Trying to quit chess addiction? Welcome to our digital detox series! This series focuses on how to stop digital and screen addictions. Findall our posts about digital addictions. Today, let’s talk about how to quit the chess addiction.

- What’s the chess addiction?
- Addiction to chess, a “real” addiction?
- What’s considered chess addiction?
- How much chess is too much?
- Some online entertainment addiction facts & statistics
- Symptoms & Causes of the chess addiction
- Why is chess so addictive?
- Possible causes of chess dependency
- Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of chess addiction
- Problems, impacts & bad effects of chess
- Some benefits of chess
- Health problems
- Impact on brain & mental health
- Impact on relationships
- How to stop & quit your chess addiction
- Main steps and solutions to break the chess addiction
- Best chess blocker apps & functionalities
- Where to seek extra help?
- Conclusion
- To Go Further
- How to help someone with chess addiction
- Best books about online entertainment addiction
- Research about online entertainment addiction
What is the chess addiction?
About chess
Chess is a strategic board game for two players, involving 16 pieces each on a checkered 64-square board. The objective is to checkmate the opponent’s king, meaning it is under threat of capture with no legal moves left.
Addiction to chess, a “real” addiction?
Officially an addiction?
First, let’s have a look at the DSM-5,the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Does it include chess addiction?
As of the latest update, chess addiction is not specifically listed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5.. The DSM-5, published by the American Psychiatric Association, is a comprehensive classification of mental disorders used by mental health professionals. It includes criteria for diagnosing a wide range of psychological conditions.
While chess addiction is not explicitly mentioned, the DSM-5 does include criteria for behavioral addictions, such as gambling disorder. These criteria could potentially be applied to other activities if they lead to significant impairment or distress in an individual’s life. However, for a behavior to be classified as an addiction, it typically must meet specific criteria, such as a loss of control over the behavior, continued engagement despite negative consequences, and a preoccupation with the activity.
If someone is concerned about their or someone else’s chess playing habits, it might be beneficial to consult a mental health professional who can provide guidance based on the individual’s specific circumstances.
So what does “chess addiction” mean?
Understanding Chess Addiction: When Passion Turns into a Compulsion
Chess is a timeless game that has captivated millions worldwide with its strategic depth and intellectual challenge. While many enjoy playing chess casually or even competitively, for some, the love for the game can evolve into what’s known as chess addiction. But what exactly does that mean?
### What is Chess Addiction?
Chess addiction refers to an excessive and compulsive involvement in playing chess that interferes with a person’s daily life, responsibilities, and overall well-being. Just like any other addiction, it goes beyond mere passion or dedication. Instead, it becomes a dominating force that can negatively impact various aspects of an individual’s life.
### Signs of Chess Addiction
Here are some common indicators that someone might be struggling with a chess addiction:
- 1. Neglecting Responsibilities: Skipping work, school, or household duties to play chess.
- 2. Social Withdrawal: Isolating from friends and family to spend more time on the game.
- 3. Loss of Interest in Other Activities: No longer finding joy in hobbies or interests outside of chess.
- 4. Emotional Distress: Feeling anxious, irritable, or depressed when not playing chess.
- 5. Inability to Cut Down: Trying to reduce playtime but failing repeatedly.
### Why Can Chess Become Addictive?
Several factors contribute to chess addiction:
– Mental Stimulation: Chess challenges the brain, providing a rewarding sense of accomplishment.
– Competitive Nature: The drive to improve and compete can become overwhelming.
– Online Accessibility: With the rise of online platforms, it’s easier than ever to play chess anytime, anywhere.
– Community and Recognition: Gaining praise and recognition can reinforce excessive play.
### Impact of Chess Addiction
While chess is beneficial in many ways, addiction can lead to:
– Academic or Career Decline: Performance may drop as more time is spent playing.
– Health Issues: Poor sleep, eye strain from screen time, and neglect of physical health.
– Strained Relationships: Friends and family may feel neglected or frustrated.
– Mental Health Problems: Increased stress, anxiety, or depression.
### Managing Chess Addiction
If you or someone you know is struggling with chess addiction, consider these steps:
- 1. Set Boundaries: Allocate specific times for playing and stick to them.
- 2. Prioritize Responsibilities: Ensure that work, studies, and personal life come first.
- 3. Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or a professional counselor.
- 4. Diversify Interests: Engage in other hobbies to create a balanced lifestyle.
- 5. Mindfulness Practices: Techniques like meditation can help manage compulsive behaviors.
### Final Thoughts
Chess is a wonderful game that offers countless benefits, from improving cognitive skills to fostering strategic thinking. However, like anything else, balance is key. Recognizing the signs of addiction early can help maintain a healthy relationship with the game, ensuring that chess remains a source of joy and growth rather than stress and imbalance.
If you find yourself or someone you know struggling with excessive chess playing, don’t hesitate to reach out for support. Finding that balance can lead to a more fulfilling and well-rounded life.
What is considered chess addiction?
Diagnosing a chess addiction, like any behavioral addiction, involves identifying patterns and behaviors that indicate an unhealthy obsession or dependence. While chess is a strategic and intellectually stimulating game, excessive engagement can lead to negative consequences in a person’s life. Here are some criteria that might be considered when diagnosing a chess addiction:
- 1. Preoccupation with Chess: Constantly thinking about chess, even when not playing. This includes planning the next game, analyzing past games, or reading about chess strategies excessively.
- 2. Loss of Control: Inability to limit the amount of time spent playing chess. Attempts to cut down or stop playing are unsuccessful.
- 3. Neglect of Responsibilities: Prioritizing chess over important obligations such as work, school, or family. This may also include neglecting personal hygiene or health.
- 4. Withdrawal Symptoms: Experiencing irritability, restlessness, or mood swings when unable to play chess.
- 5. Tolerance: Needing to play more chess or engage in more challenging games to achieve the same level of satisfaction or excitement.
- 6. Continued Use Despite Negative Consequences: Persisting in playing chess despite knowing it is causing problems in personal, professional, or social life.
- 7. Deception: Lying to family members, friends, or therapists about the extent of involvement with chess.
- 8. Escapism: Using chess as a way to escape from problems, stress, or negative emotions.
- 9. Impact on Relationships: Experiencing conflicts or distancing in relationships due to excessive chess playing.
- 10. Financial Implications: Spending excessive money on chess-related activities, such as tournaments, online memberships, or chess equipment, that is beyond one’s means.
It’s important to note that diagnosing any addiction should be done by a qualified mental health professional. They can provide a comprehensive assessment and, if necessary, recommend appropriate interventions or treatments. If you or someone you know is struggling with what might be a chess addiction, seeking professional help is a crucial step.
How much chess is too much?
Determining how much time spent on chess is too much can vary significantly depending on individual circumstances, goals, and personal well-being. Here are some factors to consider when evaluating whether your chess practice is excessive:
- 1. Personal Goals: If you’re an aspiring professional or competitive player, spending several hours a day on chess might be necessary. However, if you’re a casual player, dedicating too much time might not align with your personal goals or lifestyle.
- 2. Balance with Other Activities: It’s important to maintain a balanced life. If chess is interfering with work, school, relationships, or other hobbies and responsibilities, it might be time to reassess your schedule.
- 3. Mental and Physical Health: Excessive time spent on any activity, including chess, can lead to burnout or physical strain, such as eye fatigue or poor posture. Ensure you’re taking regular breaks and engaging in physical activities to maintain overall health.
- 4. Enjoyment and Motivation: If playing chess starts to feel like a chore rather than an enjoyable activity, it might be a sign that you’re overdoing it. It’s important to keep the experience fun and fulfilling.
- 5. Sleep and Rest: Ensure that your chess practice is not cutting into essential rest time. Adequate sleep is crucial for cognitive function and overall well-being.
- 6. Social Interaction: Spending too much time on chess might limit your social interactions. Ensure you’re maintaining healthy relationships and social activities outside of chess.
- 7. Progress and Improvement: If you’re not seeing improvement despite spending a lot of time on chess, it might be beneficial to evaluate the quality of your practice rather than just the quantity.
Ultimately, the right amount of time to spend on chess is highly individual. Regularly reassessing your priorities and how chess fits into your life can help ensure that your practice remains a positive and enriching part of your routine.
Some online entertainment addiction facts & statistics

Online entertainment addiction is an increasingly prevalent issue in today’s digital age, as people spend more time on the internet for leisure and social interaction. Although specific statistics can vary by region and demographic, several studies and surveys provide insight into the scope and impact of this phenomenon. Below are some key statistics and findings related to online entertainment addiction:
- 1. Prevalence:
– A report by we Are Social and Hootsuite in 2023 indicated that the average internet user spends approximately 6 hours and 37 minutes online each day, with a significant portion dedicated to entertainment and social media.
– Studies suggest that around 6-10% of internet users may experience some form of internet addiction, with online entertainment being a major contributing factor.
- 2. Demographics:
– Younger individuals, particularly those aged 16-24, are more susceptible to online entertainment addiction due to their high engagement with social media, video streaming, and gaming platforms.
– Males are often found to be more prone to gaming addiction, while females may be more inclined towards social media addiction.
- 3. Social Media:
– According to a 2022 survey by Pew Research Center, approximately 72% of Americans use social media, with many users reporting difficulty in reducing their time spent on these platforms.
– The average daily time spent on social media globally is around 2 hours and 31 minutes.
- 4. Gaming:
– The World Health Organization (WHO) recognized gaming disorder as a mental health condition in 2018, highlighting the growing concern over gaming addiction.
– A 2021 report by Newzoo found that there are over 3 billion gamers worldwide, with a significant number exhibiting signs of addiction or problematic gaming behavior.
- 5. Streaming Services:
– The rise of streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ has contributed to binge-watching behaviors. A 2023 survey by Deloitte found that 60% of U.S. consumers admitted to binge-watching shows regularly.
– Binge-watching can lead to sleep deprivation and reduced productivity, with 30% of binge-watchers reporting a negative impact on their daily lives.
- 6. Psychological and Physical Effects:
– Excessive use of online entertainment can lead to various psychological issues, including anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
– Physical health can also be affected, with prolonged screen time contributing to eye strain, poor posture, and a sedentary lifestyle.
- 7. Intervention and Awareness:
– Many organizations and mental health professionals advocate for digital detoxes and setting boundaries to mitigate the risks of online entertainment addiction.
– Educational programs and parental controls are being implemented to help younger users develop healthier digital habits.
As online entertainment continues to evolve, understanding and addressing the challenges of addiction will be crucial for promoting healthier interactions with digital media.
Is the chess addiction widespread?
Chess has seen a significant surge in popularity in recent years, and many people have become deeply engaged with the game, leading some to describe this engagement as an “addiction.” However, it’s important to differentiate between a healthy enthusiasm for chess and a problematic addiction.
### Factors Contributing to Chess Popularity
- 1. Online Platforms: Websites like Chess.com and Lichess have made it easy for people worldwide to play chess at any time, with players of all skill levels. These platforms also offer puzzles, lessons, and tournaments, which can be highly engaging.
- 2. Streaming and Social Media: Platforms like Twitch and YouTube have popularized chess through streams and videos. Influential personalities and grandmasters have attracted large audiences, making the game more accessible and entertaining.
- 3. Pandemic Influence: The COVID-19 pandemic led to increased interest in online activities, including chess. Many people turned to chess as a way to pass the time and engage in a mentally stimulating activity.
- 4. Pop Culture: The success of shows like “The Queen’s Gambit” on Netflix has sparked renewed interest in chess, particularly among demographics that might not have been traditionally drawn to the game.
### Enthusiasm vs. Addiction
– Enthusiasm: Many people who play chess regularly do so because they find it intellectually stimulating and enjoyable. Chess can improve cognitive abilities, strategic thinking, and concentration.
– Addiction: While chess can be consuming, it typically lacks the negative consequences associated with other forms of addiction, such as substance abuse. However, if someone is playing chess to the detriment of their personal, social, or professional life, it might be considered problematic.
### Signs of Problematic Chess Engagement
– Neglecting responsibilities in favor of playing chess.
– Experiencing distress or anxiety when unable to play.
– Using chess as a primary means of coping with stress or emotions.
– Prioritizing chess over social interactions and relationships.
### Conclusion
While many people are highly engaged with chess, describing this engagement as an “addiction” might not be entirely accurate for most. It is essential for individuals to maintain a balance and ensure that their interest in chess does not negatively impact other areas of their life. As with any hobby or interest, moderation is key.
Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of chess addiction
Why is chess so addictive?
Chess is incredibly addictive, and here’s why:
- 1. Endless Possibilities: Every game of chess is unique. With countless opening moves and strategies, no two games are the same. This variety keeps players engaged, always eager to explore new tactics.
- 2. Mental Challenge: Chess sharpens your mind. It requires planning, critical thinking, and problem-solving, which can be both stimulating and rewarding. The satisfaction of outsmarting an opponent is hard to beat
!
- 3. Progress and Growth: As you play more, you can see your skills improve. Tracking your progress, learning from mistakes, and mastering new strategies provide a continuous sense of achievement.
- 4. Competitive Spirit: Whether playing against friends or online opponents, the competitive aspect of chess is thrilling. Striving to win and improve keeps the game exciting and motivates you to keep playing.
- 5. Social Connection: Chess brings people together. Joining clubs, participating in tournaments, or playing online connects you with a community of enthusiasts who share your passion.
- 6. Accessibility: You can play chess anywhere—on a board, online, or through apps. Its simplicity in setup yet depth in play makes it easy to dive in whenever you have a few minutes.
All these factors combine to make chess not just a game, but a captivating journey that keeps players coming back for more!
Possible causes of chess dependency
Chess addiction, like any form of addiction, can arise from a combination of psychological, social, and neurological factors. Here are some key causes that might contribute to someone developing an addiction to chess:
- 1. Cognitive Engagement: Chess is a highly strategic and intellectually stimulating game that challenges the brain. This cognitive engagement can be deeply satisfying and lead to repeated play as individuals seek to improve their skills and problem-solving abilities.
- 2. Competitive Nature: The competitive aspect of chess can be addictive, especially for individuals who thrive on competition and the desire to win. The drive to improve one’s ranking or beat a challenging opponent can lead to excessive play.
- 3. Reward System Activation: Like many games, chess can activate the brain’s reward system. Winning a game or achieving a personal best can release dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, reinforcing the behavior and encouraging continued play.
- 4. Social Interaction: Chess can be a social activity, whether played in person or online. The social interaction and community aspects can be appealing and lead to increased time spent playing, especially if one builds relationships or gains social status within a chess community.
- 5. Escapism: For some, chess can serve as an escape from daily stressors or emotional challenges. Immersing oneself in the game can provide a temporary distraction from personal issues, leading to repeated play as a coping mechanism.
- 6. Sense of Achievement: The structured nature of chess, with clear rules and objectives, provides a sense of achievement and progress. This can be particularly appealing to individuals who seek validation or a sense of accomplishment.
- 7. Personality Traits: Certain personality traits, such as perfectionism, high competitiveness, or a tendency towards obsessive behavior, can make an individual more susceptible to developing a chess addiction.
- 8. Accessibility and Convenience: With the rise of online platforms and mobile apps, chess is more accessible than ever. The convenience of being able to play anytime and anywhere can lead to increased frequency and duration of play.
- 9. Cultural and Historical Significance: For some, the rich history and cultural significance of chess can add an additional layer of attraction, making the game more than just a pastime but a pursuit of mastering a timeless art.
While enjoying chess is healthy and beneficial for cognitive development, it’s important for individuals to be mindful of their playing habits and ensure that their engagement with the game does not interfere with other aspects of their life.
Signs & Symptoms of chess addiction
Now let’s see if you have the chess addiction problem.
Chess is a game that has captured the minds and hearts of millions around the world. Its blend of strategy, foresight, and creativity makes it an endlessly fascinating pursuit. However, for some, the love for chess can transform into an obsession. Here are seven signs that you might be a chess addict:
1. Constantly Thinking in Chess Terms: If you find yourself thinking about your life decisions in terms of chess moves, you might be a chess addict. Whether it’s planning your day like a series of strategic moves or seeing your relationships as a complex game of chess, this mindset indicates a deep immersion in the game.
2. Dreaming About Chess: When your dreams are filled with chessboards, pieces, and strategies, it’s a clear sign that the game has infiltrated your subconscious. Regularly dreaming about chess scenarios or famous games can be a telltale sign of addiction.
3. Playing at Every Opportunity: If you find yourself playing chess at every possible moment—during lunch breaks, on public transport, or late into the night—you might be addicted. The urge to play just one more game, even when you have other responsibilities, is a strong indicator.
4. Following Chess News Religiously: An avid chess addict will keep up with every tournament, analyze games of grandmasters, and follow the latest updates in the chess world. If you find yourself more excited about the Candidates Tournament than the latest blockbuster movie, chess might be your true passion.
5. Collecting Chess Sets and Memorabilia: Owning multiple chess sets, from classic wooden boards to themed collections, is a common trait among chess enthusiasts. If you also collect chess books, magazines, and memorabilia, it could point to a deeper obsession with the game.
6. Analyzing Every Game: A chess addict doesn’t just play; they analyze. If you spend hours reviewing your games, studying openings, and learning from your mistakes, it shows a commitment to improving your skills and a deep-seated love for the game.
7. Prioritizing Chess Over Other Activities: When chess starts taking precedence over other hobbies, social events, or even work, it might be time to reassess your relationship with the game. If you frequently choose a quiet evening with a chessboard over a night out with friends, it could be a sign of addiction.
While being passionate about chess is a wonderful thing, it’s essential to maintain a balance with other aspects of life. Recognizing these signs can help you ensure that your love for the game remains a healthy and enjoyable part of your life.
Try our digital habit & screen addiction test:
Problems, impacts & bad effects of chess: should you quit?

What are some benefits of chess
Chess is a game that has captivated minds for centuries, and its enduring popularity can be attributed to a multitude of benefits and advantages it offers. Here are some reasons why chess is considered a great game:
- 1. Cognitive Development: Chess is renowned for enhancing cognitive abilities. It requires players to think critically, strategize, and solve complex problems, which can sharpen the mind and improve intellectual skills.
- 2. Improves Concentration and Focus: The game demands intense concentration and focus, as players must anticipate their opponent’s moves and plan several steps ahead. This level of mental discipline can translate into improved focus in other areas of life.
- 3. Enhances Memory: Chess involves recalling various strategies, openings, and patterns. This constant engagement with memory can enhance both short-term and long-term memory capabilities.
- 4. Teaches Patience and Discipline: Chess is a game of patience and careful planning. It teaches players the value of waiting for the right moment and the importance of making calculated decisions.
- 5. Boosts Creativity: While chess is a game of logic, it also requires creativity. Players often need to think outside the box to develop innovative strategies and unexpected moves to outwit their opponents.
- 6. Improves Problem-Solving Skills: Each game of chess is essentially a complex problem that needs solving. Players must assess the board, identify potential threats, and devise solutions, which enhances their problem-solving skills.
- 7. Encourages Strategic Thinking: Chess players learn to think strategically, considering both immediate and long-term consequences of their actions. This skill is valuable in various real-life situations, including business and personal decision-making.
- 8. Universal Appeal and Accessibility: Chess is a universal game that transcends language and cultural barriers. It can be played by people of all ages, making it an inclusive and accessible pastime.
- 9. Promotes Social Interaction: Chess can be a social activity, whether played in person or online. It brings people together, fostering communication and camaraderie among players.
- 10. Enhances Emotional Intelligence: Chess teaches players to manage their emotions, especially under pressure. Handling wins and losses gracefully can improve emotional intelligence and resilience.
- 11. Educational Tool: Many educational institutions incorporate chess into their curriculum because of its educational benefits. It can aid in the development of mathematical and analytical skills, making it a valuable learning tool.
- 12. Encourages Lifelong Learning: Chess is a game that can be played and enjoyed throughout a lifetime. There is always something new to learn, whether it’s a new strategy, opening, or tactic, which keeps the game fresh and engaging.
In summary, chess is more than just a game; it is a powerful tool for personal development. Its ability to enhance cognitive skills, promote strategic thinking, and foster social interaction makes it a valuable and enriching activity for people of all ages.But on the other hand, what are some chess addiction problems that addicts suffer from?
General health problems
Chess, a strategic board game with a history spanning over a millennium, is not only a test of intellect and strategy but also offers several health benefits. Engaging in chess can positively impact both mental and physical health in various ways:
### Cognitive Benefits
- 1. Improved Memory:
– Chess requires players to remember complex patterns, strategies, and the positions of pieces on the board, thereby enhancing memory. Regular play can lead to improved recall abilities and better memory function.
- 2. Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills:
– The game demands strategic thinking and foresight, encouraging players to anticipate opponents’ moves and plan several steps ahead. This practice can translate into improved problem-solving skills in everyday life.
- 3. Increased IQ:
– Some studies suggest that playing chess can lead to an increase in IQ scores. The game challenges the brain, stimulating growth in cognitive abilities and intelligence.
- 4. Boosted Creativity:
– Chess is not just about logic and strategy; it also involves creativity, especially in devising unique strategies and moves. This aspect of the game can enhance creative thinking skills.
- 5. Better Concentration:
– Chess requires intense focus and concentration. Regular play can improve attention span and the ability to concentrate on tasks for extended periods.
### Mental Health Benefits
- 1. Reduced Risk of Dementia:
– Engaging in mentally stimulating activities like chess can help maintain cognitive function as people age, potentially reducing the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
- 2. Stress Relief:
– The immersive nature of chess can serve as a form of escapism, providing a break from daily stressors and helping to reduce anxiety levels.
- 3. Improved Mood and Mental Health:
– The sense of achievement from mastering chess strategies and winning games can boost self-esteem and contribute to a positive mood.
### Social and Emotional Benefits
- 1. Enhanced Social Skills:
– Chess is often played in clubs or online communities, offering opportunities for social interaction. This can improve communication skills and foster a sense of community and belonging.
- 2. Patience and Discipline:
– The game teaches patience and the importance of strategic planning over impulsive actions, fostering discipline that can be beneficial in various life situations.
### Physical Health Benefits
- 1. Lower Blood Pressure:
– The concentration and relaxation involved in playing chess can help lower blood pressure, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
- 2. Improved Hand-Eye Coordination:
– Moving pieces on the board requires coordination between the brain and hands, which can enhance fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination.
### Conclusion
Chess is more than just a game; it is a multifaceted activity that offers numerous health benefits. From cognitive improvements to mental health support, the advantages of playing chess are extensive. Whether played casually or competitively, chess can be a valuable addition to a healthy lifestyle, promoting mental agility and emotional well-being.
chess and sleep disorders
Chess, a game renowned for its strategic depth and intellectual challenge, is generally considered a healthy and stimulating activity. However, like many intense mental pursuits, it can potentially contribute to sleep disorders or sleep problems under certain circumstances. Here are a few ways in which chess might impact sleep:
- 1. Mental Stimulation: Engaging in intense mental activities, such as playing chess, especially close to bedtime, can lead to increased brain activity, making it difficult to wind down and fall asleep. The excitement or stress of a competitive game might keep your mind active, delaying the onset of sleep.
- 2. Screen Time: Many people play chess online, which involves screen exposure. The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles, potentially leading to difficulties in falling asleep.
- 3. Stress and Anxiety: Competitive chess can be stressful, especially for those who play at high levels. The pressure to perform well, coupled with the mental exhaustion from prolonged focus, can lead to stress and anxiety, which are known contributors to sleep disturbances.
- 4. Irregular Sleep Patterns: Chess tournaments and online games can sometimes lead to irregular sleep patterns, especially if games are played in different time zones or late into the night. This disruption in routine can affect the body’s internal clock, leading to sleep problems.
- 5. Obsessive Thinking: For some, chess can become an obsession, leading to excessive thinking about strategies and moves even outside of game time. This can result in difficulty relaxing and clearing the mind before sleep.
To mitigate these potential issues, it’s important for chess players to practice good sleep hygiene. This includes setting a regular sleep schedule, avoiding screens before bedtime, and engaging in relaxing activities to help the mind unwind.
Additionally, balancing chess with other activities and ensuring it doesn’t interfere with daily life can help maintain a healthy relationship with the game and promote better sleep.
chess affecting your brain & mental health: bad for brain and mental health?
Some effects of chess on your brain
### Could Playing Chess Have Negative Effects on Your Brain? Let’s Explore!
Chess is often hailed as a fantastic way to boost your brainpower, enhance strategic thinking, and improve concentration. However, like anything else, playing chess extensively might come with a few downsides. Here are some potential negative effects to keep in mind:
- 1. Mental Fatigue
– Long Sessions Can Be Draining: Intense, prolonged chess games require a lot of mental energy. Playing for hours on end without breaks can lead to exhaustion, making it harder to think clearly both during and after your games.
- 2. Stress and Pressure
– Competitive Anxiety: For those who take chess very seriously, the pressure to win can sometimes lead to stress or anxiety. This is especially true in competitive settings where expectations are high.
- 3. Obsessive Behavior
– Over-Involvement: Spending too much time on chess might lead some individuals to neglect other important areas of life, such as relationships, physical activities, or work. Balance is key!
- 4. Sleep Disruption
– Late-Night Games: Playing chess late into the night, especially online, can interfere with your sleep patterns. Lack of proper rest can negatively impact cognitive functions and overall health.
- 5. Physical Health Concerns
– Sedentary Lifestyle: Extended periods of sitting and focusing on a chessboard can contribute to a sedentary lifestyle, which is linked to various health issues like back pain, eye strain, and decreased physical fitness.
- 6. Frustration and Mood Swings
– Losing Streaks: Consistently losing games or facing tough opponents might lead to feelings of frustration or lowered self-esteem. It’s important to keep the game fun and not let it become a source of negative emotions.
### Finding a Healthy Balance
While chess has many cognitive benefits, being mindful of these potential downsides can help you enjoy the game without adverse effects. Here are a few tips to maintain a healthy balance:
– Take Regular Breaks: Short breaks during long sessions can help prevent mental fatigue.
– Stay Active: Incorporate physical activities into your routine to counteract the sedentary nature of chess.
– Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques and keep the game enjoyable to minimize stress.
– Maintain Social Connections: Ensure that chess doesn’t replace time spent with family and friends.
Remember, moderation is key! By being aware of these possible negative effects, you can enjoy chess as a rewarding and stimulating hobby without compromising your well-being.
Some effects of chess on your mental health
Chess is often celebrated for its cognitive benefits, such as improving problem-solving skills, enhancing memory, and fostering strategic thinking. However, like any intense mental activity, it can also have some negative effects on mental health if not approached with balance and moderation. Here are some potential adverse effects:
- 1. Stress and Anxiety: Competitive chess can be highly stressful. The pressure to perform well, especially in tournaments, can lead to significant anxiety. Players may experience stress due to time constraints, the fear of making mistakes, or the pressure to maintain a high ranking.
- 2. Obsessive Behavior: Chess can become an obsession for some individuals, leading them to prioritize the game over other important aspects of life, such as social interactions, work, or studies. This can result in an unhealthy balance and neglect of other responsibilities.
- 3. Burnout: Intense focus and prolonged periods of playing can lead to mental fatigue and burnout. Like any activity that requires deep concentration, chess can be mentally exhausting, especially if played for extended periods without breaks.
- 4. Frustration and Disappointment: Losing games or not performing up to one’s expectations can lead to feelings of frustration and disappointment. This can be particularly challenging for those who tie their self-worth to their performance in the game.
- 5. Isolation: While chess can be a social activity, it can also lead to isolation, especially for those who prefer playing online or who become so engrossed in the game that they withdraw from social interactions.
- 6. Over-Competitiveness: For some, the competitive nature of chess can lead to an unhealthy focus on winning at all costs. This can foster negative emotions such as envy, resentment, or hostility towards other players.
- 7. Sleep Disruption: Engaging in intense chess matches, especially late at night, can disrupt sleep patterns. The mental stimulation from the game can make it difficult to wind down and fall asleep.
- 8. Perfectionism: Chess can encourage perfectionistic tendencies, where players strive for flawless play. This can lead to excessive self-criticism and dissatisfaction, even after successful games.
To mitigate these potential negative effects, it’s important for chess players to maintain a balanced approach. Taking regular breaks, engaging in physical activities, fostering social connections, and managing stress through mindfulness or relaxation techniques can help maintain mental well-being while enjoying the game.
Does chess cause stress and anxiety?
Chess is often celebrated for its intellectual challenge and strategic depth, but like many competitive activities, it can also be a source of stress and anxiety for some players. Here are several ways in which chess might contribute to these feelings:
- 1. Performance Pressure: Competitive chess players often feel pressure to perform well, especially in tournaments or high-stakes matches. The desire to win and fear of losing can lead to significant stress.
- 2. Time Constraints: Many chess games are played with time controls, which require players to make decisions quickly. The ticking clock can create a sense of urgency and pressure, potentially leading to anxiety.
- 3. Complex Decision-Making: Chess involves complex problem-solving and strategic planning. The mental effort required to analyze positions and anticipate opponents’ moves can be overwhelming, particularly for less experienced players.
- 4. Fear of Mistakes: The possibility of making a blunder or overlooking a critical move can be a source of anxiety. The knowledge that a single mistake can change the outcome of the game adds to the pressure.
- 5. Expectation Management: Players often set high expectations for themselves, and failing to meet these expectations can lead to feelings of disappointment and stress.
- 6. Social Factors: Playing in front of an audience or against highly skilled opponents can increase anxiety levels. The social aspect of chess, including interactions with opponents and spectators, can also contribute to stress.
- 7. Cognitive Load: Chess requires intense concentration and mental stamina. Prolonged focus during a game can lead to mental fatigue, which may manifest as stress or anxiety.
- 8. Personal Investment: For some, chess is more than just a game; it’s a significant part of their identity or career. The personal investment in the game can amplify stress when outcomes don’t align with personal goals.
While chess can induce stress and anxiety, it’s important to note that these feelings are not universal. Many players find chess to be a relaxing and enjoyable activity. Managing stress in chess often involves developing coping strategies, such as practicing mindfulness, improving time management skills, and maintaining a balanced perspective on wins and losses.
Additionally, focusing on the enjoyment and learning aspects of the game rather than solely on outcomes can help mitigate stress and enhance the overall experience.
Can chess addiction lead to sadness and depression?

Chess, like any other activity or hobby, can become an obsession for some individuals, potentially leading to negative emotional outcomes such as sadness or depression. While chess is often celebrated for its cognitive benefits, strategic depth, and ability to foster critical thinking skills, excessive engagement can have adverse effects on mental health. Here are some ways in which chess addiction might contribute to feelings of sadness or depression:
- 1. Isolation: Chess is often a solitary activity, especially when played online. Individuals who spend excessive amounts of time playing chess may neglect social interactions, leading to feelings of loneliness and isolation, which are common precursors to depression.
- 2. Performance Pressure: The competitive nature of chess can create significant pressure to perform well. Players may become overly critical of their abilities, leading to low self-esteem and feelings of inadequacy, especially after losses or poor performances.
- 3. Neglect of Responsibilities: An addiction to chess can result in the neglect of personal and professional responsibilities. This neglect can lead to stress, anxiety, and guilt, further contributing to depressive symptoms.
- 4. Disruption of Routine: Spending excessive time on chess can disrupt daily routines, including sleep patterns, exercise, and other healthy habits. Such disruptions can negatively impact mental health and overall well-being.
- 5. Escapism: For some, chess may become a form of escapism from real-life problems or stressors. While this can provide temporary relief, it may also prevent individuals from addressing underlying issues, potentially exacerbating feelings of sadness or depression in the long run.
- 6. Obsessive Thinking: Chess requires intense focus and strategic thinking, which can sometimes lead to obsessive thought patterns. Constantly analyzing games, strategies, or mistakes can become mentally exhausting and contribute to a negative emotional state.
To mitigate these risks, it is important for individuals to maintain a balanced approach to chess. Setting time limits, prioritizing social interactions, and ensuring a healthy lifestyle can help prevent chess from becoming an unhealthy obsession. If someone is experiencing signs of depression or sadness related to their chess habits, it may be beneficial to seek support from mental health professionals.
Dopamine and chess
The intricate relationship between dopamine and chess is a fascinating topic that delves into the intersection of neuroscience, psychology, and the strategic allure of one of the world’s oldest games. Chess, a game of strategy, foresight, and intellectual prowess, has captivated minds for centuries. But what role does dopamine, a neurotransmitter often associated with pleasure and reward, play in this cerebral pursuit?
### Understanding Dopamine
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays several important roles in the brain and body. It is often referred to as the “feel-good” chemical because it is involved in reward, motivation, memory, attention, and even regulating body movements. When you achieve something rewarding, like winning a game of chess, dopamine is released, creating a sense of pleasure and satisfaction.
### The Role of Dopamine in Chess
- 1. Motivation and Reward: Chess is a game that requires intense concentration, strategic planning, and the ability to anticipate an opponent’s moves. The satisfaction of successfully executing a strategy or winning a game triggers the release of dopamine, reinforcing the behavior and motivating players to continue improving their skills.
- 2. Learning and Memory: Dopamine is crucial for learning and memory, two essential components of chess. As players study openings, tactics, and endgames, dopamine helps encode these patterns into memory, allowing players to recall and apply them in future games.
- 3. Focus and Attention: Chess demands sustained attention and the ability to focus on the board for extended periods. Dopamine plays a role in maintaining this focus, helping players concentrate on the game and ignore distractions.
- 4. Risk and Reward Assessment: Chess involves assessing risks and rewards with each move. Dopamine influences decision-making processes by weighing potential outcomes and guiding players toward moves that maximize positive results.
### The Chess Player’s Brain
Studies using functional MRI scans have shown that experienced chess players activate different parts of their brains compared to novices. This suggests that the brains of chess players are wired differently, potentially due to the repeated activation of neural pathways associated with strategic thinking and pattern recognition. Dopamine likely plays a role in strengthening these pathways, enhancing a player’s ability to recognize patterns and anticipate future moves.
### The Psychological Aspect
Chess can be both exhilarating and stressful. The anticipation of a well-thought-out move or the anxiety of a potential blunder can cause fluctuations in dopamine levels. This emotional rollercoaster is part of what makes chess so engaging. The highs of victory and the lows of defeat are both tied to the brain’s reward system, with dopamine at the center.
### Conclusion
The interplay between dopamine and chess highlights the complex relationship between our brain’s chemistry and our cognitive abilities. While dopamine enhances motivation, learning, and focus, it also underscores the emotional highs and lows that make chess such a captivating game. Understanding this relationship not only enriches our appreciation of chess but also provides insight into the broader workings of the human brain. As players continue to push the boundaries of their strategic thinking, dopamine remains a silent yet powerful force in the background, driving the passion and dedication that chess inspires.
chess effects on focus, productivity, attention span, academic performance…
Does Chess Affect Focus, Productivity, Attention Span, and Academic Performance? Let’s Find Out!
Hey there, chess enthusiasts and curious minds! 🧠♟️
Have you ever wondered if playing chess can influence your daily life beyond the chessboard? From boosting focus to enhancing academic performance, chess is often hailed as a brain-boosting game. Let’s dive into how chess affects your focus, productivity, attention span, and academic performance in a simple and friendly way.
—
###
- 1. Chess and Focus
Boosting Concentration Skills
Playing chess requires you to concentrate deeply on the game. You need to think ahead, anticipate your opponent’s moves, and strategize accordingly. Regularly engaging in chess can train your brain to maintain focus for extended periods.
Real-Life Application
This enhanced focus doesn’t stay only on the chessboard. You might find yourself better able to concentrate on tasks at work or school, minimizing distractions and staying on track with your goals.
—
###
- 2. Chess and Productivity
Improving Problem-Solving Abilities
Chess is all about solving complex problems. Each move presents a new challenge, encouraging you to think critically and make decisions efficiently. This sharpens your problem-solving skills, which are essential for being productive in everyday tasks.
Time Management
Balancing time between your moves teaches you how to manage time effectively. You learn to prioritize tasks, ensuring that you make the best use of the time available—an invaluable skill for boosting productivity.
—
###
- 3. Chess and Attention Span
Enhancing Mental Stamina
A game of chess can last for hours, requiring sustained mental effort. Over time, playing chess can increase your mental stamina, allowing you to pay attention for longer periods without getting easily distracted.
Attention to Detail
Chess sharpens your ability to notice small details—like a minor move from your opponent that could change the game. This heightened attention to detail can translate into better focus in other areas of your life, from studying to working on projects.
—
###
- 4. Chess and Academic Performance
Boosting Cognitive Skills
Studies have shown that chess can improve various cognitive skills, including memory, logical reasoning, and critical thinking. These skills are directly linked to better academic performance.
Encouraging Discipline and Patience
Chess teaches patience and discipline, as rushing through moves can lead to mistakes. These traits are beneficial for academic success, helping you stay disciplined in your studies and patiently work through challenging subjects.
Enhancing Creativity
While chess is a game of strategy, it also encourages creative thinking to outmaneuver opponents. This creativity can enhance your ability to think outside the box in academic settings, leading to innovative solutions and ideas.
—
### In Conclusion
Chess is more than just a game; it’s a fantastic tool for personal development. By improving your focus, productivity, attention span, and academic performance, chess can positively impact various aspects of your life. Whether you’re a seasoned player or just starting, incorporating chess into your routine can lead to meaningful benefits both on and off the board.
So, grab a chessboard and make your next move towards a sharper, more productive you! 🏆✨
—
Happy Playing!
A word about ADHD and chess
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that can affect attention, impulse control, and executive functioning. When it comes to activities like chess, individuals with ADHD might interact with the game differently compared to those without the disorder. Here are some ways ADHD might influence chess playing:
- 1. Focus and Attention: Chess requires sustained concentration and strategic thinking, which can be challenging for individuals with ADHD. They might find it difficult to maintain focus throughout a lengthy game, potentially leading to impulsive moves or oversight of strategic opportunities.
- 2. Impulsivity: People with ADHD often struggle with impulsivity, which can manifest in chess as making hasty moves without fully considering the consequences. This can lead to mistakes or missed opportunities to capitalize on an opponent’s weaknesses.
- 3. Strategic Thinking: While ADHD can make long-term strategic planning challenging, some individuals with the disorder are able to hyperfocus on activities they find engaging. In such cases, they might excel in short bursts of intense concentration, allowing them to devise creative strategies or unexpected moves.
- 4. Motivation and Interest: Interest levels can significantly impact how individuals with ADHD engage with chess. If they find the game stimulating, they may be more motivated to focus and improve their skills. Conversely, if they lose interest, their performance might decline.
- 5. Learning Styles: People with ADHD might benefit from different learning approaches when it comes to mastering chess. Visual aids, interactive lessons, or gamified learning platforms might be more effective than traditional methods.
- 6. Emotional Regulation: Chess can be an emotionally demanding game, requiring players to manage frustration and remain calm under pressure. Individuals with ADHD might find it challenging to regulate their emotions during tense moments, which can affect their decision-making process.
- 7. Adaptability: Some individuals with ADHD might excel in dynamic and fast-paced versions of chess, such as blitz chess, where quick thinking and adaptability are crucial. The shorter time controls can align well with their tendency to think quickly and act on intuition.
- 8. Social Interaction: Chess can also be a social activity, and individuals with ADHD might experience differences in how they interact with opponents. They may be more prone to conversational distractions or might use the social aspect of the game as a way to stay engaged.
Overall, while ADHD can present challenges in the context of chess, it can also offer unique strengths and perspectives. With the right strategies and accommodations, individuals with ADHD can enjoy and excel in the game.
Affecting your relationships
chess and self-esteem
### How Chess Boosts Your Self-Esteem
Playing chess isn’t just about moving pieces on a board—it can have a positive impact on your self-esteem in several meaningful ways. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned player, here’s how chess can help you feel better about yourself:
####
- 1. Enhances Problem-Solving Skills
Chess challenges you to think critically and strategize. Successfully navigating complex situations on the board can give you a sense of accomplishment, boosting your confidence in your problem-solving abilities.
####
- 2. Builds Patience and Persistence
Learning and improving at chess requires time and dedication. As you work through tough games and learn from your mistakes, you develop patience and resilience, which are key components of a healthy self-esteem.
####
- 3. Improves Focus and Concentration
Playing chess demands focus and attention to detail. Mastering this can translate to better concentration in other areas of your life, making you feel more competent and capable.
####
- 4. Encourages Setting and Achieving Goals
Whether it’s aiming to learn a new opening or striving to win a tournament, chess encourages you to set realistic goals. Achieving these goals, no matter how small, can significantly enhance your self-worth.
####
- 5. Provides a Sense of Belonging
Joining a chess club or community connects you with others who share your passion. Building friendships and being part of a group can boost your social self-esteem and provide support.
####
- 6. Offers Positive Feedback and Recognition
Winning a game or making a brilliant move can provide instant gratification and positive reinforcement. These moments of success contribute to a positive self-image.
####
- 7. Teaches Handling Success and Failure
Chess teaches you to gracefully handle wins and losses. Learning to celebrate victories and learn from defeats can strengthen your emotional resilience, which is essential for maintaining healthy self-esteem.
####
- 8. Stimulates Creativity
Chess is not just about strategy; it’s also a creative game. Expressing creativity on the chessboard can make you feel innovative and unique, enhancing your overall self-esteem.
### Final Thoughts
Incorporating chess into your routine can do wonders for your self-esteem. It challenges your mind, fosters personal growth, and connects you with a community—all of which contribute to a more confident and positive you. So, next time you sit down to play, remember that you’re not just having fun—you’re also building a stronger sense of self!
chess addiction leads to isolation and loneliness?
.jpg)
Chess is a fascinating and intellectually stimulating game that has been enjoyed by millions of people around the world for centuries. However, like any activity, when taken to an extreme, it can potentially lead to negative consequences, including isolation and loneliness. Here’s how chess addiction might contribute to these issues:
- 1. Time Consumption: Chess can be incredibly time-consuming, especially for those who become deeply engrossed in improving their skills or competing at a high level. This can lead to individuals spending excessive amounts of time playing chess, whether online or in person, at the expense of other social activities and responsibilities.
- 2. Neglect of Relationships: As with any addiction, an obsession with chess can lead individuals to neglect personal relationships. Friends and family may feel sidelined if a person prioritizes chess over spending quality time with them, which can strain relationships and lead to feelings of isolation.
- 3. Solitary Nature: Chess is often played alone or against a single opponent, which can limit social interaction. While online platforms offer the opportunity to play against people from around the world, these interactions are often limited to the game itself and may not provide the same level of social engagement as face-to-face interactions.
- 4. Competitive Pressure: For those who play chess competitively, the pressure to perform well can lead to stress and anxiety. This pressure might cause individuals to withdraw from social situations to focus on practice and preparation, further contributing to isolation.
- 5. Escapism: Chess can serve as an escape from reality, providing a structured environment where individuals can focus solely on the game. While this can be a healthy outlet in moderation, excessive reliance on chess as a form of escapism can lead to avoidance of real-world issues and responsibilities, resulting in social withdrawal.
- 6. Online Addiction: With the rise of online chess platforms, it has become easier for individuals to play chess anytime, anywhere. This accessibility can lead to excessive screen time and reduced face-to-face interactions, contributing to feelings of loneliness.
To mitigate these risks, it’s important for chess enthusiasts to maintain a balanced approach. Setting limits on the amount of time spent playing chess, ensuring that it does not interfere with personal relationships or responsibilities, and engaging in other social activities can help prevent isolation and loneliness.
Additionally, joining chess clubs or participating in local tournaments can provide opportunities for social interaction and community building.
Effects of chess on your relationships
Chess, a game of strategy and intellect, has been cherished for centuries. While it can be a rewarding hobby, its impact on personal relationships can be both positive and negative. Here are some ways chess can influence your relationships:
### Positive Effects
- 1. Bonding Over a Shared Interest: Playing chess with friends, family, or partners can strengthen bonds. It provides a common interest that can lead to engaging conversations and shared experiences.
- 2. Improved Communication: Chess encourages strategic thinking and patience, which can translate into better communication skills. Players often learn to articulate their thoughts and strategies, which can enhance verbal and non-verbal communication in relationships.
- 3. Encourages Healthy Competition: Engaging in friendly chess matches can foster a sense of healthy competition. This can be a fun way to challenge each other and grow together, as long as the competition remains friendly and respectful.
- 4. Teaches Patience and Perseverance: Chess requires patience and long-term planning, skills that are beneficial in relationships. Learning to think ahead and consider the consequences of actions can lead to more thoughtful and considerate interactions with others.
- 5. Cognitive and Emotional Growth: Chess can improve cognitive abilities such as problem-solving and critical thinking. These skills can contribute to personal growth, making individuals more adaptable and understanding in their relationships.
### Negative Effects
- 1. Time Consumption: Chess can be time-consuming, especially if one becomes deeply involved in the game. This can lead to less time spent with loved ones, potentially causing feelings of neglect or frustration.
- 2. Competitive Tensions: While healthy competition can be positive, it can also lead to tensions if one or both parties become overly competitive. This can strain relationships, especially if one person consistently wins or loses.
- 3. Obsessive Behavior: For some, chess can become an obsession, leading to an imbalance in priorities. This can cause neglect of responsibilities and relationships, as the game takes precedence over other aspects of life.
- 4. Emotional Reactions: Losing a game of chess can sometimes lead to negative emotions such as frustration or anger. If not managed properly, these emotions can spill over into relationships, causing unnecessary conflicts.
- 5. Intellectual Intimidation: Chess is often seen as a game for the intellectually inclined. If one partner feels inferior or intimidated by the other’s skill level, it could lead to feelings of inadequacy or resentment.
In conclusion, chess can have both positive and negative effects on relationships. The key is to maintain a balance, ensuring that the game enhances rather than detracts from personal connections. By being mindful of how chess influences your interactions, you can enjoy the benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks.
How To Stop & Quit Your chess Addiction
Finally, you think you are addicted to chess and you are wondering how to quit it? How to break and overcome your cravings for chess?
Here are the best solutions, steps, supports, resources, and help you can get to treat your chess addiction.
Main steps and solutions to break the chess addiction
Overcoming any form of addiction, including chess addiction, involves a combination of self-awareness, structured planning, and support. Here are some steps that could help:
- 1. Acknowledge the Problem: The first step is recognizing that your chess playing has become excessive and is negatively impacting other areas of your life, such as work, relationships, or personal well-being.
- 2. Set Clear Goals: Define what a healthy relationship with chess looks like for you. This might involve setting limits on how much time you spend playing or shifting your focus to other activities.
- 3. Identify Triggers: Understand what prompts you to play chess excessively. Is it boredom, stress, or a need for competition? Identifying these triggers can help you address the underlying issues.
- 4. Create a Schedule: Allocate specific times for playing chess and stick to them. This helps prevent impulsive playing and ensures you maintain a balanced lifestyle.
- 5. Find Alternative Activities: Engage in other hobbies or activities that you enjoy and that can provide similar satisfaction or relaxation as chess. This could include physical exercise, reading, or learning a new skill.
- 6. Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or a mental health professional about your struggle. They can offer support, encouragement, and accountability.
- 7. Join Support Groups: Consider joining groups or forums where people share similar experiences. This can provide a sense of community and shared understanding.
- 8. Practice Mindfulness: Techniques such as meditation or deep-breathing exercises can help you become more aware of your urges and manage them effectively.
- 9. Set Consequences and Rewards: Establish a system of rewards for sticking to your goals and consequences for lapses. This can help reinforce positive behavior.
- 10. Reflect and Adjust: Regularly assess your progress and make adjustments as needed. Be patient with yourself, as overcoming any addiction is a process that takes time.
Remember, if chess addiction is severely affecting your life, it may be beneficial to seek professional help from a therapist or counselor who specializes in behavioral addictions.Actually, that’s what most documentation out there is about… However, quitting a digital addiction can be a bit trickier than that.
So our team, after testing many ways, designed a bulletproof way to overcome them. Here are some clear and practical steps that are very powerful to quit a digital addiction, including chess:
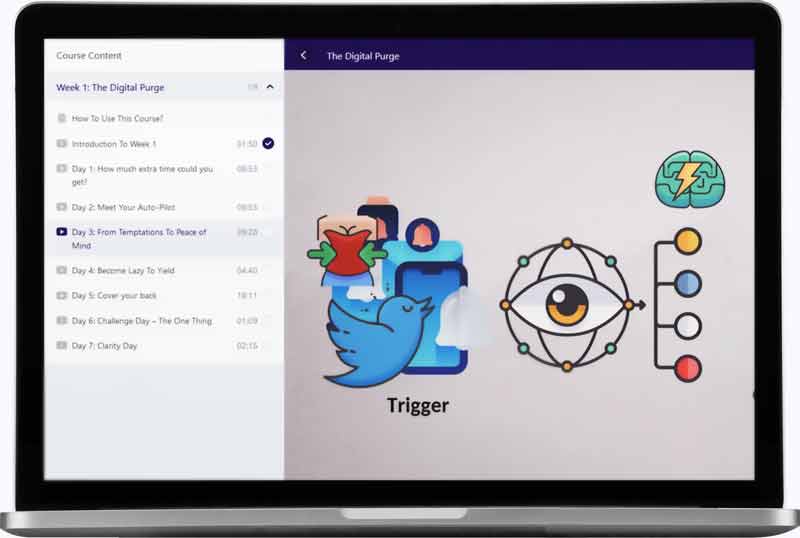
1. Purge temptations: Get rid of chess
First, cleaning your life from temptations is much easier than resisting them. Disable or delete your chess accounts, change the password and hide it somewhere you can’t access easily, keep your phone / computer far away… Out of sight, out of mind.
Here is a video from our course The Digital Purge. on how to add resistance to your temptations, so you become so lazy to engage with them that you give them up:
2. Spot & Reveal your emotional triggers
Second, there are some reasons, often hidden ones, that your brain and your heart love so much chess. Those reasons act as triggers to pull your cravings. Rather than chasing the addiction, it’s a more efficient strategy to look at the feelings driving you toward it. That way you can cure and heal the feeling. You’ll feel better, and the cravings will magically disappear. Just get away.
3. Rewire to life

An addiction FOMO (fear of missing out) can be huge and really painful to resist, especially if it was here for a long time. However, learning to live with it is necessary to build a life full of peace and joy. Strategies to fight FOMO and rewire to life include meditation, nature activities, social interaction, intellectual and creative projects, meaningful adventures… basically anything that fills your soul.
4. How to not relapse and fully recover from chess?
Finally, it’s important to acknowledge that quitting may take days, weeks, months, or even years. Getting over and quitting chess forever can be difficult. You may relapse a few times, but the most important thing is that you keep engaging less and less with chess. Each day you resist it is a day weakening your brain connections with chess. From your patience and discipline will arise incredible mind strength, hope, and wisdom.

Best chess blocker apps & functionalities
Additionally, you can increase your chance of withdrawal by limiting or blocking access to chess using these apps.
They will help you filter, reduce, or block chess:
In today’s digital age, maintaining focus and productivity can be challenging with the constant allure of online entertainment. Fortunately, several apps are designed to help users limit or block access to distracting websites and apps. Here are five of the best apps to consider for managing online entertainment access:
- 1. Freedom
Freedom is a versatile app that allows users to block websites, apps, and even the entire internet if necessary. It works across multiple devices, including Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android, making it an excellent choice for those who need consistent productivity tools across platforms. Users can schedule sessions in advance or start them on demand, and the app’s “Locked Mode” prevents users from easily bypassing restrictions.
- 2. Cold Turkey
Cold Turkey is a robust app for Windows and Mac users, known for its strict blocking capabilities. It allows users to block websites, applications, and even the entire internet. Cold Turkey’s “Frozen Turkey” feature can lock users out of their devices for a set period, ensuring they remain focused. The app’s flexibility in setting up schedules and exceptions makes it a favorite for those serious about limiting distractions.
- 3. StayFocusd
StayFocusd is a popular Chrome extension that helps users limit the time spent on distracting websites. Users can set daily time limits for specific sites, after which they are blocked for the rest of the day. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a great choice for those who primarily need to manage distractions while browsing the web.
- 4. RescueTime
RescueTime is more than just a blocking app; it’s a comprehensive time management tool that provides insights into how users spend their time online. Available for Windows, Mac, Android, and Linux, RescueTime tracks time spent on different websites and applications, offering detailed reports. Users can set alerts for when they exceed their desired time on entertainment sites and block them during focus sessions.
- 5. Focus
@Will
While not a traditional blockingCheck our full online entertainment addiction tool list (ranked):
Where to seek extra help?
Do you need some support and help to stop, overcome, and recover from your chess addiction? If you or someone you know is struggling with chess addiction, there are a few places to seek help.
The Ultimate Rewiring Program For chess Addicts
Our course The Digital Purge. This course has already helped many digital addicts to rewire to what matters.
Is there a “treatment” to cure online entertainment addiction?
### Can Online Entertainment Addiction Be Treated?
Absolutely, you can address and overcome an addiction to online entertainment! Here are some effective strategies and treatments:
- 1. Acknowledge the Issue
– Recognizing that your online habits are affecting your life is the first step toward change.
- 2. Set Clear Boundaries
– Limit the time you spend on social media, streaming platforms, or gaming. Use timers or apps that help monitor and restrict usage.
- 3. Establish a Routine
– Create a daily schedule that includes time for work, hobbies, exercise, and social activities to reduce idle time spent online.
- 4. Find Alternative Activities
– Engage in offline hobbies like reading, painting, sports, or cooking to shift your focus away from screens.
- 5. Seek Professional Help
– Therapists or counselors can provide personalized strategies and support. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in treating behavioral addictions.
- 6. Join Support Groups
– Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges can offer encouragement and practical advice.
- 7. Practice Mindfulness
– Techniques like meditation and deep breathing can help you stay present and reduce the urge to seek constant online stimulation.
- 8. Educate Yourself
– Understanding how online entertainment affects your brain and behavior can motivate you to make healthier choices.
Remember, overcoming any addiction takes time and patience. Be kind to yourself throughout the process and celebrate small victories along the way. You’ve got this!
Does online entertainment therapy exist?
Yes, therapy for online entertainment addiction does exist and is becoming increasingly recognized as a necessary treatment due to the growing prevalence of digital addiction. As more people find themselves spending excessive amounts of time on social media, video streaming platforms, online gaming, and other forms of digital entertainment, mental health professionals have developed strategies to address these behaviors.
Here are some common therapeutic approaches used to treat online entertainment addiction:
- 1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is one of the most widely used methods for treating various types of addiction. It helps individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with their addiction. By identifying triggers and developing healthier coping mechanisms, individuals can reduce their dependency on online entertainment.
- 2. Motivational Interviewing (MI): This approach involves working with individuals to enhance their motivation to change their behavior. Through guided conversations, therapists help clients explore their ambivalence about their addiction and encourage them to commit to change.
- 3. Mindfulness and Meditation: These techniques are used to help individuals become more aware of their online habits and develop a more balanced relationship with technology. Mindfulness can reduce impulsivity and increase self-control, helping individuals resist the urge to engage in excessive online entertainment.
- 4. Family Therapy: Since online entertainment addiction can affect relationships, family therapy may be beneficial. It involves working with family members to improve communication, set boundaries, and support the individual in their recovery process.
- 5. Group Therapy and Support Groups: Connecting with others who are experiencing similar challenges can provide a sense of community and accountability. Group therapy sessions and support groups offer a platform for sharing experiences and strategies for overcoming addiction.
- 6. Digital Detox Programs: These programs involve structured breaks from technology to help individuals reset their relationship with digital devices. They often include activities that promote offline engagement and personal growth.
- 7. Behavioral Interventions: These interventions focus on modifying the individual’s environment and routines to reduce the temptation to engage in online entertainment. This might include setting time limits, using apps to block certain websites, or creating a schedule for offline activities.
It’s important to note that treatment for online entertainment addiction should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. If you or someone you know is struggling with this type of addiction, consulting a mental health professional who specializes in digital addiction can be a valuable first step.
Where to find support groups if you are addicted to chess?
Finding support groups for online entertainment addiction can be a crucial step in managing and overcoming the issue. Here are several avenues you can explore to find the right support:
- 1. Online Support Groups:
– Reddit: Subreddits like r/StopGaming or r/NoFap offer communities where individuals share experiences and support each other.
– Facebook Groups: Search for groups related to digital detox or online addiction recovery.
– InTheRooms: This platform offers online meetings for various addictions, including those related to technology and entertainment.
- 2. Therapy and Counseling Platforms:
– BetterHelp and Talkspace: These platforms connect you with licensed therapists who specialize in addiction, including online entertainment addiction.
– Psychology Today: Their website allows you to search for therapists who focus on digital addiction.
- 3. 12-Step Programs:
– Internet and Technology Addicts Anonymous (ITAA): This is a 12-step fellowship offering meetings and support for those struggling with internet and technology addiction.
- 4. Local Support Groups:
– Check with local community centers or mental health clinics to see if they offer support groups for digital addiction.
– Universities and colleges sometimes have resources or groups for students dealing with online entertainment addiction.
- 5. Healthcare Providers:
– Speak to a healthcare provider or mental health professional for recommendations on local or online support groups.
- 6. Non-Profit Organizations:
– Organizations like The Center for Internet and Technology Addiction provide resources and may offer support group recommendations.
- 7. Digital Detox Programs:
– Some retreats and programs focus on helping individuals disconnect from digital devices and can provide a supportive community.
When seeking support, it’s important to find a group or resource that resonates with your personal needs and preferences. Don’t hesitate to try different options until you find the right fit.
But other chess addiction solutions exist
If you’re seeking help with chess addiction and prefer not to engage with support groups, there are several other avenues you can explore:
- 1. Mental Health Professionals: Consider reaching out to a psychologist, psychiatrist, or counselor who specializes in addiction or behavioral issues. They can provide personalized strategies and therapeutic support to address your concerns.
- 2. Life Coaches: A certified life coach can help you set goals and develop a balanced approach to your interests, including chess, and other aspects of your life.
- 3. Healthcare Providers: Your primary care physician can offer initial advice and may refer you to specialists who can help with addiction management.
- 4. Educational Resources: Books and online courses about behavioral addiction can offer insights and self-help strategies to manage your chess addiction.
- 5. Friends and Family: Talking to trusted friends or family members can provide emotional support and accountability as you work to find balance.
- 6. Online Forums and Communities: While not support groups per se, online forums or communities focused on chess or addiction can offer advice and shared experiences from others who have faced similar challenges.
- 7. Mindfulness and Meditation Instructors: Practicing mindfulness or meditation can help you gain better control over compulsive behaviors. Instructors can guide you in techniques to reduce the urge to play excessively.
- 8. Time Management Experts: Professionals who specialize in time management can help you create a structured schedule that limits chess play and incorporates other fulfilling activities.
By exploring these options, you can find the support and guidance needed to address your chess addiction effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, overcoming chess addiction is a journey that requires self-awareness, discipline, and a balanced approach to the game. While chess is a wonderful and intellectually stimulating activity, it is important to recognize when it begins to interfere with other aspects of life. By setting clear boundaries, seeking support from friends or professionals, and exploring other interests, individuals can regain control and enjoy chess as a healthy part of their lives. Remember, the key is moderation and ensuring that chess remains a source of joy and growth rather than a compulsion. Embracing a balanced lifestyle not only enhances one’s chess skills but also enriches overall well-being, allowing for a more fulfilling and diverse life experience.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.Here is the trailer:
To Go Further
Take our 4-min test
How to help someone with chess addiction?
Helping someone with a chess addiction involves a compassionate and supportive approach. Here are some steps you can take:
- 1. Understand the Addiction: Recognize that chess addiction, like any other addiction, can have underlying causes such as stress, anxiety, or a need for escapism. Understanding these factors can help you approach the situation more empathetically.
- 2. Open Communication: Talk to the person in a non-judgmental way. Express your concerns about how their chess playing might be affecting their life, relationships, or responsibilities. Use “We” statements to avoid sounding accusatory, such as “We’ve noticed you seem stressed when you play chess for long hours.”
- 3. Encourage Balance: Help them find a balance between playing chess and other activities. Encourage them to set specific times for playing chess and to engage in other hobbies or social activities. This can help reduce the time spent on chess and introduce variety into their routine.
- 4. Set Boundaries: If the person is open to it, help them set limits on their chess playing. This could include setting a timer for how long they play or scheduling breaks to ensure they are not neglecting other aspects of their life.
- 5. Promote Healthy Habits: Encourage them to adopt healthier habits that can replace the time spent on chess. This could include physical exercise, meditation, or spending time with friends and family.
- 6. Seek Professional Help: If the addiction is severe and affecting their quality of life, suggest seeking help from a mental health professional. Therapy can provide strategies to manage addiction and address any underlying issues.
- 7. Support Groups: Look for support groups or online forums where they can connect with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and strategies can be helpful in overcoming addiction.
- 8. Be Patient and Supportive: Recovery from addiction can be a long process. Be patient and offer your support throughout their journey. Celebrate small victories and encourage them to keep moving
Best books about online entertainment addiction
Online entertainment addiction is a growing concern in today’s digital age, as more people find themselves spending excessive amounts of time on social media, streaming platforms, and online gaming. Several insightful books delve into this topic, offering research, personal stories, and strategies for managing or overcoming such addictions. Here are five of the best books on online entertainment addiction:
- 1. “Irresistible: The Rise of Addictive Technology and the Business of Keeping Us Hooked” by Adam Alter
– Adam Alter explores how technology companies design products to be addictive and the psychological effects of these designs on users. The book provides a comprehensive look at how digital platforms capture our attention and offers strategies for regaining control over our time and focus.
- 2. “The Shallows: What the Internet Is Doing to Our Brains” by Nicholas Carr
– In this Pulitzer Prize finalist, Nicholas Carr examines how the internet is reshaping our cognitive abilities. He argues that the constant distractions of online entertainment can lead to a decline in our ability to concentrate and think deeply. Carr’s book is a thought-provoking exploration of the long-term implications of internet addiction.
- 3. “Digital Minimalism: Choosing a Focused Life in a Noisy World” by Cal Newport
– Cal Newport advocates for a minimalist approach to technology use, encouraging readers to prioritize meaningful activities over mindless scrolling. The book provides practical advice on how to reduce dependency on digital entertainment and focus on more fulfilling pursuits.
- 4. “Glow Kids: How Screen Addiction Is Hijacking Our Kids—and How to Break the Trance” by Nicholas Kardaras
– Nicholas Kardaras focuses on the impact of screen addiction on children and adolescents. He discusses the neurological and psychological effects of excessive screen time and offers strategies for parents to help their children develop healthier relationships with technology.
- 5. “Hooked: How to Build Habit-Forming Products” by Nir Eyal
– While this book is primarily aimed at product designers and marketers
Research about online entertainment addiction
Online entertainment addiction, often referred to as internet addiction or digital addiction, has become a growing concern as digital platforms become increasingly integrated into daily life. Here are some official studies that have explored this phenomenon:
1. “Internet Addiction: A Brief Summary of Research and Practice” (2017. by Kuss, D. J., & Lopez-Fernandez, O.
– This study provides a comprehensive overview of internet addiction, focusing on its prevalence, assessment, and treatment. The authors discuss how internet addiction is characterized by excessive use of online activities, leading to negative impacts on personal, social, and occupational functioning. The study highlights the need for standardized diagnostic criteria and effective intervention strategies.
2. “Problematic Internet Use and Its Relationship to Psychological Distress: A Multinational Analysis” (2018. by Cheng, C., & Li, A. Y.
– This research examines the relationship between problematic internet use and psychological distress across different countries. The study found that excessive use of the internet is linked to increased levels of anxiety, depression, and stress. The authors emphasize the importance of cross-cultural studies to understand the global impact of internet addiction and to develop culturally sensitive interventions.
3. “The Relationship Between Social Media Addiction and Depression: A Quantitative Study” (2019. by Andreassen, C. S., et al.
– This study explores the connection between social media addiction and depression among young adults. The researchers used a large sample size to investigate how excessive engagement with social media platforms can lead to depressive symptoms. The findings suggest that social media addiction is a significant predictor of depression, highlighting the need for awareness and preventive measures.
4. “Gaming Addiction: An Overview of Its Characteristics, Assessment, and Treatment” (2020. by Pontes, H. M., & Griffiths, M. D.
– Focusing on gaming addiction, a specific form of online entertainment addiction, this study reviews the characteristics, assessment tools, and treatment options available. The authors discuss the inclusion of gaming disorder in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11. and emphasize the importance of early identification and intervention to prevent long-term consequences.
5. “The Impact of Smartphone Addiction on Academic Performance and Mental Health Among University Students” (2021. by Alhassan, A. A., et al.
– This study investigates the effects of smartphone addiction, a prevalent form of online entertainment addiction, on academic performance and mental health. The research found that excessive smartphone use negatively affects students’ academic achievements and is associated with increased levels of anxiety and depression. The authors call for educational programs to raise awareness about the risks of smartphone addiction.
These studies collectively underscore the multifaceted nature of online entertainment addiction and its significant implications for mental health and well-being. They also highlight the urgent need for further research and the development of effective strategies to address this growing issue.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.
The impact of online entertainment on our society
Online entertainment has become an integral part of modern life, offering a wide array of content and platforms that cater to diverse interests. While it provides numerous benefits, such as easy access to information, global connectivity, and a platform for creativity and expression, the rise of online entertainment addiction presents significant challenges for individuals and society as a whole. This article explores the multifaceted impact of online entertainment addiction on our society.
### Mental Health Implications
One of the most profound effects of online entertainment addiction is its impact on mental health. Excessive use of digital platforms can lead to increased levels of anxiety, depression, and stress. The constant need for validation through likes, shares, and comments can exacerbate feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem. Moreover, the addictive nature of these platforms, designed to maximize user engagement, can lead to compulsive behavior, where individuals feel compelled to stay connected at the expense of real-world interactions and responsibilities.
### Social Isolation
Paradoxically, while online entertainment platforms are designed to connect people, they can also lead to social isolation. Individuals who spend excessive amounts of time online may neglect face-to-face interactions, leading to weakened social bonds and a lack of real-world support networks. This isolation can be particularly detrimental to young people, who are in critical stages of developing social skills and emotional intelligence.
### Impact on Productivity
Online entertainment addiction can significantly impact productivity, both in educational and professional settings. Students who are addicted to online games or social media may struggle to focus on their studies, leading to poor academic performance. Similarly, employees who are unable to manage their screen time may find it challenging to concentrate on work tasks, resulting in decreased efficiency and productivity. This can have broader economic implications, affecting overall workforce performance and contributing to economic stagnation.
### Physical Health Consequences
The sedentary lifestyle associated with prolonged online entertainment consumption can lead to various physical health issues. Lack of physical activity is linked to obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and other health problems.
Additionally, excessive screen time can lead to eye strain, disrupted sleep patterns, and poor posture, further exacerbating health concerns.
### Cultural and Behavioral Shifts
Online entertainment addiction has also led to significant cultural and behavioral shifts. The constant consumption of curated and often sensationalized content can influence societal norms and values, sometimes promoting unrealistic expectations and unhealthy behaviors. Furthermore, the anonymity of online interactions can lead to a rise in cyberbullying and other negative behaviors, impacting community cohesion and trust.
### Economic Impact
The economic impact of online entertainment addiction is multifaceted. On one hand, it drives significant revenue for tech companies and content creators. On the other hand, it can lead to financial strain for individuals who spend excessively on online subscriptions, in-app purchases, and other digital content.
Additionally, the loss of productivity associated with addiction can have broader economic repercussions, affecting businesses and economies at large.
### Addressing the Issue
Addressing online entertainment addiction requires a multi-pronged approach. Education and awareness campaigns can help individuals recognize the signs of addiction and encourage healthier digital habits. Parents and educators play a crucial role in guiding young people towards balanced media consumption. Moreover, tech companies have a responsibility to create platforms that prioritize user well-being, incorporating features that promote digital wellness and limit excessive use.
In conclusion, while online entertainment offers numerous benefits, its addictive potential poses significant challenges for society. By understanding and addressing these issues, we can work towards a healthier balance between digital consumption and real-world engagement, ensuring that technology enhances rather than detracts from our quality of life.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.