute to these differences, including challenges with attention regulation, impulsivity, and a tendency toward hyperfocus. Here are some ways in which ADHD can influence social media use:
- 1. Increased Usage: Individuals with ADHD may spend more time on social media platforms due to difficulties in regulating their attention. The constant stream of new content can be particularly engaging, leading to prolonged usage.
- 2. Impulsivity: ADHD is often associated with impulsive behavior, which can manifest in social media interactions. This might include posting or commenting without fully considering the consequences, or quickly reacting to content without much deliberation.
- 3. Hyperfocus: While ADHD is characterized by attention difficulties, it can also involve periods of hyperfocus, where an individual becomes intensely absorbed in an activity. Social media can capture this hyperfocus, leading to extended periods of engagement with specific content or platforms.
- 4. Distraction and Procrastination: Social media can serve as a significant source of distraction for individuals with ADHD, potentially exacerbating procrastination. The easy access to entertainment and social interaction can divert attention from tasks that require sustained focus.
- 5. Emotional Sensitivity: People with ADHD often experience heightened emotional sensitivity, which can affect how they perceive and react to social media content. They may be more susceptible to emotional responses from online interactions, such as feeling overwhelmed by negative comments or intensely engaged with supportive ones.
- 6. Seeking Stimulation: The fast-paced, dynamic nature of social media can provide the stimulation that individuals with ADHD often seek. The variety of content and the interactive nature of social media can be particularly appealing.
- 7. Challenges with Social Cues: Some individuals with ADHD may struggle with interpreting social cues, which can affect online interactions. The lack of non-verbal cues in digital communication might lead to misunderstandings or misinterpretations.
- 8. Time Management Issues: Managing time effectively can be challenging for people with ADHD, and social media can exacerbate these difficulties. The tendency to lose track of time while browsing can interfere with daily responsibilities and routines.
While these tendencies are common, it’s important to note that the impact of ADHD on social media use can vary widely among individuals. Some people with ADHD may develop strategies to manage their social media use effectively, while others may find it more challenging. Understanding these patterns can help individuals with ADHD, their families, and professionals develop strategies to use social media in a balanced and healthy way.
Affecting your relationships
social media and self-esteem
How Social Media Affects Self-Esteem: A Friendly Look
Hey there! 🌟 Let’s chat about something that’s on many of our minds these days—how social media affects our self-esteem. Whether you’re scrolling through Instagram, tweeting your thoughts, or sharing moments on Facebook, social media plays a big role in how we feel about ourselves. Let’s break it down in a simple and friendly way!
### The Good Side of Social Media
First off, social media isn’t all bad! It has some awesome benefits that can boost our self-esteem:
– Connection & Community: Staying in touch with friends and family, no matter where they are, can make us feel supported and loved.
– Inspiration & Motivation: Seeing others achieve their goals or share their creativity can inspire us to pursue our own dreams.
– Self-Expression: Platforms like Instagram and TikTok allow us to showcase our talents, hobbies, and unique personalities, which can build confidence.
### The Not-So-Good Side
But, like anything, there are some downsides to keep in mind:
– Comparison Trap: It’s easy to compare your everyday life to someone else’s highlight reel. Seeing others’ perfect photos and success stories can make you feel like you’re not measuring up.
– Cyberbullying: Negative comments or online harassment can seriously hurt your feelings and lower your self-esteem.
– Pressure to Be Perfect: The urge to present a flawless image can lead to stress and anxiety, making you feel like you have to live up to unrealistic standards.
### Balancing Act: Finding the Sweet Spot
So, how can we enjoy social media without letting it mess with our self-esteem? Here are a few tips:
– Be Mindful: Pay attention to how social media makes you feel. If certain accounts or activities bring you down, it might be time to take a break or unfollow.
– Limit Screen Time: Setting boundaries on how much time you spend online can help you stay grounded and reduce stress.
– Stay Authentic: Share your true self, not just the highlight moments. Authenticity can build genuine connections and boost your confidence.
– Positive Engagement: Focus on uplifting content and engage with supportive communities that make you feel good about yourself.
### Remember, You’re Not Alone!
It’s important to remember that everyone experiences ups and downs with their self-esteem. Social media is just one piece of the puzzle. Surround yourself with positive influences, practice self-love, and take breaks when you need to. Your worth isn’t defined by likes, comments, or shares!
In Conclusion
Social media has a significant impact on our self-esteem, both positively and negatively. By being aware of its effects and taking steps to manage your online experience, you can enjoy the benefits of staying connected without letting it take a toll on how you feel about yourself. Stay confident and keep shining! ✨
social media addiction leads to isolation and loneliness?
.jpg)
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, offering a platform for connection, communication, and information sharing. However, its pervasive presence has also raised concerns about its potential impact on mental health, particularly regarding social media addiction and its relationship with isolation and loneliness.
### Understanding Social Media Addiction
Social media addiction is characterized by excessive use of social media platforms to the point where it interferes with daily life. This compulsive behavior often leads to neglect of real-world responsibilities, relationships, and activities. The design of social media platforms, which often includes features like infinite scrolling and notifications, can contribute to this addictive behavior by providing constant stimulation and immediate gratification.
### The Paradox of Connection
Social media is designed to connect people, yet paradoxically, it can also lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness. Here’s how:
- 1. Superficial Interactions: Social media often promotes surface-level interactions rather than deep, meaningful connections. Likes, comments, and shares can give the illusion of engagement without the depth of face-to-face communication.
- 2. Comparison and Envy: Social media platforms are replete with curated images and stories that often portray an idealized version of life. Constant exposure to these can lead individuals to compare their own lives unfavorably, fostering feelings of inadequacy and loneliness.
- 3. Reduced In-Person Interactions: Excessive use of social media can lead to a decrease in real-world social interactions. Time spent online can replace time that might otherwise be spent engaging in face-to-face activities, which are crucial for building strong social bonds.
- 4. Social Anxiety: For some, social media can exacerbate social anxiety. The pressure to maintain an online persona and the fear of missing out (FOMO) can lead to stress and withdrawal from real-world social settings.
### The Cycle of Loneliness
Social media addiction can create a cycle of loneliness. Individuals may turn to social media to alleviate feelings of loneliness, but the superficial nature of online interactions can leave them feeling even more isolated. This can lead to increased social media use in an attempt to find connection, perpetuating the cycle.
### Breaking the Cycle
Addressing social media addiction and its impact on loneliness involves a multifaceted approach:
- 1. Mindful Usage: Being conscious of the time spent on social media and setting boundaries can help mitigate its negative effects. This includes scheduling regular breaks and prioritizing offline interactions.
- 2. Fostering Real Connections: Encouraging face-to-face interactions and meaningful conversations can help counteract the superficiality of online interactions.
- 3. Digital Detox: Periodically disconnecting from social media can provide a reset, allowing individuals to focus on real-world relationships and activities.
- 4. Seeking Support: For those struggling with social media addiction, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide strategies to manage usage and address underlying issues contributing to loneliness.
### Conclusion
While social media offers valuable opportunities for connection, its addictive potential can lead to isolation and loneliness. By fostering awareness and promoting healthy usage habits, individuals can enjoy the benefits of social media without falling into the trap of addiction and its associated emotional consequences. Balancing online interactions with real-world connections is key to mitigating the negative impacts of social media on mental health.
Effects of social media on your relationships
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, influencing how we connect, communicate, and maintain relationships. While it offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges. Here’s a look at the positive and negative effects of social media on relationships:
### Positive Effects
- 1. Enhanced Communication:
– Social media platforms provide easy and instant communication channels, allowing people to stay connected regardless of geographical distances. This is particularly beneficial for long-distance relationships or maintaining connections with family and friends who live far away.
- 2. Strengthening Bonds:
– Sharing life updates, photos, and experiences on social media can help strengthen relationships by keeping people informed and engaged with each other’s lives. It provides a platform for shared experiences and memories.
- 3. Reconnecting with Old Friends:
– Social media makes it easier to reconnect with old friends or acquaintances, potentially reviving and strengthening past relationships that might have faded over time.
- 4. Community Building:
– Social media allows individuals to find and join communities of like-minded people, fostering new friendships and support networks. This can be particularly beneficial for those with niche interests or those seeking support for specific life challenges.
- 5. Increased Awareness:
– By sharing articles, videos, and other content, social media can help partners and friends become more aware of each other’s interests, values, and perspectives, potentially leading to deeper understanding and connection.
### Negative Effects
- 1. Miscommunication:
– The lack of non-verbal cues in online communication can lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations, potentially causing conflicts or tensions in relationships.
- 2. Jealousy and Insecurity:
– Seeing partners or friends interact with others on social media can sometimes lead to feelings of jealousy or insecurity. This can be exacerbated by the tendency to compare oneself to others, which social media often encourages.
- 3. Privacy Concerns:
– Oversharing on social media can lead to privacy issues, where personal information or relationship details become public, potentially causing discomfort or conflict.
- 4. Time Consumption:
– Excessive use of social media can detract from face-to-face interactions, leading to a decrease in the quality of personal relationships. It can also lead to neglect of responsibilities or other important aspects of life.
- 5. Superficial Connections:
– Social media can sometimes encourage shallow interactions, where the quantity of connections is valued over the quality. This can lead to feelings of loneliness or dissatisfaction despite having many online “friends.”
- 6. Pressure to Maintain an Image:
– The pressure to present a perfect life or relationship on social media can lead to stress and strain. This can result in individuals hiding real issues or feelings to maintain an idealized online persona.
In conclusion, while social media offers valuable tools for enhancing and maintaining relationships, it also requires mindful use to avoid potential pitfalls. Balancing online interactions with offline connections and being aware of the impact of social media on personal relationships can help individuals maximize its benefits while minimizing its drawbacks.
How To Stop & Quit Your social media Addiction
Finally, you think you are addicted to social media and you are wondering how to quit it? How to break and overcome your cravings for social media?
Here are the best solutions, steps, supports, resources, and help you can get to treat your social media addiction.
Main steps and solutions to break the social media addiction
Overcoming social media addiction can be challenging, but with commitment and a structured approach, it is possible to regain control over your digital habits. Here are some main steps to help you get started:
- 1. Acknowledge the Problem: The first step is recognizing that social media usage has become problematic and is affecting your daily life, productivity, or mental health.
- 2. Set Clear Goals: Define what you want to achieve by reducing your social media usage. This could include spending more time with family, focusing on work or studies, or improving mental well-being.
- 3. Monitor Usage: Use apps or built-in phone features to track how much time you spend on social media. This will help you understand the extent of your usage and identify patterns.
- 4. Create a Schedule: Allocate specific times of the day for checking social media and stick to this schedule. This will help you avoid mindless scrolling.
- 5. Limit Notifications: Turn off non-essential notifications to reduce the temptation to check your phone every time it buzzes.
- 6. Find Alternatives: Engage in other activities that you enjoy or that are productive, such as reading, exercising, or spending time with friends and family.
- 7. Set Boundaries: Designate tech-free zones or times, such as during meals or before bedtime, to help reduce dependency.
- 8. Use Technology Wisely: Consider using apps that block social media during certain hours or limit your daily usage.
- 9. Seek Support: Share your goals with friends or family who can support you in your efforts. You might also consider joining a support group or seeking professional help if needed.
- 10. Reflect and Adjust: Regularly assess your progress and make adjustments as necessary. Celebrate small victories to stay motivated.
- 11. Practice Mindfulness: Engage in mindfulness or meditation practices to help reduce stress and improve your ability to focus on the present moment.
- 12. Stay Informed: Educate yourself about the effects of social media on mental health to reinforce your commitment to reducing usage.
By following these steps, you can gradually reduce your reliance on social media and develop healthier digital habits. Remember, the goal is not necessarily to eliminate social media entirely but to use it in a way that enhances your life rather than detracts from it.Actually, that’s what most documentation out there is about… However, quitting a digital addiction can be a bit trickier than that.
So our team, after testing many ways, designed a bulletproof way to overcome them. Here are some clear and practical steps that are very powerful to quit a digital addiction, including social media:
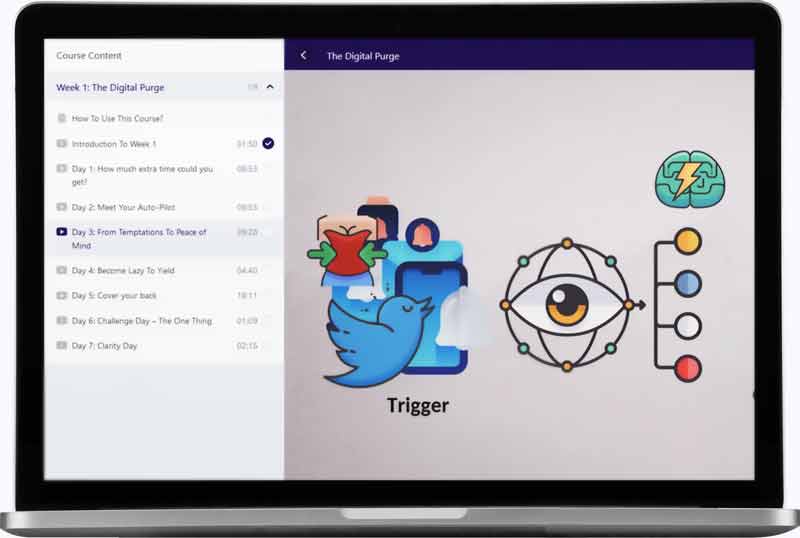
1. Purge temptations: Get rid of social media
First, cleaning your life from temptations is much easier than resisting them. Disable or delete your social media accounts, change the password and hide it somewhere you can’t access easily, keep your phone / computer far away… Out of sight, out of mind.
Here is a video from our course The Digital Purge. on how to add resistance to your temptations, so you become so lazy to engage with them that you give them up:
2. Spot & Reveal your emotional triggers
Second, there are some reasons, often hidden ones, that your brain and your heart love so much social media. Those reasons act as triggers to pull your cravings. Rather than chasing the addiction, it’s a more efficient strategy to look at the feelings driving you toward it. That way you can cure and heal the feeling. You’ll feel better, and the cravings will magically disappear. Just get away.
3. Rewire to life

An addiction FOMO (fear of missing out) can be huge and really painful to resist, especially if it was here for a long time. However, learning to live with it is necessary to build a life full of peace and joy. Strategies to fight FOMO and rewire to life include meditation, nature activities, social interaction, intellectual and creative projects, meaningful adventures… basically anything that fills your soul.
4. How to not relapse and fully recover from social media?
Finally, it’s important to acknowledge that quitting may take days, weeks, months, or even years. Getting over and quitting social media forever can be difficult. You may relapse a few times, but the most important thing is that you keep engaging less and less with social media. Each day you resist it is a day weakening your brain connections with social media. From your patience and discipline will arise incredible mind strength, hope, and wisdom.

Best social media blocker apps & functionalities
Additionally, you can increase your chance of withdrawal by limiting or blocking access to social media using these apps.
They will help you filter, reduce, or block social media:
In today’s digital age, social media can be both a blessing and a curse. While it offers a platform for connection and information, it can also become a significant distraction. For those looking to regain control over their time and productivity, several apps are designed to help limit or block social media access. Here are five of the best apps for this purpose:
- 1. Freedom
– Overview: Freedom is a versatile app that allows users to block distracting websites and apps across all devices simultaneously. It’s perfect for those who need to focus on work or study without interruptions.
– Features: Customizable block lists, scheduled sessions, and the ability to block the entire internet if needed. It also offers a locked mode to prevent changes during a session.
– Platforms: Available on Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and Chrome.
- 2. Cold Turkey
– Overview: Cold Turkey is a robust app that provides powerful blocking features to help users stay focused. It’s particularly useful for those who need a hardcore solution to curb their social media usage.
– Features: Allows blocking of websites, applications, and even the entire internet. It includes a “Frozen Turkey” mode, which prevents users from accessing blocked content until a timer runs out.
– Platforms: Available on Windows and macOS.
- 3. StayFocusd
– Overview: StayFocusd is a Chrome extension designed to help users limit the time spent on distracting websites. It’s a straightforward tool for those who primarily use Chrome for browsing.
– Features: Users can set time limits for specific sites, after which they become inaccessible for the rest of the day. It also offers the “Nuclear Option” to block sites entirely for a set period.
– Platforms: Available as a Chrome extension.
- 4. Forest
– Overview: Forest is a unique app that combines productivity with environmentalCheck our full social media addiction tool list (ranked):
Where to seek extra help?
Do you need some support and help to stop, overcome, and recover from your social media addiction? If you or someone you know is struggling with social media addiction, there are a few places to seek help.
The Ultimate Rewiring Program For social media Addicts
Our course The Digital Purge. This course has already helped many digital addicts to rewire to what matters.
Is there a “treatment” to cure social media addiction?
Absolutely, there are several effective ways to address and overcome social media addiction. Here are some strategies you might find helpful:
- 1. Set Clear Limits: Decide how much time you want to spend on social media each day and stick to it. Use timers or app features that track and limit your usage.
- 2. Create No-Phone Zones: Designate certain areas of your home, like the bedroom or dining table, as phone-free zones to reduce temptation.
- 3. Turn Off Notifications: Disable non-essential notifications to minimize distractions and interruptions throughout your day.
- 4. Schedule Social Media Breaks: Plan specific times to check your accounts instead of constantly refreshing your feed. This helps you stay in control of your usage.
- 5. Engage in Other Activities: Find hobbies or activities you enjoy, such as reading, exercising, or spending time with friends and family, to fill the time you’d typically spend on social media.
- 6. Practice Mindfulness: Techniques like meditation and deep breathing can help you become more aware of your habits and reduce the urge to check social media impulsively.
- 7. Seek Support: Talk to friends or family about your goal to cut back. Sometimes, having someone to encourage and hold you accountable can make a big difference.
- 8. Consider Professional Help: If you find it particularly challenging to manage on your own, a therapist or counselor can provide personalized strategies and support.
Remember, it’s all about finding a balance that works for you and making gradual changes. You’re not alone, and many people successfully reduce their social media use with the right approach!
Does social media therapy exist?
Yes, therapy to address social media addiction does exist, and it is becoming increasingly important as more people recognize the impact excessive social media use can have on mental health and daily functioning. While social media addiction is not officially classified as a distinct disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-
- 5., many mental health professionals acknowledge it as a behavioral addiction that can significantly affect an individual’s life.
Here are some therapeutic approaches commonly used to address social media addiction:
- 1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is one of the most effective therapeutic approaches for treating various behavioral addictions, including social media addiction. It helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to their social media use. CBT can assist in developing healthier coping strategies and improving self-control.
- 2. Motivational Interviewing (MI): This client-centered approach helps individuals explore their ambivalence about changing their social media habits. By enhancing motivation, MI can empower individuals to make positive changes in their behavior.
- 3. Mindfulness-Based Therapies: Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), can help individuals become more aware of their social media habits and reduce compulsive use. These practices encourage living in the moment and can improve emotional regulation.
- 4. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Originally developed for borderline personality disorder, DBT is effective in treating various addictive behaviors. It focuses on building skills in distress tolerance, emotional regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness.
- 5. Group Therapy: Participating in group therapy sessions can provide individuals with support from others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and strategies can be beneficial for overcoming social media addiction.
- 6. Digital Detox Programs: Some therapeutic programs specifically focus on helping individuals take a break from digital devices and social media. These programs often include structured activities and counseling to support the detox process.
- 7. Psychoeducation: Educating individuals about the effects of social media addiction on mental health and well-being can increase awareness and motivate change. Understanding the impact of social media can be a crucial step in reducing dependency.
- 8. Family Therapy: In cases where social media addiction affects family dynamics, family therapy can help address underlying issues and improve communication and support within the family unit.
It’s important for individuals struggling with social media addiction to seek help from qualified mental health professionals who can tailor treatment to their specific needs. As awareness of social media addiction grows, more resources and specialized treatment options are becoming available.
Where to find support groups if you are addicted to social media?
Finding support groups for social media addiction can be an important step in addressing and managing the challenges associated with excessive social media use. Here are several avenues you can explore to find such support groups:
- 1. Online Support Communities:
– Websites like Reddit have forums such as r/StopGaming and r/nosurf, where individuals share experiences and support each other in reducing screen time and social media use.
– Platforms like Facebook itself have groups dedicated to social media detox and digital minimalism.
- 2. Therapy and Counseling Services:
– Many therapists and counselors specialize in digital addiction. They can often recommend local or online support groups.
– Websites like Psychology Today have directories where you can find professionals who focus on technology addiction.
- 3. Non-Profit Organizations:
– Organizations such as the Center for Humane Technology and the Digital Wellness Collective offer resources and may have information on support groups or initiatives aimed at reducing social media addiction.
- 4. Local Community Centers:
– Check with local community centers or libraries, which may host support groups or workshops focused on digital wellness and managing screen time.
- 5. Educational Institutions:
– Universities and colleges often have mental health resources that include support for digital addiction, and they may offer group sessions for students and staff.
- 6. 12-Step Programs:
– Some areas have adapted 12-step programs to address technology and social media addiction. These groups can offer a structured approach to managing addiction.
- 7. Apps and Digital Tools:
– Apps like Meetup can help you find local groups focused on digital detox and reducing screen time.
– Apps designed to manage screen time can also have community features where users support each other.
- 8. Professional Organizations:
– The American Psychological Association and similar organizations may have resources or can direct you to support groups.
- 9. Healthcare Providers:
– Speak with your healthcare provider, who might know of local resources or support groups for managing social media addiction.
When seeking a support group, consider whether you prefer in-person meetings or online interactions, as both have their benefits. Online groups offer convenience and anonymity, while in-person meetings can provide a more personal connection.
But other social media addiction solutions exist
If you’re seeking help with social media addiction, there are several professionals and resources you can turn to for support:
- 1. Therapists or Counselors: Licensed mental health professionals, such as psychologists or counselors, can provide individual therapy to help you understand and manage your social media use. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one approach that can be effective in addressing addictive behaviors.
- 2. Psychiatrists: If your social media use is impacting your mental health significantly, a psychiatrist can assess whether medication might be appropriate, especially if there are underlying issues like anxiety or depression.
- 3. Digital Detox Coaches: These are specialists who focus on helping individuals reduce their screen time and develop healthier digital habits. They can offer personalized strategies to manage your social media use.
- 4. Life Coaches: Some life coaches specialize in digital wellness and can provide guidance on balancing your online and offline life, setting boundaries, and achieving personal goals without excessive reliance on social media.
- 5. School or University Counselors: If you’re a student, school counselors can be a valuable resource. They can offer support and strategies to help manage your time and reduce social media use.
- 6. Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): If you’re employed, your workplace might offer an EAP, which can provide access to counseling services and resources to help with personal issues, including social media addiction.
- 7. Family Doctors or General Practitioners: Your primary care physician can be a good starting point. They can provide referrals to mental health professionals or other resources that can help you address your social media use.
- 8. Digital Well-being Apps: While not a direct human contact, apps designed to promote digital well-being can offer tools and insights to help you monitor and reduce your social media usage.
Remember, acknowledging the need for help is a significant first step, and reaching out to any of these professionals can set you on the path to healthier social media habits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, overcoming social media addiction is a journey that requires self-awareness, discipline, and a commitment to personal well-being. By recognizing the signs of addiction and implementing practical strategies, such as setting boundaries, engaging in offline activities, and seeking support, individuals can regain control over their digital lives. It’s important to remember that social media, when used mindfully, can be a valuable tool for connection and learning. However, prioritizing real-world interactions and nurturing a balanced lifestyle is essential for mental health and overall happiness. As we navigate the digital age, let us strive to use technology in ways that enhance our lives, rather than detract from them. Through intentional choices and mindful practices, we can break free from the grips of social media addiction and cultivate a more fulfilling and connected existence.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.Here is the trailer:
To Go Further
Take our 4-min test
How to help someone with social media addiction?
Helping someone with social media addiction requires a compassionate and supportive approach. Here are some steps you can take:
- 1. Understand the Issue: Educate yourself about social media addiction. Recognize that it can have serious impacts on mental health, including anxiety, depression, and decreased self-esteem.
- 2. Open a Dialogue: Approach the person in a non-judgmental way. Express your concerns and let them know you’re there to support them. Use “We” statements to avoid sounding accusatory, such as “We’ve noticed you seem stressed when you’re on social media.”
- 3. Encourage Self-Reflection: Help them reflect on how social media is affecting their life. Discuss the time they spend on it and how it impacts their mood, productivity, and relationships.
- 4. Suggest Setting Limits: Encourage them to set specific boundaries for social media use. This could include time limits, turning off notifications, or designating certain times of the day as social media-free.
- 5. Promote Alternative Activities: Encourage them to engage in activities that don’t involve screens, such as reading, exercising, or spending time outdoors. Finding fulfilling offline activities can reduce the urge to check social media.
- 6. Model Healthy Behavior: Be a role model by managing your own social media use. Demonstrate a balanced approach to technology and prioritize face-to-face interactions.
- 7. Seek Professional Help: If the addiction is severe, suggest seeking help from a mental health professional. Therapists can provide strategies and support for overcoming addiction.
- 8. Support Their Journey: Be patient and supportive. Change takes time, and setbacks can happen. Celebrate their successes, no matter how small, and encourage them to keep going.
- 9. Use Technology Wisely: Introduce them to apps or features that track and limit social media usage. These tools can provide insights into their habits and help them make informed decisions.
- 10. Foster Real-Life Connections
Best books about social media addiction
Social media addiction is a growing concern, and several books explore its impact on individuals and society. Here are five insightful books that delve into the topic:
- 1. “Irresistible: The Rise of Addictive Technology and the Business of Keeping Us Hooked” by Adam Alter
– Adam Alter examines how technology, particularly social media, is designed to be addictive. He explores the psychological mechanisms that keep us glued to our screens and offers insights into how we can regain control over our habits.
- 2. “Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right Now” by Jaron Lanier
– Jaron Lanier, a pioneer in virtual reality, presents a compelling case for why we should consider stepping away from social media. He provides ten arguments that highlight the negative effects of social media on our well-being, privacy, and society.
- 3. “Digital Minimalism: Choosing a Focused Life in a Noisy World” by Cal Newport
– Cal Newport advocates for a more intentional approach to technology use. He introduces the concept of digital minimalism, which encourages people to focus on what truly matters and reduce the noise created by constant social media engagement.
- 4. “The Shallows: What the Internet Is Doing to Our Brains” by Nicholas Carr
– Nicholas Carr explores how the internet, including social media, is reshaping our brains and altering the way we think. He delves into the cognitive effects of digital consumption and raises important questions about the future of our mental capabilities.
- 5. “Alone Together: Why we Expect More from Technology and Less from Each Other” by Sherry Turkle
– Sherry Turkle investigates how technology, including social media, affects our relationships and sense of self. She argues that while we are more connected than ever, we are also experiencing increased feelings of isolation and loneliness.
These books provide a comprehensive look at the complexities of social media addiction and offer valuable insights for anyone looking to understand
Research about social media addiction
Social media addiction has become a significant area of research as platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have become integral parts of daily life for millions of people worldwide. Below are summaries of three to five official studies that have explored various aspects of social media addiction:
1. Study by Andreassen et al. (2012.:
– Title: “Development of a Facebook Addiction Scale”
– Journal: Psychological Reports
– Summary: This study aimed to develop a reliable and valid scale to measure Facebook addiction. The researchers surveyed over 400 students and identified key components of addiction, such as salience, mood modification, tolerance, withdrawal, conflict, and relapse. The study found that Facebook addiction shares similarities with other behavioral addictions and is associated with traits like neuroticism and extraversion.
2. Study by Kuss and Griffiths (2011.:
– Title: “Online Social Networking and Addiction—A Review of the Psychological Literature”
– Journal: International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
– Summary: This comprehensive review examined existing literature on social media addiction, highlighting its psychological underpinnings. The authors discussed how social media platforms can lead to addictive behaviors due to their interactive and rewarding nature. They also pointed out that individuals with social anxiety or low self-esteem are more prone to developing addictive patterns.
3. Study by Przybylski et al. (2013.:
– Title: “Motivational, Emotional, and Behavioral Correlates of Fear of Missing Out”
– Journal: Computers in Human Behavior
– Summary: This study explored the concept of “Fear of Missing Out” (FoMO) and its relationship with social media usage. The researchers found that individuals with high levels of FoMO tend to engage more frequently with social media, which can contribute to addictive behaviors. The study emphasized the role of FoMO as a significant motivator for social media engagement and its potential to exacerbate addiction.
4. Study by Andreassen et al. (2016.:
– Title: “The Relationship Between Addictive Use of Social Media and Video Games and Symptoms of Psychiatric Disorders: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study”
– Journal: Psychology of Addictive Behaviors
– Summary: This large-scale study investigated the link between social media addiction and psychiatric disorders. The findings suggested that addictive use of social media is associated with symptoms of ADHD, OCD, anxiety, and depression. The study highlighted the need for awareness and intervention strategies to address these co-occurring issues.
5. Study by Bányai et al. (2017.:
– Title: “Problematic Social Media Use: Results from a Large-Scale Nationally Representative Adolescent Sample”
– Journal: PLOS ONE
– Summary: This study focused on adolescents and their problematic use of social media. The researchers surveyed over 5,000 teenagers and found that excessive use is linked to poor mental health outcomes, including increased stress and decreased life satisfaction. The study underscored the importance of monitoring social media use among young people to prevent potential negative impacts on their well-being.
These studies collectively highlight the complexity of social media addiction, its psychological correlates, and its impact on mental health, emphasizing the need for further research and intervention strategies.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.
The impact of social media on our society
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, offering unprecedented opportunities for communication, information sharing, and community building. However, its pervasive presence has also led to a growing concern about social media addiction and its impact on society. This phenomenon, characterized by excessive use and an inability to control one’s engagement with social media platforms, has significant implications for individuals and communities.
### Mental Health Implications
One of the most profound effects of social media addiction is its impact on mental health. Studies have shown that excessive use of social media can lead to increased feelings of anxiety, depression, and loneliness. The constant comparison with others, driven by curated and often idealized portrayals of life, can lead to a negative self-image and decreased self-esteem. Furthermore, the addictive nature of social media, with its endless scroll and instant gratification, can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to stress.
### Impact on Relationships
Social media addiction can also strain personal relationships. As individuals become more engrossed in their online interactions, they may neglect face-to-face communication with family and friends. This can lead to misunderstandings, feelings of neglect, and weakened emotional bonds. Moreover, the public nature of social media can sometimes lead to conflicts and misunderstandings that spill over into real-life interactions.
### Productivity and Academic Performance
The addictive nature of social media can significantly impact productivity and academic performance. The constant notifications and the temptation to check social media can lead to procrastination and decreased focus. For students, this can result in lower academic achievement and a diminished ability to concentrate on studies. In the workplace, social media addiction can lead to decreased efficiency and a lack of engagement with work tasks.
### Societal Implications
On a broader scale, social media addiction can influence societal dynamics. The spread of misinformation and the echo chamber effect, where users are exposed predominantly to information that reinforces their existing beliefs, can polarize communities and contribute to social fragmentation.
Additionally, the emphasis on viral content can sometimes prioritize sensationalism over accuracy, affecting public discourse and decision-making.
### Economic Consequences
The economic impact of social media addiction is also noteworthy. Businesses may experience reduced productivity as employees spend significant amounts of time on social media during work hours. Moreover, the pressure to maintain a social media presence can lead to increased spending on technology and related services, impacting personal finances.
### Addressing the Issue
Addressing social media addiction requires a multifaceted approach. Education and awareness are crucial in helping individuals recognize the signs of addiction and understand its potential consequences. Encouraging digital literacy and promoting healthy online habits can empower users to take control of their social media use.
Additionally, platforms themselves can play a role by implementing features that promote mindful usage, such as screen time reminders and tools to limit notifications.
In conclusion, while social media offers numerous benefits, its addictive potential poses significant challenges to individual well-being and societal cohesion. By fostering a balanced approach to social media use, society can harness its positive aspects while mitigating its negative impacts.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.