Trying to quit combat addiction? Welcome to our digital detox series! This series focuses on how to stop digital and screen addictions. Findall our posts about digital addictions. Today, let’s talk about how to quit the combat addiction.

- What’s the combat addiction?
- Addiction to combat, a “real” addiction?
- What’s considered combat addiction?
- How much combat is too much?
- Some video games addiction facts & statistics
- Symptoms & Causes of the combat addiction
- Why is combat so addictive?
- Possible causes of combat dependency
- Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of combat addiction
- Problems, impacts & bad effects of combat
- Some benefits of combat
- Health problems
- Impact on brain & mental health
- Impact on relationships
- How to stop & quit your combat addiction
- Main steps and solutions to break the combat addiction
- Best combat blocker apps & functionalities
- Where to seek extra help?
- Conclusion
- To Go Further
- How to help someone with combat addiction
- Best books about video games addiction
- Research about video games addiction
What is the combat addiction?
About combat
Combat refers to active fighting or engagement between armed forces or individuals, typically involving weapons and physical confrontation. It encompasses military battles, skirmishes, or any conflict where opposing parties engage in direct, often violent, confrontation to achieve strategic or tactical objectives.
Addiction to combat, a “real” addiction?
Officially an addiction?
First, let’s have a look at the DSM-5,the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Does it include combat addiction?
Combat addiction is not explicitly listed as a distinct disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5.. The DSM-5 is a comprehensive classification of mental disorders used by mental health professionals, and while it includes a wide range of conditions, combat addiction as a specific diagnosis is not among them.
However, individuals who may be experiencing issues related to combat or military service might be diagnosed with other conditions that are included in the DSM-5. For example, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a common diagnosis for individuals who have experienced traumatic events, including combat.
Additionally, some individuals might struggle with substance use disorders or other behavioral issues as a result of their experiences in combat.
If you or someone you know is dealing with issues related to combat experiences, it is important to seek help from a qualified mental health professional who can provide a comprehensive assessment and appropriate treatment.
So what does “combat addiction” mean?
Combat Addiction: Taking Control and Finding Freedom
Combatting addiction is about actively battling against dependencies that can take a toll on your life. Whether it’s substances like alcohol or drugs, or behaviors such as gambling or excessive screen time, addiction can feel overwhelming. Here’s a simple breakdown of what combatting addiction involves:
- 1. Recognition: The first step is acknowledging there’s a problem. Understanding how addiction affects your daily life is crucial.
- 2. Seeking Support: You don’t have to go through this alone. Reaching out to friends, family, or support groups can provide the encouragement you need.
- 3. Professional Help: Therapists and counselors specialize in helping people overcome addiction. They can offer strategies and treatments tailored to your situation.
- 4. Healthy Habits: Replacing negative behaviors with positive ones, like exercising or pursuing a hobby, can make a big difference.
- 5. Stay Committed: Recovery is a journey with ups and downs. Staying focused and patient with yourself is key to long-term success.
Remember, overcoming addiction is entirely possible with the right mindset and support system. Taking that first step to combat addiction can lead to a healthier, happier life.
What is considered combat addiction?
Combat addiction, while not officially recognized as a distinct clinical diagnosis in major psychiatric manuals such as the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) or ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases), is a concept often discussed in the context of military psychology and veteran care. It refers to a condition where individuals develop a dependence on the adrenaline and intensity of combat situations. This can lead to challenges in adjusting to civilian life and potentially seeking out dangerous situations to replicate the combat experience.
While there are no formal criteria for diagnosing combat addiction, the following considerations might be relevant in assessing whether someone is experiencing issues related to combat addiction:
- 1. Behavioral Patterns: Repeatedly seeking out high-risk situations or environments that mimic the intensity of combat, even when not required or advised.
- 2. Emotional Dependence: A strong emotional or psychological craving for the adrenaline rush associated with combat situations. This might manifest as feelings of restlessness or dissatisfaction with everyday life.
- 3. Impact on Daily Life: Difficulty in adjusting to civilian life, including challenges in maintaining relationships, employment, or other responsibilities due to a preoccupation with combat experiences or seeking similar thrills.
- 4. Psychological Symptoms: Symptoms such as anxiety, depression, or irritability when not engaged in combat or high-adrenaline activities. This might also include symptoms of PTSD, although the two are distinct conditions.
- 5. Avoidance of Normalcy: Avoidance of situations or environments perceived as mundane or lacking excitement, leading to a preference for chaos or conflict.
- 6. Re-experiencing Combat: Frequent and intense flashbacks, dreams, or thoughts about combat experiences, sometimes accompanied by a desire to return to combat zones.
- 7. Interpersonal Conflicts: Strained relationships due to a preoccupation with combat experiences or a perceived inability to connect with those who have not shared similar experiences.
- 8. Risk-Taking Behavior: Engaging in reckless or dangerous activities, such as extreme sports or illicit activities, to replicate the combat experience.
It’s important to note that these are not official diagnostic criteria but rather considerations that might be used by mental health professionals when assessing individuals who have served in combat roles. Proper diagnosis and treatment should involve a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified mental health professional, who can differentiate between combat addiction, PTSD, and other related conditions. Treatment approaches might include therapy, support groups, and interventions designed to help individuals find healthy ways to channel their need for adrenaline and excitement.
How much combat is too much?
The question of how much time spent on combat is too much can be approached from various perspectives, including physical, psychological, and ethical considerations. Here’s a breakdown of these aspects:
### Physical Considerations
- 1. Fatigue and Readiness: Prolonged combat can lead to physical exhaustion, which diminishes a soldier’s effectiveness and increases the risk of accidents or mistakes. Military organizations often have guidelines on duty cycles to ensure that personnel are rested and alert.
- 2. Injury and Recovery: Extended periods in combat increase the likelihood of injuries. Adequate time for recovery and medical attention is crucial to prevent long-term health issues.
### Psychological Considerations
- 1. Mental Health: Continuous exposure to combat situations can lead to significant psychological stress, resulting in conditions such as PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder), anxiety, and depression. Mental health support and adequate downtime are essential to mitigate these risks.
- 2. Moral Injury: Prolonged engagement in combat can lead to moral injury, where individuals struggle with actions that conflict with their ethical or moral beliefs. This can have lasting impacts on mental health and well-being.
### Ethical Considerations
- 1. Rules of Engagement: Ethical guidelines and rules of engagement are designed to limit unnecessary harm and ensure that combat operations are conducted with respect for human rights. Extended combat operations can strain adherence to these principles.
- 2. Impact on Civilians: Prolonged combat often affects civilian populations, leading to displacement, casualties, and humanitarian crises. The ethical implications of these impacts must be carefully considered.
### Operational Considerations
- 1. Mission Objectives: The duration of combat should be aligned with clear and achievable mission objectives. Prolonged engagements without clear goals can lead to mission creep and unnecessary loss of life and resources.
- 2. Sustainability: Military operations require logistical support, including supplies, reinforcements, and maintenance. Extended combat can strain these resources, affecting overall operational sustainability.
### Conclusion
Determining how much time spent on combat is too much is complex and context-dependent. It requires balancing operational needs with the health and well-being of personnel, ethical considerations, and the impact on civilian populations. Military planners and policymakers must continuously assess these factors to make informed decisions about the duration and nature of combat operations.
Some video games addiction facts & statistics

Video game addiction, often referred to as gaming disorder, has been a topic of increasing concern among researchers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers. While the landscape of video game addiction is complex and multifaceted, several key statistics and findings have emerged over recent years:
- 1. Prevalence:
– The World Health Organization (WHO) included “gaming disorder” in its International Classification of Diseases (ICD-
- 11. in 2019, highlighting its growing recognition as a mental health issue.
– Estimates of the prevalence of gaming disorder vary widely. Research suggests that approximately 1% to 10% of gamers may exhibit behaviors consistent with gaming addiction, depending on the criteria used and the population studied.
- 2. Demographics:
– Gaming addiction is more commonly reported among males than females, with young males being particularly susceptible.
– Adolescents and young adults are the most affected age groups, with many studies focusing on individuals aged 12 to 24.
- 3. Associated Factors:
– Psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, and ADHD have been linked to a higher risk of developing gaming addiction.
– Social factors, including peer pressure and a lack of social support, can also contribute to excessive gaming behaviors.
- 4. Impact on Life:
– Individuals with gaming addiction may experience negative consequences in various aspects of life, including academic performance, social relationships, and physical health.
– Excessive gaming can lead to sleep disturbances, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor dietary habits, increasing the risk of obesity and related health issues.
- 5. Economic Impact:
– The gaming industry is a multi-billion-dollar market, and while it provides entertainment and economic benefits, the costs associated with gaming addiction, such as healthcare expenses and lost productivity, are significant.
- 6. Treatment and Intervention:
– Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most common treatment approaches for gaming addiction.
– Some countries, like South Korea and China, have implemented policies to limit gaming time among youth to combat addiction.
- 7. Research and Controversy:
– The classification of gaming disorder remains controversial, with some experts arguing that it pathologizes normal gaming behavior.
– Ongoing research aims to better understand the neurobiological and psychological mechanisms underlying gaming addiction.
- 8. Global Perspectives:
– Different countries report varying prevalence rates, influenced by cultural attitudes towards gaming and the availability of gaming platforms.
– In Asia, particularly in countries like China and South Korea, gaming addiction is recognized as a significant public health issue, leading to the implementation of specific interventions and regulations.
As the gaming industry continues to evolve, ongoing research is essential to better understand the nuances of gaming addiction and develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Is the combat addiction widespread?
Addiction to combat, often referred to as “combat addiction” or “war addiction,” is a complex and somewhat controversial topic. It involves individuals, typically military personnel, who develop a psychological dependency on the adrenaline and heightened sense of purpose experienced during combat situations. While not officially recognized as a distinct psychological disorder in major diagnostic manuals like the DSM-5, it is a phenomenon that some veterans and mental health professionals acknowledge.
### Factors Contributing to Combat Addiction
- 1. Adrenaline Rush: Combat situations often involve high-stakes scenarios that trigger adrenaline surges. Some individuals may become addicted to this heightened state of alertness and energy.
- 2. Sense of Purpose: Many soldiers find a strong sense of purpose and camaraderie in combat situations, which can be difficult to replicate in civilian life.
- 3. Identity: For some veterans, their identity is closely tied to their role in the military and combat experiences, making it challenging to adjust to a different lifestyle.
- 4. Avoidance of Civilian Life: Transitioning back to civilian life can be difficult, and some veterans may prefer the familiarity and structure of military life, even if it involves combat.
### Prevalence and Recognition
– Prevalence: It’s difficult to quantify how many people are affected by combat addiction due to the lack of formal recognition and standardized diagnostic criteria. However, anecdotal evidence and some studies suggest that a subset of veterans may experience symptoms consistent with this phenomenon.
– Recognition: While not officially recognized as a disorder, combat addiction shares similarities with other behavioral addictions and can coexist with conditions like PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder).
### Addressing Combat Addiction
- 1. Therapy and Counseling: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can help individuals address underlying issues and develop coping strategies.
- 2. Support Groups: Veteran support groups can provide a sense of community and understanding among those with similar experiences.
- 3. Reintegration Programs: Programs designed to assist veterans in transitioning to civilian life can help address issues related to identity and purpose.
- 4. Mindfulness and Stress Reduction: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and stress reduction exercises can help manage the desire for adrenaline and combat-related experiences.
### Conclusion
While combat addiction is not widely recognized or understood, it is an important topic that highlights the challenges some veterans face when transitioning to civilian life. Continued research and awareness are essential to better understand and support those who may be struggling with this issue.
Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of combat addiction
Why is combat so addictive?
Why is Combat So Addictive?
Have you ever found yourself glued to a game or movie just because of the intense combat scenes? You’re not alone! Combat—whether in video games, movies, or even sports—has a magnetic pull that keeps us coming back for more. But why is it so addictive? Let’s break it down:
- 1. Adrenaline Rush: Combat situations trigger your body’s fight-or-flight response, releasing adrenaline. This surge makes you feel energized and exhilarated, creating a thrilling experience that many crave.
- 2. Challenge and Skill-building: Engaging in combat requires strategy, quick thinking, and skill. Overcoming tough opponents or mastering complex moves gives a sense of achievement, encouraging you to keep improving and facing new challenges.
- 3. Narrative Engagement: In stories and games, combat often drives the plot forward. It creates tension and excitement, keeping you invested in the outcome and eager to see what happens next.
- 4. Escapism: Combat scenarios allow you to step into different roles and worlds. Whether you’re a heroic warrior or a cunning tactician, it offers a break from everyday life and the chance to experience something intense and dramatic.
- 5. Social Interaction: Many combat-focused games and activities are social. Competing or cooperating with others adds a layer of interaction that can enhance the fun and make the experience more memorable.
- 6. Reward Systems: Games often incorporate reward systems like leveling up, unlocking new abilities, or earning achievements. These incentives keep you motivated to continue engaging in combat to reap the rewards.
- 7. Psychological Satisfaction: There’s a primal satisfaction in mastering conflict and overcoming obstacles. Combat scenarios tap into deep-seated instincts, providing a sense of control and competence.
In a nutshell, combat captivates us by combining excitement, challenge, and the opportunity for growth and connection. Whether it’s the rush of victory or the thrill of the fight, combat elements tap into fundamental human desires, making them irresistibly addictive.
Possible causes of combat dependency
Combat addiction, also known as the addiction to the adrenaline and intensity of combat situations, is a complex phenomenon often observed in military personnel and others exposed to high-stress, high-risk environments. Several factors contribute to the development of combat addiction:
- 1. Adrenaline Rush: Combat situations trigger the body’s fight-or-flight response, releasing adrenaline and other stress hormones. This physiological response can create a heightened state of alertness and energy, which some individuals find exhilarating and addictive.
- 2. Sense of Purpose and Identity: Many individuals in combat roles derive a strong sense of purpose and identity from their work. The structured environment, clear objectives, and camaraderie can be deeply fulfilling, making it difficult to adjust to civilian life where these elements may be lacking.
- 3. Camaraderie and Brotherhood: The intense bonds formed between soldiers in combat can be profoundly meaningful. The shared experiences and reliance on one another for survival create a unique sense of brotherhood that can be hard to replicate in civilian life.
- 4. Escape from Civilian Life: For some, combat provides an escape from personal issues or dissatisfaction with civilian life. The focus and intensity of combat can serve as a distraction from personal problems or a lack of direction outside the military.
- 5. Psychological Conditioning: Repeated exposure to combat conditions can lead to psychological conditioning, where individuals become accustomed to the stress and chaos of battle. Over time, they may begin to crave these conditions as they become a normalized part of their experience.
- 6. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): While PTSD is a distinct condition, its symptoms can sometimes overlap with combat addiction. Individuals with PTSD might seek out combat-like situations to regain a sense of control or to re-experience the heightened emotions associated with their trauma.
- 7. Lack of Support Systems: The transition from military to civilian life can be challenging, especially if there is a lack of support systems. Without adequate mental health resources and community support, individuals may seek out combat-like situations to cope with feelings of isolation or purposelessness.
- 8. Cultural and Institutional Factors: Military culture often valorizes bravery, toughness, and resilience, which can reinforce the appeal of combat. Institutional pressures and expectations can also play a role in encouraging repeated deployments or engagement in high-risk roles.
Understanding combat addiction requires a nuanced approach that considers both the psychological and social dimensions of military life. Addressing it effectively involves providing comprehensive support for veterans and active-duty personnel, including mental health services, community reintegration programs, and initiatives that foster a sense of purpose outside of combat roles.
Signs & Symptoms of combat addiction
Now let’s see if you have the combat addiction problem.
Combat addiction, much like any other form of addiction, can have profound effects on an individual’s life and well-being. It often manifests in those who have experienced combat, such as military personnel or those involved in high-stakes environments. Recognizing the signs of combat addiction is crucial for seeking appropriate help and support. Here are seven signs that may indicate someone is a combat addict:
- 1. Craving for Adrenaline: One of the most prominent signs of combat addiction is a constant craving for adrenaline. Individuals may seek out high-risk situations or engage in dangerous activities to replicate the intense rush they experienced in combat.
- 2. Difficulty Adjusting to Civilian Life: A combat addict might struggle with the transition back to civilian life. They may find everyday activities mundane or unfulfilling and often express a desire to return to the combat environment where they felt a sense of purpose and excitement.
- 3. Recurrent Thoughts and Flashbacks: Persistent thoughts or flashbacks of combat experiences can indicate an unhealthy fixation. These intrusive memories might be accompanied by emotional distress and can interfere with daily functioning.
- 4. Emotional Numbness: Combat addicts may exhibit emotional numbness, where they find it difficult to connect with others on an emotional level. This detachment can affect personal relationships and lead to feelings of isolation.
- 5. Aggression and Irritability: Heightened aggression or irritability can be a sign of combat addiction. Individuals may have a short temper and react disproportionately to minor provocations, reflecting a lingering combat mindset.
- 6. Neglect of Responsibilities: A person addicted to combat might neglect personal and professional responsibilities, prioritizing activities that remind them of combat or seeking environments that simulate those experiences.
- 7. Substance Abuse: To cope with the psychological effects of combat addiction, individuals might turn to alcohol or drugs. Substance abuse can serve as a temporary escape but ultimately exacerbates the underlying issues.
Recognizing these signs is the first step toward addressing combat addiction. It’s important for individuals exhibiting these symptoms to seek professional help, such as therapy or counseling, to work through their experiences and find healthier ways to cope with their emotions and desires. Support from family and friends is also vital in helping combat addicts reintegrate into civilian life and find fulfillment outside of combat scenarios.
Try our digital habit & screen addiction test:
Problems, impacts & bad effects of combat: should you quit?

What are some benefits of combat
Combat, in its various forms, has been a part of human history for millennia. While the concept of combat often carries negative connotations due to its association with violence and conflict, there are contexts in which combat can be seen as beneficial or even advantageous. Here are some perspectives on the potential pros and advantages of combat:
- 1. Self-Defense and Protection: Combat skills are essential for self-defense. Knowing how to protect oneself and others can be empowering and provide a sense of security. This is particularly important for individuals in dangerous environments or professions that require personal protection.
- 2. Discipline and Focus: Training in combat sports or martial arts requires discipline, focus, and dedication. Practitioners often develop a strong work ethic, improved concentration, and the ability to set and achieve goals, which can be beneficial in many areas of life.
- 3. Physical Fitness: Engaging in combat sports or martial arts is an excellent way to improve physical fitness. These activities enhance strength, endurance, flexibility, and coordination. The rigorous training involved can lead to better overall health and well-being.
- 4. Mental Resilience: Combat training often involves facing challenging situations and overcoming adversity. This can build mental toughness, resilience, and the ability to remain calm under pressure. Such skills are valuable in both personal and professional settings.
- 5. Camaraderie and Community: Many combat sports and martial arts foster a sense of community and camaraderie among participants. Training together can build strong bonds and friendships, providing social support and a sense of belonging.
- 6. Cultural and Historical Significance: Combat sports and martial arts often have deep cultural and historical roots. Practicing these disciplines can provide insights into different cultures and traditions, promoting cultural appreciation and understanding.
- 7. Confidence and Self-Esteem: Mastering combat skills can boost confidence and self-esteem. Achieving proficiency in a challenging discipline can lead to a greater sense of self-worth and accomplishment.
- 8. Strategic Thinking: Combat, particularly in sports like boxing, wrestling, or martial arts, involves strategic thinking and quick decision-making. Practitioners learn to anticipate opponents’ moves and develop strategies, which can enhance problem-solving skills.
- 9. Career Opportunities: For some, combat skills can lead to career opportunities in fields such as law enforcement, military, security, or professional sports. These careers often require specialized training and offer unique challenges and rewards.
- 10. Artistic Expression: Some forms of combat, such as martial arts, are also viewed as forms of artistic expression. They emphasize grace, form, and technique, allowing practitioners to express themselves creatively.
It’s important to note that while there are advantages to combat in certain contexts, it should always be approached with respect for its potential risks and consequences. Ensuring safety, ethical considerations, and a focus on personal growth and development are crucial when engaging in any form of combat training or activity.But on the other hand, what are some combat addiction problems that addicts suffer from?
General health problems
Combat, whether experienced by military personnel, law enforcement officers, or civilians in conflict zones, can have profound and lasting effects on an individual’s health. These effects can be broadly categorized into physical, psychological, and social impacts. Understanding these consequences is crucial for providing appropriate support and interventions for those affected.
### Physical Health Effects
- 1. Injuries and Disabilities: Combat often results in physical injuries ranging from minor wounds to severe trauma such as amputations, spinal cord injuries, and traumatic brain injuries (TBI). These can lead to long-term disabilities and require extensive rehabilitation.
- 2. Chronic Pain: Many veterans and combat survivors experience chronic pain due to injuries sustained during combat. This can affect daily functioning and quality of life.
- 3. Hearing Loss: Exposure to loud noises from explosions and gunfire can lead to hearing loss or tinnitus, a persistent ringing in the ears.
- 4. Cardiovascular Issues: The stress of combat can exacerbate cardiovascular problems, increasing the risk of heart disease and hypertension.
- 5. Exposure to Hazardous Substances: Combat environments may expose individuals to hazardous substances like chemicals, leading to respiratory issues, cancer, or other long-term health problems.
### Psychological Health Effects
- 1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): One of the most common psychological effects of combat, PTSD can cause flashbacks, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the traumatic event.
- 2. Depression and Anxiety: Combat can lead to depression and anxiety disorders, affecting mood, behavior, and overall mental well-being.
- 3. Substance Abuse: Some individuals may turn to alcohol or drugs as a coping mechanism for dealing with the stress and trauma of combat.
- 4. Moral Injury: This involves psychological distress resulting from actions, or the lack of them, which violate one’s moral or ethical code.
- 5. Suicidal Ideation: The mental health challenges faced by combat veterans can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
### Social and Behavioral Effects
- 1. Relationship Strain: The psychological impact of combat can strain relationships with family and friends, leading to social isolation or difficulties in maintaining personal connections.
- 2. Difficulty Transitioning to Civilian Life: Veterans may struggle with reintegration into civilian life, facing challenges in employment, education, and social interactions.
- 3. Aggression and Violence: Some individuals may exhibit increased aggression or violent behavior as a result of combat-related stress and trauma.
- 4. Homelessness: The combination of mental health issues and difficulty in reintegration can contribute to homelessness among veterans.
### Coping and Support
Addressing the effects of combat on health requires a comprehensive approach:
– Medical Treatment: Access to quality medical care for physical injuries and chronic conditions is essential.
– Mental Health Services: Counseling, therapy, and support groups can help individuals cope with PTSD, depression, and other psychological issues.
– Rehabilitation Programs: These can aid in recovery from physical injuries and help individuals regain independence.
– Social Support: Building a strong support network of family, friends, and fellow veterans can provide emotional and practical assistance.
– Vocational Training and Education: Programs that facilitate skill development and employment can ease the transition to civilian life.
In conclusion, the effects of combat on health are multifaceted and can have a profound impact on an individual’s life. Recognizing and addressing these effects through comprehensive care and support systems is crucial for the well-being of those who have experienced combat.
combat and sleep disorders
Combat and exposure to combat-related environments can indeed lead to sleep disorders or sleep problems. This is a well-documented issue among military personnel and veterans. Several factors contribute to the development of sleep disturbances in this population:
- 1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Many individuals who have been in combat situations develop PTSD, a condition that is often accompanied by sleep disturbances. Nightmares and night terrors are common symptoms, leading to interrupted sleep and insomnia.
- 2. Stress and Anxiety: The high-stress environment of combat can lead to chronic stress and anxiety, both of which are known to interfere with normal sleep patterns. Hyperarousal, a heightened state of alertness, can make it difficult for individuals to relax and fall asleep.
- 3. Depression: Combat exposure can lead to depression, which is frequently associated with sleep problems. Individuals with depression may experience insomnia or, conversely, hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness).
- 4. Physical Injuries: Injuries sustained during combat can cause pain and discomfort, making it difficult to find a comfortable sleeping position and leading to disrupted sleep.
- 5. Irregular Sleep Schedules: Military operations often require personnel to work irregular hours, disrupting their natural sleep-wake cycles. This can lead to circadian rhythm disorders, making it difficult to establish a regular sleep pattern even after returning from deployment.
- 6. Substance Use: Some individuals may turn to alcohol or other substances as a coping mechanism for dealing with the stress of combat, which can further exacerbate sleep problems.
- 7. Environmental Factors: The sleeping conditions in combat zones are often less than ideal, with noise, uncomfortable sleeping arrangements, and the need to remain vigilant contributing to poor sleep quality.
Addressing sleep disorders in individuals exposed to combat is crucial, as inadequate sleep can have significant impacts on physical and mental health. Treatment may involve a combination of therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-We), medication, stress management techniques, and lifestyle changes. It is important for those affected to seek help from healthcare professionals who are experienced in dealing with combat-related sleep issues.
combat affecting your brain & mental health: bad for brain and mental health?
Some effects of combat on your brain
The Hidden Toll: How Combat Affects Your Brain
Hey there! Today, let’s talk about something serious but important—the impact combat can have on your brain. While serving your country is incredibly brave, it can come with some tough mental challenges. Here are some of the key ways combat can affect your brain:
###
- 1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Experiencing or witnessing traumatic events in combat can lead to PTSD. Symptoms include flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the event. It’s like your brain is stuck replaying the worst moments.
###
- 2. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Combat often involves exposure to blasts, explosions, or physical impacts, which can cause TBIs. Even mild TBIs, also known as concussions, can result in headaches, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating.
###
- 3. Depression and Anxiety
The stress of combat can lead to persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and overwhelming worry. These mental health challenges can make everyday tasks feel impossible and impact overall quality of life.
###
- 4. Sleep Disorders
Nightmares and insomnia are common among those who’ve served in combat. Poor sleep can further exacerbate other mental health issues, making it hard to stay focused and energized.
###
- 5. Substance Abuse
Some veterans might turn to alcohol or drugs as a way to cope with their experiences. While it might offer temporary relief, it often leads to further mental and physical health problems.
###
- 6. Cognitive Impairments
Combat stress can affect memory, attention, and decision-making abilities. This can make it difficult to perform tasks that were once easy and enjoy activities that used to bring joy.
###
- 7. Emotional Numbness
To protect themselves, some veterans may shut down emotionally. This can lead to difficulties in forming and maintaining relationships, feeling disconnected from loved ones, and a lack of interest in activities they once enjoyed.
### Taking Care of Your Brain
If you or someone you know is struggling with these issues, it’s important to reach out for help. Talking to a mental health professional, joining support groups, and staying connected with loved ones can make a big difference. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Thank you for taking the time to read about this important topic. Let’s support our heroes and ensure they have the resources they need to heal and thrive!
Some effects of combat on your mental health
Combat can have profound and lasting effects on mental health, impacting individuals in numerous ways. Here are some of the most common mental health challenges faced by those who have experienced combat:
- 1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): One of the most well-known consequences of combat is PTSD. Symptoms include flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the traumatic event. These symptoms can be debilitating and interfere with daily life.
- 2. Depression: Combat veterans may experience depression, characterized by persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and feelings of hopelessness or worthlessness.
- 3. Anxiety Disorders: Beyond PTSD, veterans may suffer from generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, or other anxiety-related conditions, leading to excessive worry, restlessness, and physical symptoms like heart palpitations.
- 4. Substance Abuse: Some veterans turn to alcohol or drugs as a way to cope with the stress and trauma of combat. This can lead to addiction and further exacerbate mental health issues.
- 5. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Exposure to blasts and other combat-related injuries can result in TBI, which can cause cognitive impairments, emotional instability, and increased risk of mental health disorders.
- 6. Moral Injury: This occurs when individuals feel they have violated their moral or ethical beliefs during combat, leading to profound guilt, shame, and spiritual distress.
- 7. Adjustment Disorders: Transitioning from military to civilian life can be challenging, leading to adjustment disorders characterized by difficulty coping with change, stress, and new environments.
- 8. Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors: The combination of PTSD, depression, and other mental health issues can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors among veterans.
- 9. Relationship Strain: Combat-related mental health issues can strain relationships with family and friends, leading to isolation and further emotional distress.
- 10. Hypervigilance: Many combat veterans experience heightened alertness and a constant sense of danger, which can be exhausting and interfere with normal functioning.
Addressing these mental health challenges requires comprehensive support, including therapy, medication, peer support, and community resources. Early intervention and ongoing care are crucial in helping veterans manage these effects and improve their quality of life.
Does combat cause stress and anxiety?
Yes, combat can indeed cause stress and anxiety. Individuals who have experienced combat situations, such as military personnel, often face a range of psychological challenges due to the intense and life-threatening nature of these experiences. Here are some key points to consider:
- 1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): One of the most common psychological effects of combat is PTSD. This condition can develop after exposure to traumatic events, such as those experienced in combat. Symptoms include flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the event.
- 2. Acute Stress Reaction: Immediately following a combat situation, individuals may experience acute stress reactions. This can include symptoms such as confusion, disorientation, and intense emotional distress.
- 3. Anxiety Disorders: Combat veterans may develop generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or other anxiety-related conditions. These disorders can manifest as persistent worry, restlessness, and physical symptoms like increased heart rate and sweating.
- 4. Depression: The stress and trauma of combat can also lead to depression. This may include feelings of hopelessness, loss of interest in activities, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns.
- 5. Survivor’s Guilt: Individuals who survive combat situations while others do not may experience survivor’s guilt, which can contribute to anxiety and depression.
- 6. Adjustment Disorders: Transitioning back to civilian life can be challenging for veterans, leading to adjustment disorders characterized by stress, anxiety, and difficulty coping with the change.
- 7. Substance Abuse: Some individuals may turn to alcohol or drugs as a way to cope with the stress and anxiety resulting from combat experiences, which can lead to substance abuse issues.
- 8. Support Systems: Access to strong support systems, including family, friends, and mental health professionals, can play a critical role in helping individuals manage stress and anxiety related to combat.
- 9. Therapeutic Interventions: Various therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), have been effective in treating combat-related stress and anxiety.
- 10. Resilience and Coping Strategies: Building resilience and developing healthy coping strategies can help individuals manage stress and anxiety more effectively.
Overall, while combat can be a significant source of stress and anxiety, understanding these challenges and seeking appropriate support and treatment can lead to better mental health outcomes for those affected.
Can combat addiction lead to sadness and depression?

Combat addiction, like any form of addiction, can indeed lead to sadness and depression. The relationship between addiction and mental health is complex and multifaceted. Here are several ways in which combat addiction can contribute to feelings of sadness and depression:
- 1. Biochemical Changes: Addiction often alters brain chemistry. Substances or behaviors that are addictive can lead to changes in neurotransmitter levels, such as dopamine and serotonin, which are closely linked to mood regulation. When the addictive behavior is not engaged in, individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms, including depression.
- 2. Life Consequences: Addiction can lead to significant negative consequences in various areas of life, including relationships, employment, and financial stability. These consequences can create stress, anxiety, and sadness, contributing to a cycle of depression.
- 3. Isolation: Many individuals struggling with addiction become isolated from family and friends. This isolation can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and sadness, which are risk factors for depression.
- 4. Self-Esteem Issues: Addiction often leads to feelings of guilt and shame, which can severely impact self-esteem. Low self-esteem is a common feature of depression.
- 5. Co-occurring Disorders: It is not uncommon for individuals with addiction to have co-occurring mental health disorders, such as depression or anxiety. These disorders can feed into each other, making it difficult to break the cycle of addiction and depression.
- 6. Loss of Control: The feeling of being unable to control one’s behavior or the addiction itself can lead to hopelessness and despair, key components of depression.
Addressing combat addiction and its associated mental health challenges often requires a comprehensive approach, including therapy, support groups, and sometimes medication. It’s crucial for individuals struggling with addiction and depression to seek professional help to address both issues simultaneously. Early intervention can improve outcomes and help individuals regain control of their lives.
Dopamine and combat
Dopamine, a neurotransmitter in the brain, plays a crucial role in regulating mood, motivation, reward, and pleasure. It is often associated with feelings of happiness and satisfaction, but its influence extends far beyond these emotions. In the context of combat, dopamine can have significant implications for both psychological and physical performance.
### The Role of Dopamine in Combat
- 1. Motivation and Focus: Dopamine is integral in maintaining focus and motivation, which are essential in combat situations. Soldiers and combatants need to remain alert and attentive to their surroundings, and dopamine helps in sustaining this level of concentration.
- 2. Reward System: The brain’s reward system, driven by dopamine, reinforces behaviors that are beneficial for survival. In combat, this can translate to the reinforcement of strategic actions and decision-making that lead to successful outcomes.
- 3. Stress Response: Combat is inherently stressful, and dopamine interacts with other neurotransmitters like adrenaline to modulate the body’s response to stress. Adequate dopamine levels can help manage stress, allowing combatants to remain calm under pressure.
- 4. Learning and Memory: Dopamine is involved in learning and memory, crucial for adapting to rapidly changing combat environments. It aids in the retention of tactical information and the learning of new skills or strategies.
- 5. Risk and Reward Assessment: In combat, assessing risks and rewards is vital. Dopamine influences how risks are perceived and can affect decision-making processes, potentially leading to more calculated and strategic actions.
### Implications for Military Training
Understanding the role of dopamine in combat can inform military training and operational strategies. Here are a few implications:
– Training Programs: Incorporating elements that stimulate dopamine release, such as rewards for successful training exercises, can enhance learning and motivation.
– Stress Management Techniques: Training soldiers in stress management techniques that naturally boost dopamine levels, like mindfulness and physical exercise, can improve their performance in high-pressure situations.
– Nutritional and Lifestyle Interventions: Ensuring that combatants maintain a diet and lifestyle that supports healthy dopamine levels can be beneficial. This includes adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, and regular physical activity.
– Psychological Support: Providing psychological support to manage stress and mental health can help maintain optimal dopamine function, which is crucial for performance and well-being in combat scenarios.
### Conclusion
Dopamine plays a multifaceted role in combat, influencing motivation, stress response, learning, and decision-making. By understanding and leveraging the effects of dopamine, military training programs can enhance the performance and resilience of soldiers in combat situations. As research continues to uncover the complexities of neurotransmitter functions, strategies to optimize dopamine levels could become a key component of military preparedness and effectiveness.
combat effects on focus, productivity, attention span, academic performance…
How Combat Can Impact Focus, Productivity, Attention Span, and Academic Performance
Hey there! 🌟 Today, let’s dive into an important topic: how combat experiences can affect focus, productivity, attention span, and even academic performance. Whether you’re a veteran, a student, or just curious, understanding these impacts is crucial. Let’s break it down in a simple and friendly way!
###
- 1. Focus and Attention Span
Combat Exposure:
– High-Stress Environments: Combat situations are intense and stressful, which can lead to lasting effects on the brain.
– Hypervigilance: Constant alertness during combat can make it hard to relax, affecting the ability to concentrate in everyday tasks.
Impact:
– Difficulty Concentrating: Veterans may find it challenging to maintain focus on tasks that don’t require the same level of vigilance.
– Shortened Attention Span: Sustained attention might be tougher, making it hard to engage in lengthy activities like studying or working on projects.
###
- 2. Productivity
Combat Exposure:
– Mental Fatigue: The mental toll of combat can lead to exhaustion, even after returning to civilian life.
– Emotional Struggles: Experiences in combat can result in anxiety, depression, or PTSD, all of which can drain energy and reduce motivation.
Impact:
– Lower Efficiency: Tasks may take longer to complete, and the quality of work might decline.
– Decreased Motivation: A lack of enthusiasm can lead to procrastination and reduced overall productivity.
###
- 3. Academic Performance
Combat Exposure:
– Disrupted Education: Time spent in combat can interrupt schooling or higher education pursuits.
– Mental Health Challenges: Struggles with mental health can make it hard to keep up with studies.
Impact:
– Lower Grades: Difficulty concentrating and completing assignments can result in poorer academic performance.
– Reduced Engagement: Less participation in classes and academic discussions can hinder learning and retention of information.
###
- 4. Coping Strategies and Support
What Helps:
– Therapy and Counseling: Professional support can address mental health challenges and improve coping mechanisms.
– Support Groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide comfort and understanding.
– Healthy Habits: Regular exercise, proper sleep, and a balanced diet can enhance mental clarity and overall well-being.
How to Improve:
– Mindfulness Practices: Techniques like meditation can help increase focus and reduce stress.
– Structured Routine: Creating a consistent daily schedule can aid in managing time and maintaining productivity.
– Seeking Help: Don’t hesitate to reach out to mental health professionals or support networks when needed.
### Wrapping Up
Combat experiences can significantly impact focus, productivity, attention span, and academic performance. However, with the right support and strategies, it’s possible to overcome these challenges and thrive. If you or someone you know is struggling, remember that help is available, and taking the first step can make a world of difference.
Stay strong and take care! 💪✨
A word about ADHD and combat
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) can influence how individuals interact with various environments, including high-stress situations like combat. It’s important to note that ADHD affects individuals differently, and experiences can vary widely. However, some general patterns can be observed regarding how people with ADHD might interact with combat situations:
- 1. Hyperfocus: One of the characteristics of ADHD is the ability to hyperfocus on tasks that are stimulating or of high interest. In combat, this could mean that individuals with ADHD might become intensely focused on specific tasks or objectives, potentially enhancing their performance in certain situations.
- 2. Impulsivity: ADHD is often associated with impulsivity, which can manifest as quick decision-making without fully considering the consequences. In combat, this might lead to taking risks that others might avoid. While this can sometimes be advantageous, it can also lead to potentially dangerous situations.
- 3. Stress Response: Individuals with ADHD may have a different physiological and psychological response to stress. Some may thrive in high-pressure environments, finding the constant stimulation engaging. Others might find the stress overwhelming, leading to difficulties in maintaining focus and composure.
- 4. Attention Shifts: People with ADHD often experience difficulty maintaining attention on tasks that are not inherently stimulating. In a combat situation, this might mean they are more easily distracted by their surroundings, which could be both a disadvantage and an advantage, depending on the context.
- 5. Adaptability: The ability to think quickly and adapt to changing situations can be a strength in combat. Individuals with ADHD might excel in dynamic environments where quick thinking and adaptability are crucial.
- 6. Team Dynamics: ADHD can affect social interactions and communication, which are critical in a team-based combat environment. Some individuals might struggle with following orders or communicating effectively under stress, while others might bring creativity and problem-solving skills to the team.
- 7. Emotional Regulation: Managing emotions can be challenging for individuals with ADHD. In combat, where emotions can run high, this might lead to difficulties in maintaining emotional control, potentially affecting decision-making and interactions with others.
It’s crucial to approach this topic with sensitivity and an understanding that ADHD is a diverse condition. Individuals with ADHD can bring unique strengths and challenges to combat situations, and support systems, training, and accommodations can help maximize their potential and ensure their well-being.
Additionally, ongoing research continues to enhance our understanding of ADHD and its impact on various life experiences, including military service and combat.
Affecting your relationships
combat and self-esteem
How Combat Affects Self-Esteem: Understanding the Impact
Combat experiences can deeply influence a person’s self-esteem in various ways. Whether someone has served in the military, faced challenging situations, or dealt with personal battles, understanding these effects is crucial for healing and growth. Let’s explore how combat can shape self-esteem:
###
- 1. Building Confidence Through Accomplishments
– Skill Mastery: Successfully navigating combat situations can boost confidence. Mastering survival skills, teamwork, and leadership often leads to a sense of achievement.
– Overcoming Challenges: Facing and overcoming intense challenges reinforces the belief in one’s abilities, enhancing self-worth.
###
- 2. Dealing with Trauma and Anxiety
– Post-Traumatic Stress: Combat can lead to PTSD, which may diminish self-esteem. Flashbacks, nightmares, and anxiety can make individuals feel powerless or worthless.
– Emotional Struggles: Persistent stress and emotional turmoil can lead to negative self-perception and reduced confidence.
###
- 3. Strengthening Resilience
– Adaptability: Combat teaches adaptability and resilience. Recognizing one’s ability to endure and bounce back from tough times can improve self-esteem.
– Sense of Purpose: Serving in combat often provides a strong sense of purpose and belonging, contributing positively to self-worth.
###
- 4. Impact of Relationships and Support Systems
– Support from Peers: Camaraderie and support from fellow service members can enhance self-esteem by fostering a sense of community and acceptance.
– Isolation: Conversely, feeling isolated or misunderstood after combat can negatively impact self-esteem, making individuals feel disconnected and undervalued.
###
- 5. Reintegration into Civilian Life
– Identity Shift: Transitioning from combat to civilian life may lead to an identity crisis, affecting self-esteem as individuals struggle to redefine themselves outside the military context.
– Achievement in New Roles: Successfully adapting to new roles and responsibilities can rebuild and even boost self-esteem.
###
- 6. Personal Reflection and Growth
– Self-Awareness: Combat experiences often lead to deep personal reflection, enhancing self-awareness and self-understanding, which can support healthier self-esteem.
– Growth Mindset: Embracing personal growth and learning from combat experiences can foster a positive self-image.
### Supporting Healthy Self-Esteem Post-Combat
– Therapy and Counseling: Seeking professional help can address trauma and build strategies to improve self-esteem.
– Community Engagement: Engaging with supportive communities and building strong relationships can reinforce a positive self-view.
– Self-Care Practices: Prioritizing physical and mental health through exercise, hobbies, and relaxation techniques supports overall well-being and self-esteem.
Combat undeniably leaves a lasting mark on individuals, influencing their self-esteem in multifaceted ways. By recognizing both the challenges and strengths gained through these experiences, individuals can work towards a balanced and healthy self-esteem.
combat addiction leads to isolation and loneliness?
.jpg)
Combat addiction can indeed lead to isolation and loneliness, which are often intertwined with the struggles faced by individuals dealing with this issue. Here’s how:
- 1. Social Withdrawal: People battling addiction may withdraw from social circles to hide their behavior or due to shame and guilt associated with their addiction. This withdrawal can lead to isolation as they distance themselves from friends, family, and colleagues.
- 2. Strained Relationships: Addiction often strains relationships, as loved ones may find it challenging to understand or cope with the behavior of the person struggling with addiction. This strain can lead to broken relationships, further contributing to feelings of loneliness.
- 3. Stigma and Judgment: The stigma surrounding addiction can make individuals feel judged or misunderstood by society. This fear of judgment can discourage them from seeking help or reaching out to others, deepening their sense of isolation.
- 4. Mental Health Issues: Addiction is frequently accompanied by mental health issues such as depression and anxiety, which can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and isolation. These mental health challenges can make it difficult for individuals to engage socially or maintain healthy relationships.
- 5. Lifestyle Changes: The lifestyle associated with addiction can lead to significant changes in daily routines and priorities, often alienating individuals from their previous social networks. As addiction takes precedence, social activities and interactions may become less frequent.
- 6. Recovery Process: Even during recovery, individuals may experience isolation as they navigate the challenges of sobriety. They might feel disconnected from their previous social circles, especially if those circles were centered around substance use.
Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive approach, including therapy, support groups, and community engagement, to help individuals rebuild their social networks and foster a sense of belonging. Encouraging open conversations about addiction and reducing stigma can also play a crucial role in mitigating isolation and loneliness for those affected.
Effects of combat on your relationships
Combat experiences can have profound effects on personal relationships, influencing them in both positive and negative ways. Understanding these impacts is crucial for veterans, their families, and support networks.
### Positive Effects
- 1. Strengthened Bonds:
– Shared experiences in combat can create deep bonds among service members. This camaraderie often extends beyond the battlefield, fostering lifelong friendships based on mutual trust and understanding.
- 2. Enhanced Appreciation:
– Experiencing the fragility of life can lead to a greater appreciation for loved ones. Many veterans develop a renewed focus on family and relationships, prioritizing time with loved ones more than before.
- 3. Improved Communication Skills:
– The necessity for clear and effective communication in combat can translate to improved communication skills in personal relationships, helping veterans express their needs and emotions more effectively.
- 4. Resilience and Problem-Solving:
– The challenges faced in combat can enhance resilience and problem-solving skills, which can be beneficial in navigating and resolving conflicts within personal relationships.
- 5. Community and Support Networks:
– Veterans often become part of strong support networks, such as veteran groups, which can provide additional social connections and a sense of belonging that positively impacts personal relationships.
### Negative Effects
- 1. Emotional Distress:
– Combat can lead to emotional issues such as PTSD, anxiety, and depression. These conditions can strain relationships, as they may lead to withdrawal, irritability, or difficulty in expressing emotions.
- 2. Communication Barriers:
– Veterans may struggle to communicate their experiences to those who have not served, leading to feelings of isolation and misunderstanding within their personal relationships.
- 3. Hyper-vigilance and Stress:
– The heightened state of alertness required in combat can persist, causing stress and tension in everyday situations, which can be challenging for partners and family members to understand and cope with.
- 4. Role Changes:
– Deployment and combat can lead to shifts in family dynamics and roles, which can be difficult to readjust once the veteran returns home. This can lead to conflicts and confusion within family relationships.
- 5. Substance Abuse:
– Some veterans may turn to alcohol or drugs as a coping mechanism for dealing with combat-related stress, which can have detrimental effects on relationships and family life.
### Conclusion
The effects of combat on relationships are complex and multifaceted. While combat can enhance certain aspects of personal relationships, it can also introduce significant challenges. Support from mental health professionals, veteran organizations, and understanding from loved ones can help mitigate negative effects and foster positive outcomes. Encouraging open communication and seeking professional help when needed are crucial steps in maintaining healthy relationships post-combat.
How To Stop & Quit Your combat Addiction
Finally, you think you are addicted to combat and you are wondering how to quit it? How to break and overcome your cravings for combat?
Here are the best solutions, steps, supports, resources, and help you can get to treat your combat addiction.
Main steps and solutions to break the combat addiction
Combat addiction, often related to the adrenaline rush and heightened sense of purpose experienced during combat, can be challenging to overcome. It is essential to approach this issue with sensitivity, understanding, and professional guidance. Here are the main steps to address and manage combat addiction:
- 1. Acknowledgment and Acceptance:
– Recognize the problem: The first step is acknowledging that combat addiction exists and is affecting your life negatively.
– Accept the need for change: Understand that seeking help is a strength, not a weakness.
- 2. Seek Professional Help:
– Consult mental health professionals: Engage with therapists or counselors who specialize in trauma and addiction.
– Consider therapy options: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), or other trauma-focused therapies can be beneficial.
- 3. Build a Support Network:
– Connect with peers: Join support groups or veteran organizations where you can share experiences and find understanding.
– Involve family and friends: Educate your loved ones about combat addiction so they can provide informed support.
- 4. Develop Coping Strategies:
– Learn stress management techniques: Practice mindfulness, meditation, or yoga to help manage anxiety and stress.
– Find healthy outlets: Engage in physical activities or hobbies that provide a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
- 5. Address Underlying Issues:
– Explore trauma: Work with professionals to address any underlying trauma or PTSD that may be contributing to the addiction.
– Identify triggers: Recognize situations or environments that trigger the desire for combat-like experiences and develop strategies to manage them.
- 6. Set Goals and Monitor Progress:
– Establish realistic goals: Set achievable milestones in your recovery journey to maintain motivation.
– Track progress: Regularly assess your progress with the help of a therapist to adjust strategies as needed.
- 7. Consider Medication:
– Evaluate medication options: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of anxiety, depression, or PTSD.
- 8. Commit to Long-Term Recovery:
– Stay engaged in treatment: Continuously participate in therapy and support groups even after initial improvements.
– Prepare for setbacks: Understand that relapses may occur and have a plan in place to address them without losing hope.
- 9. Promote Lifestyle Changes:
– Adopt a healthy lifestyle: Focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep to support overall well-being.
– Limit exposure to triggers: Avoid environments or media that may exacerbate cravings for combat experiences.
- 10. Focus on Personal Growth:
– Pursue new skills: Engage in education or training that can lead to new career opportunities or personal development.
– Volunteer or mentor: Helping others can provide a sense of purpose and fulfillment outside of combat.
Overcoming combat addiction is a complex process that requires time, patience, and a comprehensive approach. It’s important to remember that recovery is a personal journey and may look different for everyone.Actually, that’s what most documentation out there is about… However, quitting a digital addiction can be a bit trickier than that.
So our team, after testing many ways, designed a bulletproof way to overcome them. Here are some clear and practical steps that are very powerful to quit a digital addiction, including combat:
1. Purge temptations: Get rid of combat
First, cleaning your life from temptations is much easier than resisting them. Disable or delete your combat accounts, change the password and hide it somewhere you can’t access easily, keep your phone / computer far away… Out of sight, out of mind.
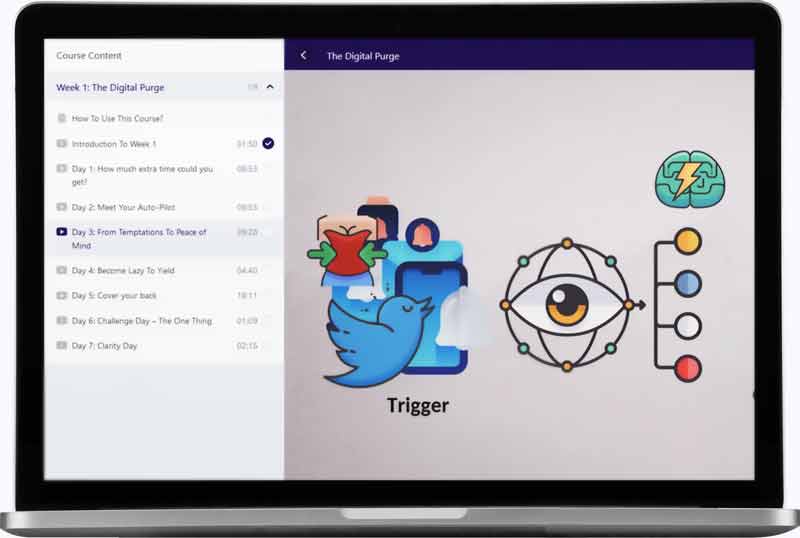
Here is a video from our course The Digital Purge. on how to add resistance to your temptations, so you become so lazy to engage with them that you give them up:
2. Spot & Reveal your emotional triggers
Second, there are some reasons, often hidden ones, that your brain and your heart love so much combat. Those reasons act as triggers to pull your cravings. Rather than chasing the addiction, it’s a more efficient strategy to look at the feelings driving you toward it. That way you can cure and heal the feeling. You’ll feel better, and the cravings will magically disappear. Just get away.
3. Rewire to life

An addiction FOMO (fear of missing out) can be huge and really painful to resist, especially if it was here for a long time. However, learning to live with it is necessary to build a life full of peace and joy. Strategies to fight FOMO and rewire to life include meditation, nature activities, social interaction, intellectual and creative projects, meaningful adventures… basically anything that fills your soul.
4. How to not relapse and fully recover from combat?
Finally, it’s important to acknowledge that quitting may take days, weeks, months, or even years. Getting over and quitting combat forever can be difficult. You may relapse a few times, but the most important thing is that you keep engaging less and less with combat. Each day you resist it is a day weakening your brain connections with combat. From your patience and discipline will arise incredible mind strength, hope, and wisdom.

Best combat blocker apps & functionalities
Additionally, you can increase your chance of withdrawal by limiting or blocking access to combat using these apps.
They will help you filter, reduce, or block combat:
In today’s digital age, video games can be both entertaining and addictive. For parents, educators, or individuals looking to manage screen time, finding effective tools to limit or block access to video games is crucial. Here are five of the best apps designed to help manage and control video game usage:
- 1. Qustodio
– Overview: Qustodio is a comprehensive parental control app that offers a wide range of features to manage and monitor digital activity.
– Features: It allows you to set time limits for specific apps and games, block inappropriate content, and monitor online activity. The app also provides detailed reports on usage.
– Platforms: Available on Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Kindle.
- 2. Net Nanny
– Overview: Known for its robust internet filtering capabilities, Net Nanny also offers tools to manage video game usage.
– Features: It includes features like app blocking, screen time management, and real-time alerts. Parents can set schedules for when games can be played and receive notifications when limits are reached.
– Platforms: Compatible with Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Kindle Fire.
- 3. FamilyTime
– Overview: FamilyTime is a versatile parental control app designed to help families manage screen time and ensure safe online experiences.
– Features: The app allows parents to block or limit access to specific games and apps, set daily screen time limits, and track device usage. It also offers location tracking and geofencing features.
– Platforms: Available on Android and iOS.
- 4. FamiSafe
– Overview: FamiSafe offers an intuitive interface and a variety of features to help manage children’s digital habits.
– Features: Users can block or restrict access to specific apps and games, set screen time limits, and receive reports on app usage. The appCheck our full video games addiction tool list (ranked):
Where to seek extra help?
Do you need some support and help to stop, overcome, and recover from your combat addiction? If you or someone you know is struggling with combat addiction, there are a few places to seek help.
The Ultimate Rewiring Program For combat Addicts
Our course The Digital Purge. This course has already helped many digital addicts to rewire to what matters.
Is there a “treatment” to cure video games addiction?
Absolutely, there are effective treatments to help overcome video game addiction! If you or someone you know is struggling, here are some approaches that can make a big difference:
###
- 1. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a popular method that helps individuals understand and change the thoughts and behaviors contributing to their gaming habits. By identifying triggers and developing healthier coping strategies, CBT can reduce the urge to play excessively.
###
- 2. Setting Boundaries
Creating a structured schedule can help manage gaming time. Setting specific limits on when and how long you play can prevent gaming from interfering with daily responsibilities and relationships.
###
- 3. Engaging in Alternative Activities
Finding other hobbies or activities that are enjoyable can replace the time spent on video games. Whether it’s sports, reading, or learning a new skill, diversifying your interests can reduce the reliance on gaming for satisfaction.
###
- 4. Support Groups
Connecting with others who are facing similar challenges can provide encouragement and accountability. Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences and strategies for overcoming addiction.
###
- 5. Mindfulness and Stress Management
Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can help manage stress and reduce the impulse to turn to video games for relief.
###
- 6. Professional Help
Sometimes, seeking help from a mental health professional is the best step. Therapists can offer personalized guidance and support tailored to your specific situation.
###
- 7. Parental Involvement (for Younger Gamers)
For younger individuals, parental support is crucial. Setting rules around gaming, monitoring game content, and encouraging other activities can help mitigate addiction risks.
Remember, overcoming video game addiction is entirely possible with the right strategies and support. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for assistance. Taking the first step towards change is a brave and positive move!
Does video games therapy exist?
Yes, therapy to address video game addiction does exist. As video games have become an integral part of modern entertainment, concerns about excessive gaming and its impact on individuals’ lives have grown. Video game addiction, often referred to as gaming disorder, is characterized by impaired control over gaming, increasing priority given to gaming over other activities, and continuation or escalation of gaming despite negative consequences.
Various therapeutic approaches are used to help individuals struggling with video game addiction:
- 1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This is one of the most common forms of therapy for gaming addiction. CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with excessive gaming. It also focuses on developing healthier coping mechanisms and improving time management skills.
- 2. Motivational Interviewing (MI): This approach involves working with individuals to enhance their motivation to change their gaming habits. It helps them explore and resolve ambivalence about reducing gaming time.
- 3. Family Therapy: Since gaming addiction can affect family dynamics, family therapy can be beneficial. It addresses communication issues, sets boundaries, and helps family members support the individual in their recovery process.
- 4. Group Therapy: Group sessions provide a supportive environment where individuals can share their experiences and learn from others facing similar challenges. It can also help reduce feelings of isolation.
- 5. Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques: These techniques can help individuals manage stress and anxiety, which may contribute to excessive gaming. Practices like meditation and yoga can promote relaxation and self-awareness.
- 6. Digital Detox Programs: Some treatment centers offer structured programs that include a period of abstinence from digital devices, combined with therapy and activities that promote healthy lifestyle changes.
- 7. Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to address underlying mental health issues such as depression or anxiety, which can contribute to gaming addiction.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of treatment can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the addiction. Seeking help from a mental health professional who specializes in gaming addiction can provide a tailored approach to recovery.
Additionally, as research in this area continues to evolve, new strategies and interventions may emerge to better address this issue.
Where to find support groups if you are addicted to combat?
If you or someone you know is struggling with video game addiction, finding the right support group can be an essential step towards recovery. Here are some places where you can find support groups for video game addicts:
- 1. Online Support Groups:
– OLGA (Online Gamers Anonymous): This is a well-known online community that offers support for individuals struggling with gaming addiction. They provide forums, chat rooms, and resources for both addicts and their families.
– Reddit: Subreddits like r/StopGaming offer a community of individuals who share experiences and strategies for overcoming gaming addiction.
- 2. Local Support Groups:
– Therapists and Counselors: Many therapists specialize in addiction and can recommend local support groups or create one-on-one therapy plans.
– Community Centers: Check with local community centers or libraries, which may host support groups or have information on local meetings.
- 3. 12-Step Programs:
– Some areas have adapted 12-step programs similar to those used for alcohol and drug addiction to address video game addiction.
- 4. Mental Health Organizations:
– Organizations like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) or Mental Health America may offer resources or support groups for behavioral addictions, including gaming.
- 5. Healthcare Providers:
– Speak with a primary care doctor or mental health professional who may have recommendations for local support groups or treatment programs.
- 6. Educational Institutions:
– Schools and universities often have counseling services that can provide support or direct students to appropriate resources.
- 7. Social Media Groups:
– Platforms like Facebook have groups dedicated to supporting individuals with gaming addiction, where members can share experiences and advice.
When seeking support, it’s important to find a group or resource that feels comfortable and supportive. Each person’s journey with addiction is unique, so it may take some time to find the right fit.
But other combat addiction solutions exist
If you’re seeking help for combat addiction and prefer not to engage with support groups, there are several other professionals and resources you can consider:
- 1. Therapists or Counselors: Licensed therapists or counselors who specialize in addiction can provide one-on-one therapy. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can be effective in addressing addiction.
- 2. Psychiatrists: A psychiatrist can assess whether medication might be helpful in managing addiction or any co-occurring mental health issues, such as anxiety or depression.
- 3. Primary Care Physicians: Your primary care doctor can be a good starting point. They can provide referrals to specialists and discuss treatment options.
- 4. Addiction Specialists: These are healthcare professionals with specialized training in addiction medicine who can offer comprehensive treatment plans.
- 5. Clinical Psychologists: They can provide psychological assessments and therapy tailored to address the underlying causes of addiction.
- 6. Social Workers: Licensed clinical social workers can offer counseling and connect you with resources and services that support recovery.
- 7. Rehabilitation Centers: These centers offer inpatient or outpatient treatment programs that provide medical and psychological support.
- 8. Online Therapy Platforms: If in-person visits are challenging, online therapy platforms can connect you with licensed professionals for virtual sessions.
- 9. Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): If your workplace offers an EAP, it can provide confidential counseling and resources for addiction treatment.
- 10. Holistic Practitioners: Some individuals find alternative therapies, such as mindfulness, yoga, or acupuncture, helpful as complementary treatments.
It’s important to find a professional or service that you feel comfortable with and that meets your specific needs. Recovery is a personal journey, and there are various paths to achieving it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, overcoming combat addiction is a challenging yet achievable journey that requires a multifaceted approach. It begins with acknowledging the problem and seeking help, whether through therapy, support groups, or rehabilitation programs. Building a strong support network of family, friends, and fellow veterans can provide the emotional backing necessary to navigate this difficult path.
Additionally, adopting healthy coping mechanisms, such as exercise, mindfulness, and engaging in fulfilling activities, can significantly aid in the recovery process. It’s crucial to remember that recovery is not a linear journey; setbacks may occur, but perseverance and resilience are key. By fostering a sense of purpose and focusing on personal growth, individuals can transform their lives, moving beyond the shadows of addiction to embrace a future filled with hope and possibility. Ultimately, the journey to overcoming combat addiction is deeply personal, but with the right resources and support, it is a path that leads to healing and renewal.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.Here is the trailer:
To Go Further
Take our 4-min test
How to help someone with combat addiction?
Helping someone with combat addiction is a sensitive and challenging process that requires understanding, patience, and the right resources. Combat addiction, often related to substance abuse or behavioral issues stemming from military experiences, can be complex due to the unique stressors faced by military personnel. Here are some steps to consider:
- 1. Educate Yourself: Understanding the nature of combat addiction and its effects is crucial. Learn about the specific substances or behaviors involved and how they relate to the individual’s military experiences. Familiarize yourself with PTSD and other mental health issues that might accompany addiction.
- 2. Open Communication: Approach the person with empathy and without judgment. Let them know you are concerned about their well-being and are there to support them. Create a safe space for them to express their feelings and experiences.
- 3. Encourage Professional Help: Encourage them to seek professional help. This could include therapy, counseling, or medical treatment. Professionals who specialize in addiction and have experience with veterans or military personnel can provide tailored support.
- 4. Support Groups: Suggest joining support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), Narcotics Anonymous (NA), or groups specifically for veterans like Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW). These groups offer community support and understanding from those with similar experiences.
- 5. Develop a Support Network: Help them build a support network of friends, family, and other veterans who can provide encouragement and accountability. Having a strong support system is crucial for recovery.
- 6. Promote Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Encourage the adoption of healthy habits and coping mechanisms such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies that can serve as positive outlets for stress and emotions.
- 7. Monitor Progress and Setbacks: Recovery is often a long process with ups and downs. Be patient and supportive through setbacks, and celebrate progress, no matter how small.
- 8. Respect Their Autonomy: While you can offer support and resources, ultimately, the decision to seek help and change must come
Best books about video games addiction
Video game addiction is a topic that has garnered increasing attention as gaming becomes more integrated into daily life. Several authors have explored this subject, offering insights into its psychological, social, and personal impacts. Here are five noteworthy books that delve into video game addiction:
- 1. “Irresistible: The Rise of Addictive Technology and the Business of Keeping Us Hooked” by Adam Alter
This book examines the broader scope of addictive technologies, including video games. Alter explores how game designers use psychological principles to keep players engaged, often leading to addictive behaviors. He provides a comprehensive look at the impact of these technologies on our lives and suggests ways to mitigate their addictive nature.
- 2. “Game Addiction: The Untold Stories of Game Addicts” by Neils Clark and P. Shavaun Scott
Clark and Scott delve into the personal stories of individuals affected by video game addiction. The book combines these narratives with scientific research to provide a balanced view of the issue. It discusses the psychological mechanisms behind gaming addiction and offers practical advice for those struggling with it.
- 3. “Unplugged: My Journey into the Dark World of Video Game Addiction” by Ryan Van Cleave
This memoir offers a personal account of the author’s battle with video game addiction. Van Cleave shares his experiences of how gaming took over his life, affecting his relationships and career. His story is both a cautionary tale and a source of hope for those seeking to overcome similar challenges.
- 4. “Video Game Addiction: The Essential Guide for Parents and Gamers” by Alexis Leon
Aimed at both parents and gamers, this book provides an overview of video game addiction and its effects. Leon offers practical strategies for managing gaming habits and fostering a healthy balance between gaming and other life activities. It’s a valuable resource for anyone looking to understand and address gaming addiction.
- 5. “Reset: Gaming and the Psychology of Video Game Addiction” by Michael R.
Research about video games addiction
Video game addiction, often referred to as gaming disorder, has been the subject of numerous studies as researchers seek to understand its prevalence, causes, and effects. Below are summaries of several official studies that have contributed significantly to the field:
1. Gentile et al. (2011. – “Pathological Video Game Use Among Youths: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study”:
– Published In: Pediatrics
– Summary: This study tracked over 3,000 children in Singapore over two years to assess the prevalence and impact of pathological gaming. It found that approximately 9% of gamers were classified as pathological, exhibiting behaviors similar to other addictive disorders. The study highlighted that pathological gaming was associated with increased depression, anxiety, social phobias, and lower academic performance.
2. Weinstein et al. (2017. – “Internet Gaming Disorder: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature”:
– Published In: Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment
– Summary: This systematic review analyzed existing literature on Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) to understand its characteristics and impact. The study emphasized the need for standardized diagnostic criteria and found that IGD was associated with various psychological issues, including depression and anxiety. The review also discussed the neurobiological underpinnings of gaming addiction, suggesting similarities with other addictive behaviors.
3. Przybylski et al. (2017. – “Motivational, Emotional, and Behavioral Correlates of Fear of Missing Out”:
– Published In: Computers in Human Behavior
– Summary: While not exclusively focused on gaming addiction, this study explored the concept of “Fear of Missing Out” (FoMO) and its relationship with online behaviors, including gaming. The research found that FoMO could drive excessive gaming as individuals seek to remain connected and engaged with online communities. This behavioral pattern can contribute to gaming addiction, highlighting the social aspects of the disorder.
4. Király et al. (2018. – “Ten-Item Internet Gaming Disorder Test (IGDT-10.: Measurement Invariance and Cross-Cultural Validation Across Seven Language-Based Samples”:
– Published In: Psychology of Addictive Behaviors
– Summary: This study focused on the development and validation of the IGDT-10, a tool designed to assess Internet Gaming Disorder across different cultures. The research involved participants from multiple countries and languages, confirming the tool’s reliability and validity. The study underscored the importance of a standardized assessment for better understanding and diagnosing gaming addiction globally.
5. King et al. (2019. – “Clinical Interventions for Technology-Based Problems: Excessive Internet and Video Game Use”:
– Published In: Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy
– Summary: This study reviewed various clinical interventions aimed at addressing excessive gaming and internet use. It highlighted cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) as an effective treatment for gaming disorder, alongside other therapeutic approaches. The research provided insights into the challenges of treating gaming addiction and emphasized the need for tailored interventions based on individual needs.
These studies collectively contribute to a deeper understanding of video game addiction, its psychological and social implications, and potential treatment strategies. They also highlight the importance of continued research to refine diagnostic criteria and develop effective interventions.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.
The impact of video games on our society
Video game addiction has emerged as a significant concern in modern society, affecting individuals across various age groups and demographics. As video games have evolved from simple pixelated screens to immersive, complex virtual worlds, their influence has grown exponentially, leading to both positive and negative societal impacts. While gaming can offer cognitive benefits and foster social connections, excessive and compulsive gaming can lead to addiction, with profound implications for individuals and society at large.
### Psychological and Health Impacts
One of the most immediate effects of video game addiction is on mental health. Individuals who are addicted to gaming often experience increased levels of anxiety, depression, and stress. The immersive nature of games can lead to a detachment from reality, where players find it difficult to balance their virtual achievements with real-world responsibilities. This detachment can exacerbate feelings of isolation and loneliness, particularly if gaming becomes a substitute for real-world social interactions.
Physically, prolonged gaming sessions can lead to a sedentary lifestyle, contributing to obesity, poor posture, and repetitive strain injuries. Sleep deprivation is another common issue, as individuals may sacrifice rest to continue gaming, leading to fatigue and impaired cognitive function.
### Social Consequences
On a social level, video game addiction can strain relationships with family and friends. Individuals may prioritize gaming over spending time with loved ones, leading to conflicts and misunderstandings. The isolation that often accompanies addiction can further erode social skills, making it challenging for individuals to engage in face-to-face interactions.
Moreover, the online communities within games can sometimes propagate toxic behaviors, such as cyberbullying and harassment. These negative interactions can have a lasting impact on individuals, particularly younger players who may be more impressionable.
### Economic Impact
The economic implications of video game addiction are multifaceted. On one hand, the gaming industry is a significant economic driver, generating billions in revenue and creating numerous jobs. However, addiction can lead to decreased productivity in the workplace or academic settings, as individuals may neglect responsibilities in favor of gaming. This can result in job loss or poor academic performance, which has broader economic repercussions.
### Educational Challenges
For students, video game addiction can interfere with educational attainment. The time and energy devoted to gaming can detract from homework, study, and other academic pursuits. This distraction can lead to a decline in academic performance, which may have long-term consequences for future career opportunities.
### Addressing the Issue
Addressing video game addiction requires a multifaceted approach. Education and awareness are crucial in helping individuals recognize the signs of addiction and understand its potential impacts. Parents, educators, and mental health professionals play a vital role in monitoring gaming habits and encouraging healthy gaming practices.
Regulation and policy can also help mitigate the effects of gaming addiction. Some countries have implemented measures such as gaming curfews for minors and restrictions on in-game purchases to prevent excessive gaming. Game developers can contribute by designing games that encourage breaks and promote balanced gaming habits.
### Conclusion
While video games are an integral part of modern entertainment and culture, the potential for addiction poses significant challenges for individuals and society. By fostering awareness and promoting responsible gaming, society can harness the benefits of video games while minimizing their negative impacts. Balancing the virtual with the real world is essential to ensuring that gaming remains a healthy and enjoyable activity.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.