Trying to quit cold turkey addiction? Welcome to our digital detox series! This series focuses on how to stop digital and screen addictions. Findall our posts about digital addictions. Today, let’s talk about how to quit the cold turkey addiction.

- What’s the cold turkey addiction?
- Addiction to cold turkey, a “real” addiction?
- What’s considered cold turkey addiction?
- How much cold turkey is too much?
- Some work and productivity addiction facts & statistics
- Symptoms & Causes of the cold turkey addiction
- Why is cold turkey so addictive?
- Possible causes of cold turkey dependency
- Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of cold turkey addiction
- Problems, impacts & bad effects of cold turkey
- Some benefits of cold turkey
- Health problems
- Impact on brain & mental health
- Impact on relationships
- How to stop & quit your cold turkey addiction
- Main steps and solutions to break the cold turkey addiction
- Best cold turkey blocker apps & functionalities
- Where to seek extra help?
- Conclusion
- To Go Further
- How to help someone with cold turkey addiction
- Best books about work and productivity addiction
- Research about work and productivity addiction
What is the cold turkey addiction?
About cold turkey
“Cold turkey” refers to the abrupt cessation of an addictive substance or habit without gradual reduction, often leading to withdrawal symptoms. It is commonly used in the context of quitting smoking or drug use.
Addiction to cold turkey, a “real” addiction?
Officially an addiction?
First, let’s have a look at the DSM-5,the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Does it include cold turkey addiction?
The term “cold turkey” itself is not listed as an addiction in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5.. Rather, “cold turkey” is a colloquial term used to describe the abrupt cessation of a substance or behavior to which a person is addicted. The DSM-5 does include criteria for diagnosing substance use disorders, which cover a range of addictions related to alcohol, drugs, and other substances.
When someone quits a substance “cold turkey,” they may experience withdrawal symptoms, which are recognized in the DSM-5 as part of the diagnostic criteria for substance use disorders. Withdrawal symptoms can vary depending on the substance and the severity of the addiction. The DSM-5 provides specific criteria for diagnosing withdrawal from various substances, such as alcohol, opioids, and nicotine, among others.
In summary, while “cold turkey” is not an addiction listed in the DSM-5, the manual does address the concept of withdrawal and substance use disorders, which are relevant to understanding the challenges and symptoms associated with abruptly stopping substance use.
So what does “cold turkey addiction” mean?
What is Cold Turkey Addiction?
“Cold turkey” refers to the sudden and complete stopping of a substance or habit that someone is addicted to, without gradually reducing its use or seeking alternative treatments. Imagine deciding to quit smoking or drinking all at once, without any assistance or step-by-step plan—that’s going cold turkey.
While some people choose this method because it’s straightforward and doesn’t require a lot of planning, it can be really challenging. Going cold turkey often means dealing with intense withdrawal symptoms and strong cravings, which can make the process tough to stick with. It’s important to consider reaching out for support or professional help when trying to overcome an addiction, as they can provide strategies and resources to make the journey a bit easier.
What is considered cold turkey addiction?
Diagnosing a “cold turkey” addiction typically involves understanding the process of withdrawal from a substance or behavior and recognizing the symptoms associated with it. “Cold turkey” refers to the abrupt cessation of a substance or behavior, which can lead to withdrawal symptoms. However, it’s important to note that “cold turkey” itself is not an addiction but a method of quitting. Here are some criteria and considerations for diagnosing addiction and understanding withdrawal:
- 1. Substance Use History: Understanding the individual’s history with the substance or behavior is crucial. This includes the duration, frequency, and amount of use.
- 2. Withdrawal Symptoms: When someone quits “cold turkey,” they may experience withdrawal symptoms. These can vary depending on the substance or behavior but often include:
– Physical symptoms: nausea, vomiting, headaches, sweating, tremors.
– Psychological symptoms: anxiety, depression, irritability, mood swings.
– Behavioral symptoms: restlessness, insomnia, difficulty concentrating.
- 3. Impact on Daily Life: Assess how the substance or behavior has impacted the individual’s daily life. This includes their ability to work, maintain relationships, and fulfill responsibilities.
- 4. Cravings and Urges: A strong desire or urge to use the substance or engage in the behavior again is a common sign of addiction.
- 5. Attempts to Quit: Consider previous attempts to quit and whether these were successful or not. Frequent unsuccessful attempts can indicate a strong addiction.
- 6. Tolerance and Dependence: Evaluate whether there is a need to increase the amount of substance used to achieve the same effect (tolerance) and whether there are withdrawal symptoms when not using the substance (dependence).
- 7. Behavioral Changes: Notice any significant changes in behavior, such as increased secrecy, social withdrawal, or changes in daily routines.
- 8. Physical and Mental Health: Assess the overall physical and mental health of the individual, as addiction can often lead to or exacerbate health issues.
- 9. Professional Assessment: A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough assessment using standardized criteria, such as those outlined in the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) for substance use disorders.
- 10. Support Systems: Evaluate the availability and effectiveness of support systems, such as family, friends, or professional counseling, which can play a crucial role in recovery.
It’s important to approach this process with sensitivity and care, as addiction is a complex condition that requires comprehensive evaluation and often professional intervention. If you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, consulting a healthcare professional is a critical step towards recovery.
How much cold turkey is too much?
The concept of “cold turkey” typically refers to the abrupt cessation of a habit or addiction, most commonly associated with quitting substances like nicotine, alcohol, or drugs. The question of how much time spent on cold turkey is “too much” can be interpreted in a few ways, depending on the context:
- 1. Withdrawal Duration: When quitting cold turkey, the withdrawal symptoms can vary significantly depending on the substance and the individual’s physiology. For example, nicotine withdrawal symptoms often peak within the first few days and gradually subside over a few weeks. However, for substances like alcohol or opioids, withdrawal can be more severe and potentially dangerous, requiring medical supervision. If withdrawal symptoms persist beyond the typical duration or become unmanageable, it may be necessary to seek medical advice.
- 2. Psychological Impact: The psychological challenges of quitting cold turkey can also vary. If the emotional or mental strain of quitting cold turkey becomes overwhelming or leads to significant distress, it might be beneficial to seek support from a counselor or therapist. Support groups or structured programs can also provide guidance and encouragement.
- 3. Sustainability: The sustainability of quitting cold turkey is another consideration. If an individual finds that they are repeatedly attempting to quit cold turkey but relapsing, it might indicate that a different approach, such as a gradual reduction or a medically supervised program, could be more effective.
- 4. Health Risks: For some substances, quitting cold turkey can pose health risks. For example, abruptly stopping alcohol in individuals with severe alcohol dependence can lead to severe withdrawal symptoms, including seizures. In such cases, medical supervision is crucial.
Ultimately, the decision to quit cold turkey and the duration of time spent in this process should be guided by individual circumstances, the specific substance involved, and professional medical advice. It’s important to prioritize safety and well-being, and to seek support when needed.
Some work and productivity addiction facts & statistics

Work and productivity addiction, often referred to as “workaholism,” is a growing concern in modern society, particularly in cultures that highly value productivity and achievement. While comprehensive statistics can be challenging to pinpoint due to varying definitions and methodologies, several studies and surveys provide insight into the prevalence and impact of this phenomenon.
### Prevalence of Work Addiction
- 1. General Prevalence:
– Estimates suggest that between 5% to 10% of the workforce in developed countries may be classified as workaholics, although this can vary significantly depending on the criteria used.
- 2. Demographic Variations:
– Work addiction can affect individuals across different demographics, but some studies indicate that it is more prevalent among certain groups, such as middle-aged professionals, high achievers, and those in managerial or executive positions.
- 3. Industry-Specific Trends:
– Certain industries, such as finance, law, and technology, tend to have higher rates of work addiction due to their demanding nature and cultural expectations of long working hours.
### Impact on Health and Well-being
- 1. Physical Health:
– Work addiction is associated with various health issues, including cardiovascular problems, sleep disorders, and a weakened immune system. Chronic stress from overwork can exacerbate these conditions.
- 2. Mental Health:
– Individuals with work addiction are more likely to experience anxiety, depression, and burnout. The constant pressure to perform can lead to significant mental health challenges.
- 3. Social and Family Life:
– Workaholics often struggle with maintaining healthy relationships, as their work commitments can lead to neglect of family and social responsibilities. This can result in marital problems and strained family dynamics.
### Economic and Organizational Impact
- 1. Productivity Paradox:
– While workaholics may initially contribute to higher productivity, over time, the negative effects of burnout and decreased mental health can lead to reduced efficiency and increased absenteeism.
- 2. Turnover and Retention:
– Organizations with cultures that inadvertently promote workaholism may face higher turnover rates, as employees eventually seek healthier work environments.
- 3. Healthcare Costs:
– The health issues associated with work addiction can lead to increased healthcare costs for both individuals and employers, due to the need for medical treatment and mental health support.
### Addressing Work Addiction
- 1. Organizational Strategies:
– Companies can implement policies that promote work-life balance, such as flexible working hours, remote work options, and encouraging regular breaks.
- 2. Individual Interventions:
– Therapy and counseling can be effective for individuals struggling with work addiction. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and stress management techniques are commonly used approaches.
- 3. Cultural Shifts:
– Broader cultural changes that value quality over quantity of work, and recognize the importance of mental health, are essential in addressing the root causes of work addiction.
### Conclusion
Work and productivity addiction is a multifaceted issue with significant implications for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. Understanding its prevalence and impact is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its negative effects and promote healthier work environments. Continued research and awareness are key to addressing this modern challenge.
Is the cold turkey addiction widespread?
The phrase “cold turkey” typically refers to the abrupt cessation of a substance or behavior, often used in the context of quitting smoking, alcohol, or drugs. It is not something people get “addicted” to, but rather a method of quitting an addiction. The phrase itself implies a sudden and complete stop, without tapering off or using replacement therapies.
When people quit an addictive substance cold turkey, they often experience withdrawal symptoms, which can be challenging and uncomfortable. This method can be effective for some, but it also carries risks, especially with substances that have severe withdrawal symptoms, such as alcohol or opioids. In such cases, medical supervision is often recommended.
If you meant to ask about a different context or if “Cold Turkey” refers to something else, such as a product or a concept, please provide additional details for a more accurate response.
Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of cold turkey addiction
Why is cold turkey so addictive?
Hey there!
It sounds like you’re curious about why “cold turkey” can feel so addictive or why quitting something abruptly is so challenging. Let’s break it down in a friendly and simple way!
Understanding “Cold Turkey”:
“Cold turkey” is a term commonly used to describe the sudden and complete cessation of a habit, especially when it comes to quitting addictive substances like smoking, drugs, or alcohol without any gradual reduction or support.
Why Is Quitting Cold Turkey So Challenging?
- 1. Immediate Withdrawal Symptoms:
– Physical Reactions: When you stop using an addictive substance suddenly, your body reacts to the absence. This can lead to symptoms like headaches, nausea, sweating, or even more severe issues depending on the substance.
– Emotional Struggles: Abruptly quitting can also cause irritability, anxiety, depression, or intense cravings as your brain adjusts to functioning without the addictive substance.
- 2. Brain Chemistry Changes:
– Dopamine Levels: Addictive substances often increase dopamine in the brain, which makes you feel good. Stopping them suddenly drops dopamine levels, leading to feelings of sadness or lack of pleasure.
– Dependence Formation: Over time, your brain becomes accustomed to the substance, making its absence feel stark and difficult to handle.
- 3. Psychological Factors:
– Habit and Routine: Many addictions are tied to daily routines or specific triggers. Breaking these patterns all at once can be mentally exhausting.
– Lack of Coping Mechanisms: Without gradual reduction or support, finding new ways to cope with stress or triggers can be tough, making the urge to return to the old habit stronger.
- 4. Support Systems:
– Isolation: Quitting cold turkey often means facing the challenge alone, which can increase feelings of loneliness and make the process feel more daunting.
– Lack of Guidance: Without professional help or a support group, navigating the emotional and physical challenges becomes harder.
Is Cold Turkey Itself Addictive?
The term “cold turkey” refers to the method of quitting, not something addictive. However, the process of quitting cold turkey can feel so overwhelming because of the intense withdrawal and cravings that mimic addictive behaviors.
Tips to Make Quitting Easier:
– Seek Support: Friends, family, or support groups can provide encouragement and accountability.
– Professional Help: Therapists or counselors can offer strategies to manage withdrawal and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
– Gradual Reduction: Sometimes, slowly reducing the substance or behavior can make the transition smoother.
– Stay Busy: Engaging in new activities or hobbies can distract you from cravings and build new routines.
Remember, everyone’s journey is unique, and what works for one person might not work for another. It’s important to find the method that best supports your path to a healthier, addiction-free life.
Stay strong and take it one step at a time!
Possible causes of cold turkey dependency
The phrase “cold turkey” is commonly used to describe the abrupt cessation of a substance or behavior to which a person is addicted, rather than a type of addiction itself. However, if you’re referring to the challenges and causes of addiction that might lead someone to quit “cold turkey,” there are several factors to consider:
- 1. Biological Factors: Genetics can play a significant role in addiction. Individuals with a family history of addiction may be more predisposed to developing similar issues.
Additionally, neurobiological changes in the brain due to substance use can reinforce addictive behaviors.
- 2. Psychological Factors: Mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, or trauma can contribute to addiction. People may use substances as a form of self-medication to cope with these conditions, leading to dependency.
- 3. Environmental Influences: Exposure to environments where substance use is prevalent can increase the likelihood of addiction. This includes peer pressure, family dynamics, and accessibility to substances.
- 4. Social Factors: Social isolation, lack of support systems, or stressful life events can contribute to the development of addiction. People might turn to substances to fill a void or cope with loneliness.
- 5. Behavioral Factors: Certain personality traits, such as impulsivity or a tendency to seek out novel experiences, can increase the risk of addiction. These traits can lead individuals to experiment with substances and potentially develop dependencies.
- 6. Coping Mechanisms: Some individuals may lack healthy coping mechanisms for stress, leading them to rely on substances as a way to manage their emotions or escape reality.
When someone decides to quit “cold turkey,” it often means they are trying to stop their addictive behavior abruptly without tapering off or using medical assistance. This approach can be challenging and may lead to withdrawal symptoms, which vary depending on the substance and the level of dependency. It’s important for individuals considering this method to seek support from healthcare professionals, as withdrawal can sometimes be dangerous without proper guidance.
Signs & Symptoms of cold turkey addiction
Now let’s see if you have the cold turkey addiction problem.
When it comes to overcoming addiction, the term “cold turkey” refers to quitting a substance or behavior abruptly and completely, without any gradual reduction or use of aids. However, the phrase “cold turkey addict” is somewhat contradictory, as it suggests an addiction to the process of quitting itself. This could imply a pattern of repeatedly quitting and relapsing. Here are seven signs that might indicate someone is caught in this cycle:
- 1. Frequent Relapses: One of the most telling signs is a pattern of quitting a substance or behavior and then returning to it repeatedly. This cycle can indicate an addiction to the process of quitting, rather than successfully overcoming the addiction.
- 2. Obsessive Planning: Constantly planning the next quit attempt, researching methods, and setting dates can indicate an obsession with the idea of quitting rather than focusing on sustained recovery.
- 3. Emotional Highs and Lows: Experiencing a rush of excitement or euphoria when deciding to quit, followed by significant disappointment or guilt upon relapsing, can suggest an addiction to the emotional rollercoaster of quitting.
- 4. Seeking Validation: Frequently seeking praise or validation from others for the decision to quit, even if past attempts have been unsuccessful, may indicate a focus on the act of quitting rather than the outcome.
- 5. Neglecting Long-Term Strategies: A lack of interest in long-term recovery strategies, such as therapy or support groups, in favor of the immediate action of quitting cold turkey, can be a sign of this cycle.
- 6. Impatience with Progress: Feeling frustrated with the gradual nature of recovery and instead preferring the dramatic change of quitting abruptly can suggest an addiction to the immediate gratification of cold turkey attempts.
- 7. Identity Tied to Quitting: If a person’s identity becomes closely tied to being someone who is always quitting or trying to quit, it may indicate that the process itself has become an addictive pattern.
Addressing this cycle often requires a shift in focus from the act of quitting to building a sustainable, long-term recovery plan. This might involve seeking professional help, joining support groups, or developing coping strategies to manage triggers and cravings effectively.
Try our digital habit & screen addiction test:
Problems, impacts & bad effects of cold turkey: should you quit?

What are some benefits of cold turkey
Quitting a habit “cold turkey” refers to stopping it abruptly and completely, without any gradual reduction or the use of replacement aids. While this method can be challenging, it offers several potential advantages:
- 1. Immediate Change: One of the most significant benefits of quitting cold turkey is the immediate cessation of the habit. This can lead to quicker health benefits, such as improved lung function for smokers or better liver health for heavy drinkers.
- 2. Clear Break: Cold turkey provides a clear and definitive break from the habit. This can be psychologically empowering, as it eliminates the ambiguity of gradually reducing usage and helps reinforce the decision to quit.
- 3. Simplicity: The cold turkey approach is straightforward. There’s no need to plan a tapering schedule or purchase aids, which can sometimes complicate the quitting process. This simplicity can be appealing to those who prefer a direct approach.
- 4. Cost-Effective: By not relying on nicotine replacement therapies, medications, or other aids, quitting cold turkey can be more cost-effective. This is particularly beneficial for those who may not have the financial means to invest in quitting aids.
- 5. Avoiding Prolonged Exposure: Gradual reduction methods can extend exposure to the habit-forming substance, potentially prolonging withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Cold turkey can lead to a more intense but shorter withdrawal period.
- 6. Potential for Greater Long-Term Success: Some studies suggest that individuals who quit cold turkey may have higher long-term success rates compared to those who use gradual reduction methods. This could be due to the decisive nature of the approach and the commitment it requires.
- 7. Sense of Accomplishment: Successfully quitting cold turkey can provide a significant boost in self-esteem and confidence. Overcoming the challenge without external aids can reinforce an individual’s belief in their ability to tackle other challenges.
- 8. Reduced Risk of Substitution: Gradual reduction or replacement methods can sometimes lead to substituting one habit for another. Cold turkey eliminates this risk by cutting off the habit entirely.
- 9. Encouragement from Immediate Results: The rapid cessation of a habit can lead to noticeable improvements in health and well-being, which can serve as motivation to maintain the new lifestyle.
- 10. Support from Others: The bold decision to quit cold turkey can often garner support and encouragement from friends and family, providing additional motivation and accountability.
While quitting cold turkey can be effective for some, it’s important to note that it may not be suitable for everyone. The intensity of withdrawal symptoms can be challenging, and some individuals may benefit from medical supervision or support groups. As with any significant lifestyle change, it’s crucial to consider personal circumstances and consult with healthcare professionals when necessary.But on the other hand, what are some cold turkey addiction problems that addicts suffer from?
General health problems
Quitting a habit “cold turkey” refers to the abrupt cessation of a substance or behavior, often without tapering or the use of replacement therapies. This method is commonly associated with quitting smoking, alcohol, or other addictive substances. While some people successfully quit cold turkey, it can have various effects on health, both positive and negative. Here’s a closer look at these effects:
### Positive Effects
- 1. Immediate Health Improvements:
– Smoking: Quitting smoking cold turkey can lead to immediate health benefits. Within 20 minutes, blood pressure and heart rate drop to normal levels. Within 12 hours, carbon monoxide levels in the blood drop to normal.
– Alcohol: Stopping alcohol consumption can quickly reduce the risk of liver damage, improve sleep quality, and enhance overall mental clarity.
- 2. Psychological Benefits:
– Successfully quitting cold turkey can boost self-esteem and confidence, as it demonstrates strong willpower and determination.
– Many people experience a sense of empowerment and control over their lives.
- 3. Financial Savings:
– Eliminating the cost of purchasing cigarettes, alcohol, or drugs can lead to significant financial savings over time.
### Negative Effects
- 1. Withdrawal Symptoms:
– Nicotine: Withdrawal can include irritability, anxiety, depression, and intense cravings. Physical symptoms might include headaches, increased appetite, and difficulty concentrating.
– Alcohol: Withdrawal symptoms can be severe and include tremors, anxiety, nausea, vomiting, and, in severe cases, seizures or delirium tremens (DTs), which can be life-threatening.
– Other Substances: Depending on the substance, withdrawal can involve a range of symptoms from mild discomfort to severe physical and psychological distress.
- 2. Physical Health Risks:
– For substances like alcohol and certain drugs, quitting cold turkey without medical supervision can pose serious health risks. For example, abrupt cessation of alcohol in heavy users can lead to seizures or heart complications.
- 3. Psychological Challenges:
– The stress of withdrawal can exacerbate mental health issues such as depression or anxiety.
– The lack of a gradual transition can make the process feel overwhelming, leading to higher chances of relapse.
- 4. Social and Lifestyle Adjustments:
– Quitting cold turkey might require significant lifestyle changes, such as avoiding social situations where the substance is present, which can be socially isolating.
### Considerations and Recommendations
– Medical Supervision: For substances like alcohol, opioids, or benzodiazepines, medical supervision is often recommended due to the potential for severe withdrawal symptoms.
– Support Systems: Engaging with support groups, counseling, or therapy can provide emotional support and increase the likelihood of success.
– Alternative Methods: Some individuals may benefit from a gradual reduction or the use of replacement therapies (e.g., nicotine patches) to ease withdrawal symptoms.
In conclusion, while quitting cold turkey can lead to rapid health improvements and psychological benefits, it also carries risks, particularly for substances with severe withdrawal symptoms. Individuals considering this method should weigh the pros and cons and seek professional guidance when necessary.
cold turkey and sleep disorders
Quitting something “cold turkey,” which means stopping abruptly and completely, can indeed lead to sleep disorders or problems, particularly if the substance or behavior being ceased has a direct impact on sleep patterns. Here’s how:
- 1. Nicotine: For individuals who quit smoking or using nicotine products cold turkey, sleep disturbances are common. Nicotine is a stimulant, and withdrawal can lead to increased restlessness, difficulty falling asleep, and fragmented sleep.
- 2. Alcohol: While alcohol might initially help some people fall asleep more quickly, it disrupts the sleep cycle, particularly REM sleep. Quitting alcohol suddenly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including insomnia and vivid dreams or nightmares.
- 3. Caffeine: Abruptly stopping caffeine intake can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as headaches and irritability, which can indirectly affect sleep.
Additionally, those who are used to caffeine’s stimulating effects might experience increased fatigue and altered sleep patterns when they quit.
- 4. Medications: Discontinuing certain medications, especially those that affect the central nervous system (like antidepressants or sleep aids), can lead to rebound insomnia or other sleep disturbances.
- 5. Substance Use: Quitting recreational drugs, particularly stimulants or depressants, can also lead to significant sleep issues. Withdrawal symptoms often include insomnia, hypersomnia, or disrupted sleep cycles.
- 6. Behavioral Addictions: Even non-substance-related behaviors, such as excessive screen time or gaming, can affect sleep. Quitting these behaviors cold turkey can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms, including sleep disturbances.
Managing Sleep Problems During Withdrawal:
– Gradual Reduction: Gradually reducing the intake of the substance or behavior can help minimize withdrawal symptoms, including sleep disturbances.
– Healthy Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding screens before bed can improve sleep quality.
– Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can help manage stress and promote better sleep.
– Professional Support: Consulting with healthcare professionals can provide guidance and support, especially for substances with severe withdrawal symptoms.
– Over-the-Counter Aids: In some cases, temporary use of over-the-counter sleep aids may be appropriate, but these should be used cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
It’s important to note that while sleep disturbances are common during withdrawal, they are typically temporary. However, if sleep problems persist, it may be beneficial to seek professional advice to address underlying issues.
cold turkey affecting your brain & mental health: bad for brain and mental health?
Some effects of cold turkey on your brain
The Bad Effects of Going Cold Turkey on Your Brain
Quitting something suddenly—whether it’s smoking, drinking, or another habit—might seem like the quickest way to break free. However, going “cold turkey” can have some unexpected and not-so-great effects on your brain. Here’s a friendly breakdown of what you might experience:
- 1. Intense Withdrawal Symptoms
– Mood Swings: You might feel irritable, anxious, or even depressed as your brain adjusts to the absence of the habit.
– Physical Discomfort: Headaches, fatigue, and nausea are common as your body responds to the sudden change.
- 2. Cravings and Strong Urges
– Your brain craves the habit it’s used to, making it harder to resist the temptation to start again. These intense cravings can feel overwhelming and make staying strong a real challenge.
- 3. Difficulty Concentrating
– Suddenly removing a habit can lead to trouble focusing. You might find it hard to concentrate on tasks, which can affect your work, studies, or daily activities.
- 4. Sleep Disturbances
– Insomnia or disturbed sleep patterns are common. Your brain is adjusting, which can make falling asleep or staying asleep more difficult.
- 5. Increased Stress Levels
– Your brain perceives the sudden change as a significant stressor, leading to elevated stress hormones. This can make you feel more on edge than usual.
- 6. Risk of Relapse
– The combination of withdrawal symptoms and cravings increases the risk of going back to the old habit. It’s like your brain is signaling for comfort, making relapse more likely.
- 7. Emotional Rollercoaster
– You might experience a range of emotions, from frustration and anger to sadness and hopelessness. Managing these emotions can be tough without support.
What Can You Do?
While going cold turkey isn’t for everyone, and it does come with these challenges, there are ways to make the process easier:
– Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or a professional who can provide guidance and encouragement.
– Gradual Reduction: Sometimes, slowly reducing the habit can lessen the impact on your brain and body.
– Healthy Alternatives: Engage in activities that distract you and release feel-good chemicals in your brain, like exercise or hobbies.
– Stay Patient: Give your brain time to adjust. Recovery is a journey, and it’s okay to take it one step at a time.
Remember, everyone’s experience is unique. If you’re considering quitting something cold turkey, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional to find the best approach for you.
Some effects of cold turkey on your mental health
Quitting a substance “cold turkey,” or abruptly stopping its use without tapering off, can have significant effects on mental health. While it can be a necessary step for some individuals to overcome addiction, it’s important to be aware of the potential mental health challenges that may arise:
- 1. Increased Anxiety and Depression: Sudden cessation of substances that have been used to manage stress or emotional pain can lead to heightened anxiety and depression. The brain, accustomed to the chemical effects of the substance, may struggle to regulate mood without it.
- 2. Mood Swings: The abrupt change in brain chemistry can lead to significant mood swings. Individuals may experience irritability, agitation, and emotional instability as their body adjusts to the absence of the substance.
- 3. Cognitive Impairment: Withdrawal can affect cognitive functions, leading to difficulties with concentration, memory, and decision-making. This can be particularly challenging for those who need to maintain their daily responsibilities.
- 4. Sleep Disturbances: Many substances affect sleep patterns, and quitting cold turkey can lead to insomnia or disrupted sleep. Lack of sleep can exacerbate mental health issues, creating a vicious cycle of fatigue and emotional distress.
- 5. Increased Risk of Relapse: The intense cravings and emotional upheaval that can accompany cold turkey withdrawal may increase the risk of relapse. Without proper support, individuals may return to substance use as a way to alleviate withdrawal symptoms.
- 6. Psychiatric Symptoms: In some cases, withdrawal can trigger or worsen psychiatric symptoms such as paranoia, hallucinations, or severe depression. This is particularly true for substances like alcohol or benzodiazepines, where withdrawal can be severe.
- 7. Social Isolation: The process of withdrawal can be isolating, as individuals may withdraw from social interactions due to mood changes or the need to focus on their recovery. This isolation can further impact mental health negatively.
- 8. Increased Stress: The physical and mental strain of withdrawal can increase overall stress levels, which can have a detrimental effect on mental health, potentially leading to burnout or exacerbating existing mental health conditions.
Given these potential effects, it is often recommended that individuals seek professional guidance when deciding to quit a substance. Medical professionals can provide support, possibly recommend a tapering schedule, and offer resources such as therapy or support groups to help manage the mental health challenges associated with withdrawal.
Does cold turkey cause stress and anxiety?
Quitting an addictive substance or habit “cold turkey” can indeed lead to stress and anxiety. The term “cold turkey” refers to the abrupt cessation of a substance or behavior, without gradually reducing the intake or use. This method can be particularly challenging for individuals who have developed a physical or psychological dependence.
Here are some reasons why quitting cold turkey might cause stress or anxiety:
- 1. Withdrawal Symptoms: Many substances, such as nicotine, alcohol, caffeine, and certain drugs, can cause withdrawal symptoms when stopped suddenly. These symptoms often include anxiety, irritability, restlessness, and mood swings.
- 2. Physical Discomfort: Withdrawal can also lead to physical symptoms such as headaches, nausea, fatigue, and muscle pain, which can contribute to overall stress and anxiety levels.
- 3. Psychological Dependence: For many, the habit or substance has become a coping mechanism for dealing with stress or emotions. Suddenly removing this coping tool can leave individuals feeling vulnerable and anxious.
- 4. Lack of Preparation: Quitting cold turkey often means the individual has not developed alternative strategies for managing cravings or stress, leading to increased anxiety about how to cope without the substance or habit.
- 5. Fear of Failure: The pressure to succeed in quitting can itself be a source of stress and anxiety. The fear of relapse or not being able to manage without the substance can be overwhelming.
- 6. Social and Environmental Triggers: Being in environments or situations that previously involved the substance or behavior can trigger anxiety and stress, as the individual may not yet have the skills to handle these triggers effectively.
While quitting cold turkey can work for some, it’s essential to consider the potential mental and physical health impacts and to seek support if needed. Consulting healthcare professionals or joining support groups can provide guidance and resources to manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce stress and anxiety during the quitting process.
Can cold turkey addiction lead to sadness and depression?

Quitting an addiction “cold turkey,” or abruptly stopping the use of a substance without gradually tapering off, can indeed lead to feelings of sadness and depression. This is particularly true for substances that have a significant impact on the brain’s chemistry, such as alcohol, nicotine, opioids, and other drugs. Here’s why:
- 1. Neurochemical Changes: Many addictive substances affect neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and serotonin, which are closely linked to mood regulation. When you suddenly stop using these substances, your brain may struggle to balance these chemicals, leading to mood disturbances, including sadness and depression.
- 2. Withdrawal Symptoms: Physical and psychological withdrawal symptoms are common when quitting cold turkey. These can include anxiety, irritability, fatigue, and depression. The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the substance, the duration of use, and the individual’s physiology.
- 3. Psychological Dependence: Beyond physical dependence, there is often a psychological component to addiction. People may use substances as a way to cope with stress, anxiety, or depression. When the substance is removed, these underlying issues may resurface or intensify, contributing to feelings of sadness and depression.
- 4. Lifestyle Changes: Quitting an addiction often requires significant lifestyle changes, such as avoiding certain social situations or dealing with the loss of a coping mechanism. These changes can lead to feelings of isolation or loss, which can contribute to depression.
- 5. Lack of Support: Going cold turkey can be particularly challenging without a strong support system. The absence of support from friends, family, or professionals can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and depression.
If you’re considering quitting an addiction cold turkey, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance on the safest and most effective way to quit, which may include a gradual tapering off, therapy, or medication-assisted treatment.
Additionally, having a support system in place, whether through friends, family, or support groups, can be invaluable in managing the emotional and physical challenges of quitting an addiction.
Dopamine and cold turkey
Dopamine and quitting “cold turkey” are two concepts that often intersect in discussions about addiction and behavior change. Understanding the role of dopamine in the brain and the implications of quitting a substance or habit abruptly can provide valuable insights into the challenges and strategies involved in overcoming addiction.
### Dopamine: The Brain’s Reward Chemical
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in the brain’s reward system. It is often referred to as the “feel-good” chemical because it is released in response to pleasurable activities, reinforcing behaviors that are essential for survival, such as eating and reproduction. Beyond these basic functions, dopamine is also involved in motivation, attention, and learning.
When a person engages in activities that release dopamine, the brain creates a positive association with those activities, encouraging repetition. This mechanism is beneficial for reinforcing healthy behaviors but can become problematic when it involves addictive substances or activities. Drugs, alcohol, and certain behaviors like gambling or excessive internet use can lead to an overproduction of dopamine, creating a powerful drive to continue the behavior despite negative consequences.
### Quitting Cold Turkey: The Abrupt Cessation
The term “cold turkey” refers to the abrupt cessation of a substance or behavior without gradual reduction or the aid of replacement therapies. This method is often used by individuals seeking to quit smoking, drinking, or using drugs. While some people successfully quit cold turkey, it can be a challenging approach due to the sudden absence of the substance that the brain has become accustomed to.
### The Intersection of Dopamine and Cold Turkey
When someone quits an addictive substance or behavior cold turkey, the brain experiences a sudden drop in dopamine levels. This can lead to withdrawal symptoms, which vary depending on the substance or behavior but often include cravings, irritability, anxiety, depression, and physical discomfort. The severity of these symptoms can make it difficult for individuals to maintain abstinence.
The brain’s adaptation to high levels of dopamine from addictive substances means that, when these substances are removed, the brain’s natural production of dopamine may be insufficient to maintain normal mood and motivation levels. This can create a challenging period of adjustment where the individual must find new, healthier ways to stimulate dopamine production and feel rewarded.
### Strategies for Success
- 1. Support Systems: Having a strong support system can be crucial for those quitting cold turkey. Family, friends, support groups, or professional counseling can provide encouragement and accountability.
- 2. Healthy Alternatives: Engaging in activities that naturally boost dopamine levels, such as exercise, meditation, or creative pursuits, can help mitigate withdrawal symptoms and improve mood.
- 3. Gradual Reduction: For some individuals, gradually reducing the substance or behavior may be a more effective strategy, allowing the brain to adjust slowly and minimizing withdrawal symptoms.
- 4. Professional Help: In some cases, medical or therapeutic interventions may be necessary to manage withdrawal symptoms and support recovery.
- 5. Mindfulness and Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and stress management can help individuals cope with cravings and emotional challenges during the quitting process.
### Conclusion
Quitting cold turkey can be an effective method for some individuals, but it requires a strong commitment and often the support of others. Understanding the role of dopamine in addiction can help individuals develop strategies to manage withdrawal symptoms and build a healthier lifestyle. Whether quitting cold turkey or through gradual reduction, the journey to overcoming addiction is a personal one, and finding the right approach is key to long-term success.
cold turkey effects on focus, productivity, attention span, academic performance…
Quitting cold turkey—that is, stopping a habit or substance abruptly without tapering—can definitely impact your focus, productivity, attention span, and even academic performance. Here’s a simple breakdown of how this happens:
- 1. Focus and Attention Span:
– Withdrawal Symptoms: Suddenly stopping something like caffeine, nicotine, or other substances can lead to withdrawal symptoms. You might experience trouble concentrating or staying on task.
– Brain Adjustment: Your brain needs time to adjust to the absence of the substance, which can temporarily make it harder to maintain focus.
- 2. Productivity:
– Energy Levels: Abrupt changes can cause fatigue or irritability, making it harder to stay productive throughout the day.
– Motivation Drops: You might feel less motivated to complete tasks as your body and mind are adapting to the change.
- 3. Attention Span:
– Distractibility: Withdrawal can increase distractibility, making it harder to pay attention for extended periods.
– Mental Fog: Some people experience a “cloudy” feeling in their mind, which can shorten attention spans.
- 4. Academic Performance:
– Study Challenges: For students, decreased focus and energy can make studying and keeping up with assignments tougher.
– Class Participation: It might be harder to engage in class or retain information during lectures.
But don’t worry! While the initial phase of quitting cold turkey can be challenging, many people find that these symptoms improve after the first few days to weeks. Here are a few tips to help manage the transition:
– Stay Hydrated and Eat Well: Proper nutrition can support your body as it adjusts.
– Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can boost your mood and energy levels.
– Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or a professional if you’re struggling.
– Stay Busy: Engaging in activities can distract you from cravings and improve your mood.
Remember, everyone’s experience is different, and it’s okay to seek help if you need it. Quitting cold turkey is a brave step towards better health and well-being!
A word about ADHD and cold turkey
When discussing how individuals with ADHD interact with the concept of quitting “cold turkey,” it’s important to consider the unique challenges and characteristics associated with ADHD. “Cold turkey” refers to the abrupt cessation of a habit or substance, without gradual reduction or the use of replacement therapies. Here are some ways in which people with ADHD might interact differently with this approach:
- 1. Impulsivity: People with ADHD often exhibit impulsivity, which might lead them to decide to quit a habit suddenly without thorough planning. While this can sometimes be beneficial in taking immediate action, it can also result in a lack of preparation for the challenges that come with quitting cold turkey.
- 2. Difficulty with Sustained Attention: Maintaining focus and commitment over time can be challenging for individuals with ADHD. This might make it difficult for them to stick with the decision to quit cold turkey, especially when faced with withdrawal symptoms or cravings.
- 3. Emotional Regulation: ADHD is often associated with difficulties in emotional regulation. The stress and discomfort associated with quitting cold turkey might be more intense for individuals with ADHD, potentially leading to mood swings or increased anxiety.
- 4. Need for Structure and Support: People with ADHD may benefit from structured support systems when trying to quit a habit. The lack of a gradual reduction plan or professional support in a cold turkey approach might make it more difficult for them to succeed.
- 5. Hyperfocus: On the positive side, individuals with ADHD can sometimes experience periods of hyperfocus, where they intensely concentrate on a task or goal. This can be advantageous when quitting cold turkey, as it might allow them to channel their focus into overcoming the habit.
- 6. Comorbid Conditions: ADHD often coexists with other conditions such as anxiety or depression, which can complicate the process of quitting cold turkey. These comorbid conditions might require additional strategies or interventions to address effectively.
- 7. Individual Variability: It’s important to remember that ADHD affects individuals differently, and personal experiences with quitting cold turkey will vary. Some may find success with this method, while others may need alternative approaches.
For individuals with ADHD considering quitting a habit cold turkey, it might be beneficial to seek guidance from healthcare professionals who can provide tailored strategies and support. This can help address the specific challenges associated with ADHD and increase the likelihood of success.
Affecting your relationships
cold turkey and self-esteem
### How Going Cold Turkey Can Impact Your Self-Esteem
Quitting a habit abruptly, often referred to as going “cold turkey,” is a bold move many people take when trying to overcome challenges like smoking, drinking, or other addictive behaviors. While this approach can be effective for some, it’s essential to understand how it might affect your self-esteem along the way.
#### Boosting Confidence
Taking the plunge to quit something overnight can significantly boost your confidence. Successfully stopping a habit without a gradual plan shows immense willpower and determination. This achievement can make you feel more capable and empowered in other areas of your life, reinforcing a positive self-image.
#### Facing Temporary Struggles
However, going cold turkey isn’t always smooth sailing. The initial stages can be tough, with cravings and withdrawal symptoms testing your resolve. Struggling during this period might temporarily shake your self-esteem, making you question your ability to stick to your decision. It’s important to remember that these challenges are a normal part of the process and don’t define your overall self-worth.
#### Building Resilience
Navigating the ups and downs of quitting cold turkey can ultimately build resilience. Each hurdle you overcome strengthens your ability to handle future obstacles. As you persist through tough times, your self-esteem can grow, knowing that you have the strength to make significant changes in your life.
#### Seeking Support Matters
Your journey can also influence how you view yourself. If you go it alone, you might feel isolated, which can impact your self-esteem negatively. On the other hand, seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can provide encouragement and reinforce your sense of self-worth. Sharing your challenges and victories helps you realize you’re not alone, fostering a more positive self-image.
#### Celebrating Small Wins
Finally, recognizing and celebrating small victories along the way is crucial for maintaining healthy self-esteem. Whether it’s a day, a week, or a month without the habit, each milestone deserves acknowledgment. These celebrations remind you of your progress and motivate you to keep moving forward.
### In Conclusion
Going cold turkey can be a powerful method to break free from unwanted habits, and its impact on self-esteem varies from person to person. While the process may present challenges that test your confidence, the overall journey can lead to increased self-worth and resilience. Remember to celebrate your successes, seek support when needed, and be kind to yourself throughout the process. You’re taking a brave step toward a healthier, more confident you!
cold turkey addiction leads to isolation and loneliness?
.jpg)
Quitting an addiction “cold turkey” refers to the abrupt cessation of a substance or behavior without gradually reducing usage or seeking professional help. This approach can indeed lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness, among other challenges. Here’s how:
- 1. Withdrawal Symptoms: Abruptly stopping an addictive substance can lead to intense withdrawal symptoms, both physical and psychological. These symptoms can make it difficult for individuals to engage in social activities or maintain relationships, leading to isolation.
- 2. Emotional Instability: The process of quitting can cause mood swings, irritability, and depression. These emotional challenges can strain relationships and make social interactions overwhelming or unappealing, pushing individuals towards solitude.
- 3. Loss of Social Circles: For many, their social life may have revolved around the addictive behavior or substance. Quitting cold turkey can mean distancing oneself from these social circles, which can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- 4. Lack of Support: Without a structured support system, such as therapy or support groups, individuals may feel alone in their struggle. The absence of understanding and encouragement from others can exacerbate feelings of loneliness.
- 5. Fear of Judgment: Individuals may fear judgment from others about their addiction or their decision to quit, leading them to withdraw from social interactions to avoid perceived stigma or criticism.
- 6. Identity Crisis: Addiction can become a significant part of a person’s identity. Quitting cold turkey can lead to an identity crisis, where individuals struggle to find their place in social settings without the crutch of their addiction.
While quitting cold turkey can be effective for some, it is often recommended to seek professional guidance and support. Engaging with therapy, support groups, or counseling can provide the necessary tools and community to navigate the challenges of quitting and help mitigate feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Effects of cold turkey on your relationships
Quitting an addiction or habit “cold turkey” means stopping abruptly without gradually reducing usage or relying on substitutes. This method can have significant impacts on personal relationships, both positive and negative. Here’s a closer look at how going cold turkey might affect your relationships:
### Positive Effects:
- 1. Renewed Focus on Relationships:
– Improved Presence: Without the distraction of the addiction, individuals often become more present and attentive in their relationships, leading to improved communication and stronger connections.
– Increased Availability: The time and energy previously spent on the addiction can now be redirected towards loved ones, allowing for more quality time together.
- 2. Enhanced Trust:
– Demonstrating Commitment: Quitting cold turkey can be a powerful demonstration of commitment to change, which can help rebuild trust with family and friends who may have been affected by the addiction.
– Reliability: As individuals become more consistent in their behavior, their reliability improves, enhancing trust within relationships.
- 3. Positive Role Modeling:
– Inspiration for Others: Successfully quitting an addiction can serve as a positive example for others who may be struggling with similar issues, potentially encouraging them to seek change as well.
- 4. Emotional Growth:
– Self-Reflection: The process of quitting can lead to greater self-awareness and emotional maturity, which can enrich personal interactions and deepen relationships.
### Negative Effects:
- 1. Withdrawal Symptoms:
– Mood Swings and Irritability: The abrupt cessation of an addictive substance or behavior can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including irritability and mood swings, which may strain relationships.
– Emotional Instability: Partners and family members may find it challenging to cope with the emotional turbulence that often accompanies withdrawal.
- 2. Increased Conflict:
– Stress and Tension: The stress of quitting cold turkey can lead to increased tension and conflict within relationships, especially if loved ones are not fully supportive or understanding of the process.
– Misunderstandings: Without clear communication, loved ones may misinterpret withdrawal symptoms or behavior changes, leading to misunderstandings and potential conflicts.
- 3. Pressure and Expectations:
– High Expectations: Family and friends might have high expectations for immediate improvement in behavior and relationships, which can create pressure and stress for the individual trying to quit.
– Fear of Relapse: Loved ones may experience anxiety about the possibility of relapse, which can lead to overprotectiveness or distrust.
- 4. Social Isolation:
– Changing Social Circles: Quitting cold turkey might necessitate distancing oneself from social circles associated with the addiction, potentially leading to feelings of loneliness or isolation.
– Loss of Shared Activities: If the addiction was a shared activity with friends or partners, its absence might create a void in the relationship that needs to be filled with new, healthier activities.
### Conclusion:
Quitting cold turkey can be a challenging yet rewarding journey with profound implications for personal relationships. While it can lead to improved trust, presence, and emotional growth, it also poses risks such as withdrawal-induced conflicts and social isolation. Successful navigation of these challenges often requires open communication, support from loved ones, and possibly professional guidance to ensure that relationships emerge stronger and healthier.
How To Stop & Quit Your cold turkey Addiction
Finally, you think you are addicted to cold turkey and you are wondering how to quit it? How to break and overcome your cravings for cold turkey?
Here are the best solutions, steps, supports, resources, and help you can get to treat your cold turkey addiction.
Main steps and solutions to break the cold turkey addiction
Overcoming an addiction cold turkey, meaning stopping abruptly without gradually tapering off, can be challenging and requires careful planning and support. Here are the main steps to consider:
- 1. Acknowledge the Problem: Acceptance is the first step. Recognize that you have an addiction and that it’s impacting your life negatively.
- 2. Set a Quit Date: Choose a specific date to stop using the substance or engaging in the addictive behavior. This gives you time to prepare mentally and physically.
- 3. Educate Yourself: Understand the withdrawal symptoms you might experience and how long they typically last. This knowledge can help you prepare for the challenges ahead.
- 4. Seek Support: Inform family, friends, or support groups about your decision. Having a support network can provide encouragement and accountability.
- 5. Remove Triggers: Identify and eliminate triggers that may lead to relapse, such as certain people, places, or situations.
- 6. Develop a Plan: Create a structured plan for how you will cope with cravings and withdrawal symptoms. This might include exercise, meditation, or engaging in new hobbies.
- 7. Stay Hydrated and Eat Healthily: Proper nutrition and hydration can help your body cope with withdrawal symptoms and improve your overall well-being.
- 8. Consider Professional Help: Consult with healthcare professionals who can provide guidance, therapy, or medications to help manage withdrawal symptoms.
- 9. Monitor Progress: Keep track of your progress and celebrate small victories. This can boost your motivation and reinforce your commitment to quitting.
- 10. Stay Committed: Remind yourself of the reasons you decided to quit and the benefits of living addiction-free. This can help you stay focused during challenging times.
- 11. Prepare for Relapse: Understand that relapses can happen. Have a plan in place for how you will handle a relapse and get back on track.
- 12. Engage in Aftercare: Continue attending support groups or therapy sessions even after you’ve quit. Ongoing support can help maintain long-term sobriety.
Remember, quitting cold turkey is not suitable for everyone, especially for substances with severe withdrawal symptoms. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it is a safe option for you.Actually, that’s what most documentation out there is about… However, quitting a digital addiction can be a bit trickier than that.
So our team, after testing many ways, designed a bulletproof way to overcome them. Here are some clear and practical steps that are very powerful to quit a digital addiction, including cold turkey:
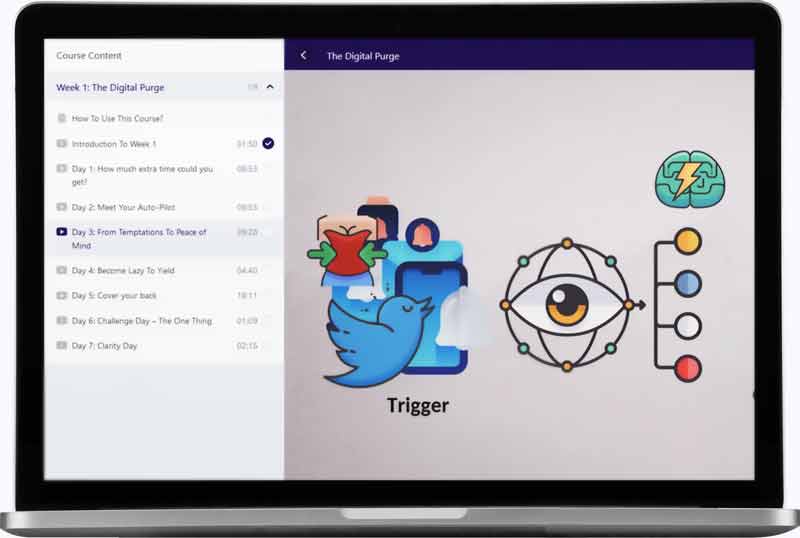
1. Purge temptations: Get rid of cold turkey
First, cleaning your life from temptations is much easier than resisting them. Disable or delete your cold turkey accounts, change the password and hide it somewhere you can’t access easily, keep your phone / computer far away… Out of sight, out of mind.
Here is a video from our course The Digital Purge. on how to add resistance to your temptations, so you become so lazy to engage with them that you give them up:
2. Spot & Reveal your emotional triggers
Second, there are some reasons, often hidden ones, that your brain and your heart love so much cold turkey. Those reasons act as triggers to pull your cravings. Rather than chasing the addiction, it’s a more efficient strategy to look at the feelings driving you toward it. That way you can cure and heal the feeling. You’ll feel better, and the cravings will magically disappear. Just get away.
3. Rewire to life

An addiction FOMO (fear of missing out) can be huge and really painful to resist, especially if it was here for a long time. However, learning to live with it is necessary to build a life full of peace and joy. Strategies to fight FOMO and rewire to life include meditation, nature activities, social interaction, intellectual and creative projects, meaningful adventures… basically anything that fills your soul.
4. How to not relapse and fully recover from cold turkey?
Finally, it’s important to acknowledge that quitting may take days, weeks, months, or even years. Getting over and quitting cold turkey forever can be difficult. You may relapse a few times, but the most important thing is that you keep engaging less and less with cold turkey. Each day you resist it is a day weakening your brain connections with cold turkey. From your patience and discipline will arise incredible mind strength, hope, and wisdom.

Best cold turkey blocker apps & functionalities
Additionally, you can increase your chance of withdrawal by limiting or blocking access to cold turkey using these apps.
They will help you filter, reduce, or block cold turkey:
In today’s digital age, maintaining focus and productivity can be challenging due to the myriad of distractions available at our fingertips. Whether it’s social media, games, or other non-work-related apps, these distractions can significantly impact your ability to concentrate on tasks. Fortunately, there are several apps designed to help limit or block access to these distractions, thereby enhancing productivity. Here are five of the best apps for this purpose:
- 1. Freedom
Freedom is a popular app that helps users block distracting websites and apps across all devices. It allows you to create custom blocklists and schedule sessions to ensure you stay focused during work hours. One of its standout features is the ability to block the entire internet if necessary, ensuring that you remain undistracted. Freedom is available on Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android.
- 2. Cold Turkey
Cold Turkey is a powerful app for blocking distractions on your computer. It offers a range of features, including the ability to block specific websites, applications, or even the entire internet. With its “Frozen Turkey” feature, you can lock yourself out of your computer for a set period, ensuring you can’t disable the app to access distractions. Cold Turkey is available for Windows and Mac.
- 3. Focus
@Will
Focus@Will takes a different approach by using music to enhance concentration. This app provides specially curated music tracks designed to improve focus and productivity. By listening to these tracks, users can enter a state of flow, reducing the likelihood of succumbing to distractions. It’s available on both desktop and mobile platforms.
- 4. StayFocusd
StayFocusd is a Google Chrome extension that helps users limit the amount of time spent on distracting websites. You can set time limits for specific sites, and once the limit is reached, the sites become inaccessible for the rest of the day. It’s a simple yet effective tool for those who primarily work within the Chrome browser.
- 5. RescueTime
RescueTimeCheck our full work and productivity addiction tool list (ranked):
Where to seek extra help?
Do you need some support and help to stop, overcome, and recover from your cold turkey addiction? If you or someone you know is struggling with cold turkey addiction, there are a few places to seek help.
The Ultimate Rewiring Program For cold turkey Addicts
Our course The Digital Purge. This course has already helped many digital addicts to rewire to what matters.
Is there a “treatment” to cure work and productivity addiction?
Absolutely, there are effective ways to address work and productivity addiction! If you find yourself constantly working, struggling to take breaks, or feeling anxious when not being productive, you’re not alone. Here are some treatments and strategies that can help:
###
- 1. Therapy and Counseling
– Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This helps you identify and change negative thought patterns related to work.
– Talk Therapy: Speaking with a counselor can provide support and strategies to manage your work habits.
###
- 2. Setting Boundaries
– Define Work Hours: Stick to specific times for work and leisure to create a healthy balance.
– Learn to Say No: It’s okay to decline extra tasks if they overwhelm you.
###
- 3. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
– Meditation: Incorporate mindfulness practices to reduce stress and increase self-awareness.
– Deep Breathing: Simple exercises can help calm your mind during hectic days.
###
- 4. Developing Hobbies and Interests
– Explore New Activities: Engage in activities outside of work to diversify your interests and reduce dependency on productivity.
– Reconnect with Passions: Rediscover what you love doing that isn’t related to your job.
###
- 5. Time Management Skills
– Prioritize Tasks: Focus on what’s most important and delegate when possible.
– Take Breaks: Regular short breaks can boost overall productivity and prevent burnout.
###
- 6. Support Systems
– Join Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide encouragement and accountability.
– Lean on Friends and Family: Share your feelings with loved ones who can offer support.
###
- 7. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
– Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can reduce stress and improve mood.
– Balanced Diet and Sleep: Proper nutrition and adequate rest are crucial for mental well-being.
Remember, overcoming work and productivity addiction is a journey, and it’s okay to seek help along the way. Consulting a mental health professional can provide personalized strategies and support to help you achieve a healthier work-life balance.
Does work and productivity therapy exist?
Yes, therapy for work and productivity addiction does exist, and it can be quite effective in helping individuals regain balance in their lives. Work addiction, often referred to as workaholism, is characterized by an excessive and compulsive need to work, which can lead to neglect of personal relationships, health, and overall well-being. Here are some therapeutic approaches that can be used to address work and productivity addiction:
- 1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a common approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. For work addiction, CBT can help individuals recognize the underlying beliefs driving their work habits, such as the need for approval or fear of failure, and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- 2. Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques: Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals become more aware of their work habits and stress levels. These techniques can aid in reducing anxiety and improving focus on the present moment, rather than being consumed by work-related thoughts.
- 3. Psychodynamic Therapy: This approach explores the unconscious motivations and emotional conflicts that may contribute to work addiction. By understanding these deeper issues, individuals can work towards resolving them and reducing their compulsive work behaviors.
- 4. Family Therapy: Work addiction often affects not just the individual, but also their family and close relationships. Family therapy can help improve communication, set healthy boundaries, and rebuild relationships that may have been strained by excessive work habits.
- 5. Coaching and Goal Setting: Working with a coach or therapist to set realistic and balanced goals can help individuals prioritize their time and energy more effectively. This approach encourages a healthier work-life balance and helps prevent burnout.
- 6. Support Groups: Joining a support group, such as Workaholics Anonymous, can provide individuals with a community of peers who understand their struggles and can offer support and accountability.
- 7. Lifestyle Changes: Therapists may also work with individuals to make lifestyle changes, such as incorporating regular exercise, hobbies, and social activities, to create a more balanced and fulfilling life outside of work.
It’s important for individuals struggling with work addiction to seek help from a qualified mental health professional who can tailor a treatment plan to their specific needs. Addressing work addiction can lead to improved mental and physical health, better relationships, and a more satisfying and balanced life.
Where to find support groups if you are addicted to cold turkey?
Finding support groups for work and productivity addicts can be a crucial step in addressing the challenges associated with workaholism and productivity obsession. Here are some avenues to explore:
- 1. Online Support Groups and Forums:
– Websites like Reddit have communities such as r/stopworking and r/productivity where individuals share experiences and advice.
– Platforms like Meetup often host virtual and in-person groups focused on work-life balance and productivity management.
- 2. Professional Organizations:
– The American Psychological Association (APA) and similar organizations in other countries may have resources or directories for support groups related to work addiction.
- 3. Therapy and Counseling Services:
– Many therapists specialize in work-life balance issues and may offer group therapy sessions. Websites like Psychology Today have directories to find professionals who may offer such groups.
– Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) often provide resources or referrals to support groups for work-related stress and addiction.
- 4. Community Centers and Nonprofits:
– Local community centers or nonprofit organizations sometimes host support groups focused on mental health and work-life balance.
- 5. Books and Online Courses:
– Authors and educators who specialize in work addiction often have associated online communities or courses that include support group elements.
- 6. Social Media Groups:
– Platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn have groups dedicated to work-life balance and overcoming work addiction, where members can share insights and support.
- 7. Workplace Initiatives:
– Some companies have internal support groups or wellness programs aimed at promoting a healthier work-life balance.
When seeking support, it’s important to find a group or community that feels comfortable and aligns with your specific needs and preferences.
But other cold turkey addiction solutions exist
If you’re looking for help with overcoming an addiction cold turkey, there are several professionals and resources you can turn to for support:
- 1. Healthcare Providers: Your primary care physician can be a good starting point. They can provide medical advice, prescribe medications to ease withdrawal symptoms, and refer you to specialists if necessary.
- 2. Therapists and Counselors: Licensed therapists or addiction counselors can offer one-on-one support, help you develop coping strategies, and address any underlying mental health issues that may be contributing to your addiction.
- 3. Psychiatrists: If your addiction is linked to mental health issues, a psychiatrist can assess your situation and prescribe medication if needed to help manage symptoms.
- 4. Detox Centers: These facilities provide medical supervision and support during the withdrawal process, ensuring your safety and comfort as you quit cold turkey.
- 5. Online Therapy Platforms: Services like BetterHelp or Talkspace offer access to licensed therapists who can provide support and guidance through digital communication, making it easier to get help from home.
- 6. Pharmacists: They can provide information about over-the-counter options that might help with withdrawal symptoms and advise on medication interactions.
- 7. Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): If your workplace offers an EAP, you can access confidential counseling and support services for addiction issues.
- 8. Family Doctors: They often have a comprehensive view of your health history and can provide personalized advice and referrals.
- 9. Social Workers: They can help connect you with community resources and provide support for both addiction recovery and any related social or economic challenges.
- 10. Holistic Practitioners: Some people find alternative therapies such as acupuncture, meditation, or yoga helpful in managing withdrawal symptoms and stress.
Each of these professionals can offer different types of support, so consider what kind of help you feel would be most beneficial for your situation.
Conclusion
Overcoming a cold turkey addiction is a challenging yet profoundly rewarding journey that requires immense courage, determination, and support. While the path to recovery is often fraught with physical, emotional, and psychological hurdles, the decision to quit abruptly can lead to significant and lasting transformation. As individuals navigate this path, it is crucial to acknowledge the importance of a strong support system, whether through friends, family, or professional counseling.
Additionally, adopting healthy coping mechanisms and lifestyle changes can significantly enhance the chances of maintaining sobriety.
The journey is unique for each person, and setbacks may occur, but these should be viewed as opportunities for growth rather than failures. Celebrating small victories and remaining patient and compassionate with oneself are key components of a successful recovery. Ultimately, overcoming a cold turkey addiction is not just about breaking free from substance dependence; it is about reclaiming one’s life, rediscovering personal strengths, and building a future filled with hope and resilience. As individuals emerge from the shadows of addiction, they not only transform their own lives but also inspire those around them, proving that change is possible and that a brighter, healthier future is within reach.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.Here is the trailer:
To Go Further
Take our 4-min test
How to help someone with cold turkey addiction?
Helping someone who is trying to quit an addiction “cold turkey” can be challenging, but your support can make a significant difference. Here are some ways you can assist:
- 1. Educate Yourself: Learn about the specific addiction they are trying to quit. Understanding the withdrawal symptoms and challenges they may face can help you provide better support.
- 2. Be Supportive and Non-Judgmental: Offer a listening ear without judgment. Let them know that you are there for them and that you believe in their ability to overcome the addiction.
- 3. Encourage Professional Help: Suggest that they seek help from a healthcare professional, therapist, or support group. Professional guidance can provide them with strategies to manage withdrawal symptoms and prevent relapse.
- 4. Help Create a Plan: Assist them in developing a plan to manage cravings and avoid triggers. This might include identifying high-risk situations and developing coping strategies.
- 5. Promote Healthy Habits: Encourage them to adopt a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep. These can help improve their mood and overall well-being.
- 6. Be Patient: Understand that quitting cold turkey can be a difficult process with ups and downs. Be patient and offer encouragement, even if they experience setbacks.
- 7. Remove Triggers: Help them identify and remove any triggers from their environment that might tempt them to relapse. This could include avoiding certain places, people, or situations.
- 8. Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge and celebrate their achievements, no matter how small. Positive reinforcement can boost their motivation and confidence.
- 9. Be Available: Let them know they can reach out to you whenever they need to talk or if they are struggling. Being available can provide them with a sense of security and support.
- 10. Take Care of Yourself: Supporting someone with an addiction can be emotionally taxing. Make sure to take care of your own mental and emotional health as well
Best books about work and productivity addiction
Exploring the themes of work and productivity addiction can offer valuable insights into how these issues impact our lives and society. Here are five notable books that delve into these topics, providing a mix of personal narratives, psychological analysis, and practical advice:
- 1. “Deep Work: Rules for Focused Success in a Distracted World” by Cal Newport
– Cal Newport’s “Deep Work” explores the importance of focused, undistracted work in an increasingly noisy world. While not directly about addiction, it addresses the cultural shift towards constant connectivity and multitasking, offering strategies to cultivate deep concentration and productivity. Newport emphasizes the value of deep work in achieving meaningful accomplishments and highlights the dangers of shallow work habits.
- 2. “Rest: Why You Get More Done When You Work Less” by Alex Soojung-Kim Pang
– Alex Soojung-Kim Pang’s “Rest” challenges the notion that longer hours equate to greater productivity. The book argues for the importance of rest and downtime in enhancing creativity and efficiency. By examining historical figures and scientific research, Pang demonstrates how deliberate rest can lead to more sustainable work habits and prevent burnout, a common consequence of work addiction.
- 3. “Do Nothing: How to Break Away from Overworking, Overdoing, and Underliving” by Celeste Headlee
– Celeste Headlee’s “Do Nothing” offers a critique of the modern obsession with busyness and productivity. Through historical analysis and personal anecdotes, Headlee explores how societal pressures have led to overworking and undervaluing leisure. The book provides practical advice for reclaiming time, setting boundaries, and finding fulfillment beyond constant productivity.
- 4. “The Joy of Missing Out: Live More by Doing Less” by Tonya Dalton
– Tonya Dalton’s “The Joy of Missing Out” focuses on the empowerment that comes from intentionally choosing what not to do. Dalton encourages readers to prioritize what truly matters and to let go of the pressure to do
Research about work and productivity addiction
Work and productivity addiction, often referred to as “workaholism,” is a phenomenon that has garnered increasing attention in recent years. Below are summaries of three to five official studies that explore various aspects of work and productivity addiction:
1. Study on Workaholism and Health Outcomes (2016.:
Conducted by researchers at the University of Bergen, this study examined the health outcomes associated with workaholism. The researchers developed the Bergen Work Addiction Scale to identify workaholics and assess their health. The study found that workaholism is significantly associated with higher levels of stress, sleep problems, and burnout. The scale has been widely used in subsequent research to measure work addiction.
2. The Impact of Workaholism on Family Life (2018.:
A study published in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology explored how workaholism affects family dynamics. The researchers found that individuals who are addicted to work often experience conflicts at home, leading to strained relationships and reduced family satisfaction. The study highlighted the importance of work-life balance and the need for interventions to address workaholic behaviors.
3. Neurobiological Perspectives on Work Addiction (2020.:
This study, published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology, investigated the neurobiological underpinnings of work addiction. The researchers used neuroimaging techniques to explore brain activity in individuals identified as workaholics. They discovered that workaholism shares similarities with other behavioral addictions, such as gambling, in terms of brain activity patterns. This study provided insights into the potential for developing targeted treatments for work addiction.
4. Workaholism and Job Performance (2019.:
Conducted by researchers at the University of Georgia, this study examined the relationship between workaholism and job performance. Contrary to the common belief that workaholics are highly productive, the study found that excessive work can lead to decreased efficiency and lower job performance over time. The researchers suggested that sustainable productivity requires a balanced approach to work.
5. Cross-Cultural Examination of Workaholism (2021.:
Published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, this study explored workaholism across different cultures. The researchers surveyed employees from various countries to understand cultural influences on work addiction. They found significant cultural variations in the prevalence and perception of workaholism, indicating that societal norms and values play a crucial role in shaping work-related behaviors.
These studies collectively highlight the complexity of work and productivity addiction, emphasizing its impact on health, family life, and job performance. They also underscore the need for a nuanced understanding of cultural factors and the potential for developing effective interventions.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.
The impact of work and productivity on our society
In today’s fast-paced world, the pressure to achieve and excel has intensified, leading to a phenomenon known as work and productivity addiction. This addiction, characterized by an overwhelming compulsion to work excessively and a constant drive to be productive, has far-reaching implications on both individuals and society as a whole.
### Individual Impacts
- 1. Mental Health Issues: Work and productivity addiction can lead to severe mental health problems, including anxiety, depression, and burnout. The relentless pursuit of productivity often results in chronic stress, which can exacerbate these conditions.
- 2. Physical Health Consequences: The physical toll of excessive work is significant. Long hours and insufficient rest can lead to fatigue, sleep disorders, and a weakened immune system. Moreover, sedentary work habits contribute to lifestyle diseases such as obesity and cardiovascular issues.
- 3. Strained Relationships: Individuals addicted to work often prioritize their jobs over personal relationships, leading to isolation and strained family dynamics. The lack of work-life balance can result in a disconnect from loved ones, causing emotional distress and relationship breakdowns.
- 4. Decreased Job Satisfaction: Ironically, the pursuit of constant productivity can lead to decreased job satisfaction. When work becomes an obsession, individuals may lose sight of their passion and purpose, leading to a sense of emptiness and dissatisfaction.
### Societal Impacts
- 1. Cultural Shift: Society increasingly values productivity and success, often equating them with personal worth. This cultural shift places immense pressure on individuals to perform, perpetuating the cycle of work addiction.
- 2. Economic Implications: While initially, high productivity levels may boost economic output, the long-term effects can be detrimental. Burnout and health issues lead to increased absenteeism and decreased efficiency, ultimately affecting economic productivity.
- 3. Impact on Innovation: A culture focused solely on productivity can stifle creativity and innovation. When individuals are pressured to constantly produce, there is little room for experimentation and creative thinking, which are essential for innovation.
- 4. Social Inequality: Work addiction often exacerbates social inequality. Those who cannot keep up with the relentless pace, whether due to personal choice or circumstances, may find themselves marginalized or undervalued in the workforce.
### Addressing the Issue
To mitigate the impact of work and productivity addiction, a multi-faceted approach is necessary:
– Promoting Work-Life Balance: Employers can play a crucial role by encouraging flexible work arrangements and emphasizing the importance of work-life balance. Policies that support mental health and well-being can help reduce the pressure to overwork.
– Redefining Success: Society needs to redefine success beyond productivity metrics. Valuing creativity, emotional intelligence, and personal fulfillment can help shift the focus from constant productivity to holistic well-being.
– Raising Awareness: Education and awareness campaigns can highlight the dangers of work addiction and promote healthier work habits. Encouraging open discussions about mental health in the workplace can also reduce stigma and support those struggling with addiction.
– Individual Responsibility: On a personal level, individuals should be encouraged to set boundaries, prioritize self-care, and seek help if they find themselves unable to disconnect from work.
In conclusion, while productivity is essential for progress, an addiction to work can have detrimental effects on both individuals and society. By fostering a culture that values balance and well-being, we can create a healthier, more sustainable approach to work and productivity.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.