Trying to quit break addiction? Welcome to our digital detox series! This series focuses on how to stop digital and screen addictions. Findall our posts about digital addictions. Today, let’s talk about how to quit the break addiction.

- What’s the break addiction?
- Addiction to break, a “real” addiction?
- What’s considered break addiction?
- How much break is too much?
- Some work and productivity addiction facts & statistics
- Symptoms & Causes of the break addiction
- Why is break so addictive?
- Possible causes of break dependency
- Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of break addiction
- Problems, impacts & bad effects of break
- Some benefits of break
- Health problems
- Impact on brain & mental health
- Impact on relationships
- How to stop & quit your break addiction
- Main steps and solutions to break the break addiction
- Best break blocker apps & functionalities
- Where to seek extra help?
- Conclusion
- To Go Further
- How to help someone with break addiction
- Best books about work and productivity addiction
- Research about work and productivity addiction
What is the break addiction?
About break
A “break” is a pause or interruption in an activity, allowing rest or change. It can refer to a short rest period during work, a fracture in a physical object, or a gap in continuity, offering a chance to recharge or reassess.
Addiction to break, a “real” addiction?
Officially an addiction?
First, let’s have a look at the DSM-5,the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Does it include break addiction?
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5., is a comprehensive classification system used by mental health professionals to diagnose mental disorders. As of my last update, “break addiction” is not specifically listed in the DSM-5. The DSM-5 includes categories for substance-related and addictive disorders, such as alcohol use disorder, opioid use disorder, and gambling disorder, among others.
If “break addiction” refers to a specific behavior or substance not explicitly covered by these categories, it might not be recognized as a distinct disorder in the DSM-5. However, the manual does acknowledge that other behavioral addictions may exist and could be considered for inclusion in future editions as more research becomes available.
For any concerns about addiction or related behaviors, it’s essential to consult a qualified mental health professional who can provide guidance and support based on the most current clinical standards and research.
So what does “break addiction” mean?
Breaking Addiction: A Friendly Guide to Regaining Control
Addiction can feel overwhelming, but breaking free is entirely possible! Whether it’s substance use, habits, or behaviors that have taken hold, understanding what addiction is and how to overcome it is the first step toward a healthier, happier you.
What Is Addiction?
Addiction is when you become dependent on something, whether it’s alcohol, drugs, gaming, or even certain habits like overeating. It often starts slowly but can take over your life, making it hard to stop despite wanting to.
Steps to Break Addiction:
- 1. Acknowledge the Problem: Admitting that you have an addiction is crucial. It’s okay to seek help—you’re not alone
!
- 2. Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or a professional counselor. Support groups can also provide encouragement and understanding.
- 3. Set Clear Goals: Decide what you want to achieve, like reducing use or quitting entirely. Clear goals help keep you focused.
- 4. Develop Healthy Habits: Replace addictive behaviors with positive activities, such as exercising, reading, or hobbies you enjoy.
- 5. Manage Triggers: Identify what leads you to the addictive behavior and find ways to avoid or cope with these triggers.
- 6. Stay Persistent: Breaking addiction takes time and effort. Celebrate small victories and don’t get discouraged by setbacks.
Remember: Everyone’s journey is unique. What works for one person might not work for another, so it’s important to find the strategies that suit you best. Reach out, stay committed, and take it one day at a time. You have the strength to overcome addiction and build a brighter future!
What is considered break addiction?
Diagnosing a behavioral addiction, such as a break addiction, involves identifying patterns and symptoms that indicate a person is excessively dependent on taking breaks to the detriment of their daily responsibilities and overall well-being. While “break addiction” is not a formally recognized medical condition, the concept can be assessed using criteria similar to those used for other behavioral addictions. Here are some potential criteria to consider:
- 1. Preoccupation: The individual spends a significant amount of time thinking about or planning their next break, even when engaged in other activities.
- 2. Loss of Control: The person finds it difficult to limit the duration or frequency of their breaks, often taking longer or more frequent breaks than intended.
- 3. Tolerance: Over time, the individual needs to take longer or more frequent breaks to achieve the same level of satisfaction or relief.
- 4. Withdrawal Symptoms: When unable to take breaks, the person experiences negative emotions such as irritability, anxiety, or restlessness.
- 5. Neglect of Responsibilities: The addiction interferes with the person’s ability to fulfill work, academic, or personal obligations, leading to negative consequences.
- 6. Continued Use Despite Problems: The individual continues to take excessive breaks despite being aware of the negative impact on their life, such as decreased productivity or strained relationships.
- 7. Deception: The person may lie to others about the amount of time they spend on breaks or conceal the extent of their behavior.
- 8. Escape: Breaks are used as a way to escape from stress, anxiety, or other negative emotions, rather than as a means of genuine relaxation or rejuvenation.
- 9. Loss of Interest: The individual loses interest in other activities or hobbies that they previously enjoyed, preferring to spend time taking breaks instead.
- 10. Failed Attempts to Cut Down: The person has made unsuccessful attempts to reduce the frequency or duration of their breaks.
If someone is concerned about a potential break addiction, it may be beneficial to seek guidance from a mental health professional who can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend appropriate interventions.
How much break is too much?
The amount of time spent on breaks can vary depending on the context, such as the nature of the work, the specific workplace policies, and individual needs. However, there are some general guidelines and considerations to help determine when break time might become excessive:
- 1. Workplace Policies: Most workplaces have established guidelines for breaks. For example, in many countries, labor laws mandate a certain amount of break time for specific hours worked. In the U.S., a common standard is a 15-minute break for every four hours worked, plus a longer meal break for shifts longer than six hours.
- 2. Nature of Work: The type of work can influence how much break time is appropriate. Physically demanding jobs may require more frequent short breaks to prevent fatigue and injury, while mentally intensive tasks might benefit from periodic breaks to maintain focus and productivity.
- 3. Productivity: If break time starts to interfere with productivity or the ability to meet work deadlines, it might be considered excessive. The key is finding a balance where breaks enhance, rather than hinder, overall work performance.
- 4. Personal Well-being: Breaks are essential for mental and physical health. If you find that you need longer breaks to maintain your well-being, it might be worth discussing with a supervisor or HR representative to find a solution that accommodates your needs without disrupting work.
- 5. Social Norms and Culture: Workplace culture can also dictate what is considered acceptable. In some environments, longer breaks might be the norm, while in others, strict adherence to break schedules is expected.
- 6. Signs of Excessive Breaks: If breaks are being used to avoid work, leading to procrastination, or if they are significantly longer than those taken by peers without justification, it might be a sign that break time is excessive.
Ultimately, the goal of breaks is to recharge and enhance productivity. If they are achieving this without negatively impacting work responsibilities or team dynamics, the amount of break time is likely appropriate. Regularly assessing how breaks affect your work and well-being can help ensure they remain beneficial.
Some work and productivity addiction facts & statistics

Work and productivity addiction, often referred to as “workaholism,” is a growing concern in modern society, particularly in cultures that highly value productivity and achievement. While comprehensive statistics can be challenging to pinpoint due to varying definitions and methodologies, several studies and surveys provide insight into the prevalence and impact of this phenomenon.
### Prevalence of Work Addiction
- 1. General Prevalence:
– Estimates suggest that between 5% to 10% of the workforce in developed countries may be classified as workaholics, although this can vary significantly depending on the criteria used.
- 2. Demographic Variations:
– Work addiction can affect individuals across different demographics, but some studies indicate that it is more prevalent among certain groups, such as middle-aged professionals, high achievers, and those in managerial or executive positions.
- 3. Industry-Specific Trends:
– Certain industries, such as finance, law, and technology, tend to have higher rates of work addiction due to their demanding nature and cultural expectations of long working hours.
### Impact on Health and Well-being
- 1. Physical Health:
– Work addiction is associated with various health issues, including cardiovascular problems, sleep disorders, and a weakened immune system. Chronic stress from overwork can exacerbate these conditions.
- 2. Mental Health:
– Individuals with work addiction are more likely to experience anxiety, depression, and burnout. The constant pressure to perform can lead to significant mental health challenges.
- 3. Social and Family Life:
– Workaholics often struggle with maintaining healthy relationships, as their work commitments can lead to neglect of family and social responsibilities. This can result in marital problems and strained family dynamics.
### Economic and Organizational Impact
- 1. Productivity Paradox:
– While workaholics may initially contribute to higher productivity, over time, the negative effects of burnout and decreased mental health can lead to reduced efficiency and increased absenteeism.
- 2. Turnover and Retention:
– Organizations with cultures that inadvertently promote workaholism may face higher turnover rates, as employees eventually seek healthier work environments.
- 3. Healthcare Costs:
– The health issues associated with work addiction can lead to increased healthcare costs for both individuals and employers, due to the need for medical treatment and mental health support.
### Addressing Work Addiction
- 1. Organizational Strategies:
– Companies can implement policies that promote work-life balance, such as flexible working hours, remote work options, and encouraging regular breaks.
- 2. Individual Interventions:
– Therapy and counseling can be effective for individuals struggling with work addiction. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and stress management techniques are commonly used approaches.
- 3. Cultural Shifts:
– Broader cultural changes that value quality over quantity of work, and recognize the importance of mental health, are essential in addressing the root causes of work addiction.
### Conclusion
Work and productivity addiction is a multifaceted issue with significant implications for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. Understanding its prevalence and impact is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its negative effects and promote healthier work environments. Continued research and awareness are key to addressing this modern challenge.
Is the break addiction widespread?
It seems like there might be a misunderstanding in your question. If you’re referring to a specific substance or activity called “break,” it might not be widely recognized or documented, which could explain the lack of available information on addiction related to it.
However, if you’re talking about addiction in general, it’s a significant issue worldwide, affecting millions of people. Addictions can range from substances like alcohol, nicotine, and drugs to behaviors such as gambling, gaming, and internet use. Each type of addiction has its own set of challenges and requires different approaches for treatment and recovery.
If you meant something else by “break,” please provide more context or clarify your question, and We’d be happy to help!
Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of break addiction
Why is break so addictive?
Hey there! Great question: Why is taking a break so addictive?
Taking breaks can feel incredibly rewarding for several reasons:
- 1. Rest and Recharge: Our brains and bodies need downtime to recover. When you take a break, you allow yourself to relax and recharge, which feels good and makes you want more of that relief.
- 2. Dopamine Boost: Taking a break can trigger the release of dopamine, the “feel-good” neurotransmitter. This makes the experience pleasurable, encouraging you to seek more breaks to feel that same happiness.
- 3. Stress Relief: Breaks help reduce stress levels. Stepping away from tasks or responsibilities can lower anxiety and create a sense of calm, making you crave that peace again and again.
- 4. Mental Reset: Breaks allow your mind to reset and refresh. After pausing, you often return to tasks with improved focus and creativity, making the break feel like a valuable reset button.
- 5. Habit Formation: Regularly taking breaks can become a positive habit. As you experience the benefits consistently, your brain starts to crave that rewarding pause in your routine.
- 6. Social Interaction: Sometimes, breaks involve chatting with friends or colleagues, which can be enjoyable and something to look forward to, adding a social element to the addictive nature of breaks.
So, breaks are addictive because they make us feel good, reduce stress, improve our performance, and can even add a social spark to our day. Just remember to balance your breaks with your tasks to stay productive and happy!
Possible causes of break dependency
Breaking an addiction is a complex process influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors can help individuals and professionals develop effective strategies for overcoming addiction. Here are some of the primary causes that can facilitate breaking an addiction:
- 1. Awareness and Acknowledgment: Realizing and admitting that there is a problem is the first crucial step. This awareness often comes from personal reflection, feedback from loved ones, or negative consequences experienced due to the addiction.
- 2. Motivation for Change: A strong personal desire to change is essential. This motivation can stem from various sources, such as health concerns, the desire to improve relationships, or the pursuit of personal goals and aspirations.
- 3. Support Systems: Having a robust support network, including family, friends, or support groups, can provide encouragement, accountability, and emotional support. Professional help from therapists or counselors can also be invaluable.
- 4. Access to Treatment: Effective treatment options, such as therapy, counseling, medication, or rehabilitation programs, can provide the necessary tools and strategies to manage withdrawal symptoms and address underlying issues.
- 5. Coping Mechanisms: Developing healthy coping strategies to deal with stress, anxiety, or triggers that may lead to relapse is vital. This can include mindfulness, exercise, or engaging in new hobbies.
- 6. Education and Awareness: Understanding the nature of addiction and its impact on the brain and behavior can empower individuals to make informed decisions and recognize the importance of maintaining sobriety.
- 7. Environmental Changes: Altering one’s environment to reduce exposure to triggers or situations that encourage addictive behavior can be beneficial. This might involve changing social circles or avoiding certain places.
- 8. Personal Growth and Self-Esteem: Building self-esteem and focusing on personal growth can help individuals see themselves beyond their addiction and work towards a healthier lifestyle.
- 9. Setting Realistic Goals: Establishing clear, achievable goals for recovery can provide direction and motivation. Celebrating small victories along the way can boost confidence and commitment.
- 10. Spiritual or Philosophical Beliefs: For some, spiritual or philosophical beliefs can provide strength and guidance in overcoming addiction, offering a sense of purpose and connection.
Each individual’s journey to breaking an addiction is unique, and a combination of these factors often contributes to successful recovery. It’s important to approach addiction with compassion and understanding, recognizing that it is a chronic condition that requires ongoing effort and support.
Signs & Symptoms of break addiction
Now let’s see if you have the break addiction problem.
In today’s fast-paced world, the concept of taking a break often carries a positive connotation, associated with self-care and maintaining a healthy work-life balance. However, like anything in excess, taking too many breaks can become counterproductive. Here are seven signs you might be a break addict:
- 1. Procrastination Disguised as Breaks: If you find yourself constantly delaying tasks under the guise of needing a break, it might be a sign of avoidance rather than rest. Break addicts often use breaks as a way to procrastinate, pushing off responsibilities indefinitely.
- 2. Frequent Breaks Without Productivity: While breaks are meant to recharge you, if you notice that you’re taking frequent breaks without any increase in productivity or focus, it might indicate that the breaks are not serving their intended purpose.
- 3. Feeling Guilty Yet Unable to Stop: A classic sign of any addiction is the feeling of guilt associated with the behavior. If you feel guilty about the number of breaks you take but find it difficult to reduce them, it might be time to reassess your habits.
- 4. Breaks Become Longer Over Time: Initially, your breaks might have been short and refreshing, but over time, they have become longer and more frequent. This gradual increase in break time can be a sign that you’re relying too heavily on them.
- 5. Disruption of Routine: If your breaks are disrupting your daily routine or causing you to miss deadlines, it’s a clear indication that they are no longer beneficial. Breaks should enhance your routine, not hinder it.
- 6. Lack of Satisfaction Post-Break: Ideally, you should feel refreshed and ready to tackle tasks after a break. If you find that you’re still feeling tired or unmotivated after a break, it might be a sign that your breaks are more of a habit than a necessity.
- 7. Neglecting Responsibilities: When breaks start to interfere with your ability to fulfill responsibilities, whether at work or in personal life, it’s a red flag. Breaks should not come at the expense of your obligations.
If you recognize these signs in yourself, it might be worth evaluating your break-taking habits. Consider setting specific times for breaks, using them mindfully, and ensuring they serve the purpose of enhancing your productivity and well-being. Balancing work and rest is key to maintaining a healthy, productive lifestyle.
Try our digital habit & screen addiction test:
Problems, impacts & bad effects of break: should you quit?

What are some benefits of break
Taking breaks, whether from work, study, or any other activity, is essential for maintaining overall well-being and productivity. Here are some of the key pros and advantages of taking breaks:
- 1. Improved Productivity: Regular breaks can help prevent burnout and maintain high levels of productivity. Short pauses allow the brain to rest, leading to better focus and efficiency when you return to the task.
- 2. Enhanced Creativity: Stepping away from a problem or task can lead to fresh perspectives and creative solutions. Breaks provide the mental space needed for ideas to incubate and develop.
- 3. Mental Health Benefits: Breaks can reduce stress and anxiety, providing a mental reset. They offer an opportunity to engage in activities that promote relaxation and well-being, such as meditation or a walk in nature.
- 4. Physical Health: For those with sedentary jobs, breaks encourage movement, which is crucial for physical health. Stretching or walking during breaks can reduce the risk of musculoskeletal issues and improve circulation.
- 5. Better Focus and Concentration: Continuous work can lead to mental fatigue, reducing the ability to concentrate. Regular breaks help maintain attention and prevent the decline in performance that comes with prolonged focus.
- 6. Improved Learning and Memory: Breaks are essential for consolidating learning and memory. They allow the brain to process and store information more effectively, enhancing retention and understanding.
- 7. Increased Job Satisfaction: Taking breaks can lead to higher job satisfaction by preventing burnout and promoting a healthier work-life balance. Employees who take breaks are often more engaged and motivated.
- 8. Social Interaction: Breaks provide opportunities for social interaction, which can improve mood and foster a sense of community and teamwork in the workplace.
- 9. Reduced Mistakes: Fatigue can lead to errors and accidents. Regular breaks help maintain alertness and accuracy, reducing the likelihood of mistakes.
- 10. Encouragement of Healthy Habits: Breaks can be a time to practice healthy habits, such as drinking water, eating nutritious snacks, or practicing mindfulness, contributing to overall well-being.
Incorporating regular breaks into your routine is a simple yet effective strategy to enhance both personal and professional life. By recognizing the importance of breaks, individuals can achieve a more balanced and fulfilling lifestyle.But on the other hand, what are some break addiction problems that addicts suffer from?
General health problems
Taking breaks is an essential aspect of maintaining both physical and mental health. In today’s fast-paced world, people often overlook the importance of stepping away from their tasks, whether it’s work, studying, or other responsibilities. Here’s a detailed look at the effects of taking breaks on your health:
### Physical Health Benefits
- 1. Reduced Risk of Injury: For those engaged in repetitive tasks or prolonged physical activity, taking breaks can reduce the risk of strain injuries. This is particularly important for jobs involving manual labor or extensive computer use, where repetitive strain injuries (RSI) are common.
- 2. Improved Posture: Regular breaks encourage individuals to change their posture, reducing the risk of developing musculoskeletal problems such as back pain and neck strain.
- 3. Eye Health: For individuals who spend long hours in front of screens, breaks can prevent eye strain and reduce the risk of computer vision syndrome. The 20-20-20 rule (looking at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes) is often recommended.
- 4. Better Circulation: Taking breaks to stand up and move around can improve blood circulation, reducing the risk of conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and promoting overall cardiovascular health.
### Mental Health Benefits
- 1. Stress Reduction: Breaks provide an opportunity to step back from stressful tasks, allowing the mind to relax and reset. This can lead to reduced stress levels and a lower risk of stress-related health issues.
- 2. Improved Focus and Productivity: Short breaks can enhance concentration and productivity. The brain can only focus intensely for a limited period, and breaks help to refresh mental resources, leading to better performance.
- 3. Enhanced Creativity: Stepping away from a problem or task can lead to new perspectives and creative solutions. Breaks provide the mental space needed for creative thinking and problem-solving.
- 4. Emotional Well-being: Regular breaks can improve mood and overall emotional well-being. They provide time to engage in activities that bring joy, such as walking, meditating, or chatting with friends.
### Cognitive Benefits
- 1. Memory Consolidation: Breaks, especially those involving physical activity or relaxation, can aid in memory consolidation, helping to retain and recall information more effectively.
- 2. Decision Making: A rested mind is better at making decisions. Breaks can lead to clearer thinking and more rational decision-making processes.
### Tips for Effective Breaks
– Schedule Regular Breaks: Use techniques like the Pomodoro Technique, which involves 25 minutes of focused work followed by a 5-minute break.
– Incorporate Movement: Stand up, stretch, or take a short walk to boost circulation and refresh the mind.
– Mindfulness and Relaxation: Practice deep breathing, meditation, or mindfulness exercises to reduce stress and enhance focus.
– Limit Screen Time: Use breaks to rest your eyes and reduce screen exposure, especially if your work involves long hours on digital devices.
– Engage in Enjoyable Activities: Use breaks as an opportunity to do something you enjoy, which can boost mood and motivation.
In conclusion, taking regular breaks is not just a luxury but a necessity for maintaining optimal physical, mental, and cognitive health. By integrating breaks into your daily routine, you can enhance your overall well-being and performance in various aspects of life.
break and sleep disorders
Yes, experiencing a breakup can potentially lead to sleep disorders or sleep problems. The end of a relationship often comes with a significant emotional impact, which can manifest in various ways, including disruptions in sleep. Here are some ways a breakup might affect sleep:
- 1. Stress and Anxiety: The emotional turmoil following a breakup can lead to increased stress and anxiety levels. This heightened state of arousal can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, as your mind may be racing with thoughts about the relationship and its end.
- 2. Depression: Breakups can sometimes trigger depressive episodes, characterized by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in activities once enjoyed. Depression is closely linked with sleep disturbances, including insomnia or, conversely, oversleeping.
- 3. Changes in Routine: A breakup often leads to changes in daily routines, which can disrupt sleep patterns. For example, if you previously shared a bedtime routine with your partner, adjusting to a new routine can be challenging and affect your sleep quality.
- 4. Loneliness and Isolation: The absence of a partner can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can contribute to difficulties in falling asleep or staying asleep. The lack of emotional support may exacerbate these feelings, further impacting sleep.
- 5. Rumination: After a breakup, individuals may find themselves ruminating over the relationship, replaying events, or questioning their actions. This mental activity can be particularly prevalent at night when there are fewer distractions, making it harder to relax and fall asleep.
- 6. Physical Symptoms: Emotional distress can also manifest physically, leading to symptoms such as headaches, muscle tension, or gastrointestinal issues, which can interfere with sleep.
To mitigate these sleep disturbances, individuals can try several strategies:
– Establish a Routine: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can help regulate your body’s internal clock and improve sleep quality.
– Create a Relaxing Environment: Ensure your sleeping environment is conducive to rest by keeping it dark, quiet, and cool.
– Practice Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep.
– Limit Stimulants: Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and heavy meals close to bedtime, as these can interfere with your ability to fall asleep.
– Seek Support: Talking to friends, family, or a mental health professional can provide emotional support and help you process your feelings.
If sleep problems persist, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare provider to explore further interventions.
break affecting your brain & mental health: bad for brain and mental health?
Some effects of break on your brain
Hey there, friend! 🌟
Taking breaks is super important for staying fresh and avoiding burnout, but did you know that too many—or poorly timed—breaks can actually have some not-so-great effects on your brain? Let’s dive into a few potential downsides:
###
- 1. Loss of Focus
When you take frequent breaks, it can be tough to maintain your concentration. Each time you step away, your brain has to work a bit harder to get back into the groove, which might slow you down.
###
- 2. Reduced Productivity
Believe it or not, too many breaks can sometimes lead to less getting done. Constantly switching between work and break times can interrupt your workflow, making it harder to complete tasks efficiently.
###
- 3. Difficulty Re-engaging
After a break, especially a long one, your brain might struggle to re-engage with what you were doing. This can make tasks feel more daunting and increase the time it takes to get back on track.
###
- 4. Memory Interruption
If you’re learning something new, taking breaks too frequently might interfere with how well you remember the information. Your brain needs time to process and consolidate what you’ve just learned.
###
- 5. Breaks Becoming Distractions
Sometimes, what starts as a quick rest can turn into a full-on distraction. Scrolling through social media or getting sidetracked by other activities during breaks can eat up more time than you intended.
###
- 6. Decreased Motivation
Overusing breaks might lead to a drop in motivation. If you’re constantly waiting for your next break, it can be harder to stay driven to complete your current task.
### Finding the Right Balance
The key is moderation! Short, intentional breaks can boost your brain’s performance, but it’s important to find a balance that keeps you productive without feeling overwhelmed. Try setting a schedule, like the popular Pomodoro Technique (25 minutes of work followed by a 5-minute break), to keep things in check.
Remember, everyone’s brain is different, so experiment to find what works best for you. Happy balancing!
Some effects of break on your mental health
Taking a break is often recommended as a way to recharge and improve mental health. However, if not managed properly, breaks can have unintended negative effects. Here are some potential downsides:
- 1. Disruption of Routine: A break can disrupt established routines, leading to feelings of disorganization or chaos. This can be particularly challenging for individuals who thrive on structure and consistency.
- 2. Increased Anxiety: For some, taking a break can lead to increased anxiety, especially if it involves stepping away from responsibilities or tasks that are piling up. The thought of returning to a backlog of work can be overwhelming.
- 3. Guilt and Self-Criticism: People who are highly driven or have perfectionist tendencies might feel guilty about taking time off, viewing it as unproductive or lazy. This self-criticism can negate the benefits of the break.
- 4. Isolation: If a break involves stepping away from social interactions, it can lead to feelings of isolation or loneliness, especially if the individual does not have a supportive network to engage with during their time off.
- 5. Loss of Motivation: While breaks are meant to rejuvenate, extended time away can sometimes lead to a loss of momentum or motivation, making it difficult to re-engage with tasks or projects.
- 6. Depression and Mood Swings: For some, the lack of daily structure and purpose during a break can exacerbate symptoms of depression or lead to mood swings.
- 7. Financial Stress: If a break involves taking unpaid leave, it can lead to financial stress, which can have a significant impact on mental well-being.
- 8. Overthinking: With more free time, some individuals might find themselves overthinking or ruminating on problems, which can increase stress and anxiety levels.
- 9. Social Pressure: There can be societal or peer pressure to be constantly productive, which can make individuals feel inadequate or pressured to justify their need for a break.
- 10. Difficulty Reintegrating: After a break, some people may struggle to reintegrate into their previous routines or work environments, leading to stress and decreased performance.
To mitigate these potential negative effects, it’s important to plan breaks mindfully, set clear boundaries, and maintain some level of routine or activity. Engaging in activities that are genuinely restorative and maintaining social connections can also help ensure that breaks have a positive impact on mental health.
Does break cause stress and anxiety?
Breaks are generally intended to provide relief and relaxation, offering a pause from work or stressful situations. However, they can sometimes cause stress or anxiety for certain individuals, depending on the circumstances. Here are some reasons why breaks might lead to stress or anxiety:
- 1. Fear of Falling Behind: For individuals with heavy workloads or tight deadlines, taking a break might induce anxiety about falling behind on tasks. The pressure to meet expectations can overshadow the benefits of taking a break.
- 2. Guilt: Some people feel guilty about taking time off, especially if they perceive their peers or colleagues as working harder or longer. This guilt can lead to stress and diminish the restorative effects of a break.
- 3. Difficulty Disconnecting: In today’s hyper-connected world, it can be challenging to fully disconnect from work or responsibilities. The inability to mentally detach during a break can prevent relaxation and increase anxiety.
- 4. Unstructured Time: For individuals who thrive on routine and structure, unstructured time during a break can be unsettling. The lack of a plan or purpose can lead to feelings of restlessness or anxiety.
- 5. Anticipation of Returning to Stressors: Knowing that a break is temporary and that stressors will still be present upon return can cause anxiety. The anticipation of facing unresolved issues can overshadow the enjoyment of the break.
- 6. Financial Concerns: For those who are self-employed or whose income is affected by taking time off, breaks can lead to financial stress. The worry about lost income can negate the benefits of relaxation.
To mitigate these feelings, individuals can try to plan breaks more effectively, ensuring they are truly restorative. Setting clear boundaries, practicing mindfulness, and scheduling breaks in a way that aligns with personal and professional responsibilities can help reduce the potential for stress and anxiety.
Can break addiction lead to sadness and depression?

Breaking an addiction is a complex and challenging process that can indeed lead to feelings of sadness and depression. Understanding why this happens involves examining both the physiological and psychological aspects of addiction and recovery.
### Physiological Factors
- 1. Neurochemical Changes: Addictive substances often alter brain chemistry, particularly affecting neurotransmitters like dopamine, which is associated with pleasure and reward. When someone stops using the substance, the brain may struggle to produce these chemicals naturally, leading to a deficit that can manifest as depression.
- 2. Withdrawal Symptoms: Many substances cause withdrawal symptoms when use is reduced or stopped. These symptoms can include mood swings, irritability, and depression, which are part of the body’s physical response to the absence of the substance.
### Psychological Factors
- 1. Loss of Coping Mechanism: For many, the substance or behavior was a way to cope with stress, anxiety, or other emotional issues. Without it, individuals may feel overwhelmed by emotions they previously managed through their addiction.
- 2. Identity and Lifestyle Changes: Addiction often becomes intertwined with one’s identity and daily routine. Breaking free from it can lead to a sense of loss or emptiness, contributing to feelings of sadness or depression.
- 3. Social Isolation: Recovery may involve distancing oneself from social circles that revolve around the addictive behavior, leading to loneliness and isolation, which can exacerbate depressive symptoms.
### Emotional and Psychological Challenges
- 1. Facing Underlying Issues: Often, addiction masks deeper psychological issues such as trauma, anxiety, or depression. In recovery, these issues may surface and need to be addressed, which can be emotionally taxing.
- 2. Fear of the Unknown: The uncertainty of life without the addiction can be daunting. Concerns about maintaining sobriety, rebuilding relationships, and finding new sources of joy can contribute to anxiety and depression.
### Coping Strategies
- 1. Therapy and Counseling: Engaging in therapy can help individuals address underlying issues and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in treating depression and addiction.
- 2. Support Groups: Joining support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) can provide a sense of community and understanding, reducing feelings of isolation.
- 3. Healthy Lifestyle Changes: Incorporating exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep can help improve mood and overall well-being.
- 4. Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like mindfulness and meditation can help individuals stay grounded and manage stress and emotional upheaval.
- 5. Medical Intervention: In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage depression, especially if it is severe or persistent.
### Conclusion
While breaking an addiction can lead to feelings of sadness and depression, these emotions are often a natural part of the recovery process. It’s important for individuals to seek support and treatment to navigate these challenges effectively. With the right strategies and support systems in place, it’s possible to overcome these emotional hurdles and build a fulfilling life in recovery.
Dopamine and break
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in how we feel pleasure, think, and plan. It is often referred to as the “feel-good” chemical because it is heavily involved in the reward and pleasure centers of the brain. Understanding dopamine and its functions can provide insights into various aspects of human behavior, including the need for breaks and rest.
### The Role of Dopamine
- 1. Reward and Pleasure: Dopamine is released during pleasurable situations and stimulates feelings of enjoyment and reinforcement, which motivates a person proactively to perform certain activities.
- 2. Motivation and Goal-Setting: It is crucial for motivation and the pursuit of goals. Higher levels of dopamine can increase drive and focus, while lower levels can lead to apathy and lack of motivation.
- 3. Cognitive Functions: Dopamine is involved in various cognitive processes, including attention, memory, and problem-solving.
- 4. Mood Regulation: It plays a role in mood regulation, and imbalances can contribute to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
### The Importance of Breaks
Taking breaks is essential for maintaining optimal dopamine levels and overall mental health. Here’s how breaks can influence dopamine and well-being:
- 1. Prevention of Burnout: Continuous work without breaks can lead to burnout, characterized by mental and physical exhaustion. Breaks help prevent this by allowing the brain to rest and recover.
- 2. Enhanced Creativity and Problem-Solving: Stepping away from tasks can lead to bursts of creativity and improved problem-solving skills. This is partly because breaks can help replenish dopamine levels, enhancing cognitive functions.
- 3. Improved Focus and Productivity: Short breaks can help reset attention spans and improve focus. This can be attributed to the regulation of dopamine levels, which are crucial for maintaining attention and motivation.
- 4. Stress Reduction: Breaks can reduce stress by providing a mental reset. Lower stress levels can help maintain balanced dopamine levels, contributing to better mood and mental health.
- 5. Physical Health: Regular breaks can also benefit physical health by reducing eye strain, preventing repetitive strain injuries, and encouraging physical activity, all of which can indirectly influence dopamine levels.
### Types of Breaks
- 1. Micro-Breaks: Short, frequent breaks (5-10 minutes) can help maintain energy and focus throughout the day.
- 2. Lunch Breaks: Taking a longer break for a meal can provide a significant mental reset and help maintain energy levels.
- 3. Vacation or Extended Breaks: Longer breaks or vacations can lead to a more profound reset, helping to alleviate stress and prevent burnout.
### Conclusion
Understanding the role of dopamine in motivation, pleasure, and cognitive function highlights the importance of taking regular breaks. By allowing time for rest and recovery, individuals can maintain balanced dopamine levels, leading to improved mental health, productivity, and overall well-being. Incorporating regular breaks into daily routines is a simple yet effective strategy for enhancing both personal and professional life.
break effects on focus, productivity, attention span, academic performance…
### The Power of Taking Breaks: Boosting Focus, Productivity, and Academic Performance
Hey there! 😊 Ever feel like you’re running on empty while trying to get things done? You’re not alone. Many of us push through without taking breaks, thinking it’s the only way to stay productive. But guess what? Taking breaks can actually enhance your focus, productivity, attention span, and even academic performance. Let’s dive into how that works!
—
####
- 1. Boosting Focus
When you work for long periods without resting, your brain gets tired. This tiredness makes it harder to concentrate on tasks. Taking regular breaks gives your mind a chance to recharge. Just a short walk, stretching, or a quick chat can help you return to your work with renewed focus and clarity.
* Quick Tip: Try the Pomodoro Technique – work for 25 minutes, then take a 5-minute break. Repeat!
—
####
- 2. Increasing Productivity
It might sound counterintuitive, but stepping away from your work can actually make you more productive. Breaks prevent burnout and reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed. When you return to your tasks, you’re more energized and efficient, getting more done in less time.
* Quick Tip: Schedule your breaks just like you schedule your work. This ensures you take them and stay on track.
—
####
- 3. Enhancing Attention Span
Your attention span can wane after prolonged periods of focus. Regular breaks help maintain your attention over longer periods. By giving your brain a rest, you can sustain better concentration throughout the day, making it easier to tackle complex tasks.
* Quick Tip: Engage in activities that relax your mind during breaks, like listening to music or doing a short meditation.
—
####
- 4. Improving Academic Performance
Students, listen up! Taking breaks during study sessions can significantly improve your learning and retention. Breaks allow your brain to process information and prevent mental fatigue. This means you’ll understand and remember your study material better.
* Quick Tip: After every hour of studying, take a 10-minute break to stretch or grab a healthy snack.
—
### Final Thoughts
Taking breaks isn’t a sign of laziness; it’s a smart strategy to keep your mind sharp and your body energized. Whether you’re working, studying, or tackling daily tasks, regular breaks can lead to better focus, increased productivity, longer attention spans, and improved academic performance.
So next time you’re feeling drained, give yourself permission to step away for a bit. Your brain – and your to-do list – will thank you!
Stay productive and take care! 🌟
A word about ADHD and break
People with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) often experience unique challenges and behaviors that can affect how they interact with breaks, whether in a work, school, or personal setting. Here are some ways in which breaks might be experienced differently by individuals with ADHD:
- 1. Need for Frequent Breaks: Individuals with ADHD may benefit from more frequent breaks than their neurotypical peers. Their brains often require regular intervals of rest to maintain focus and productivity, as sustained attention can be particularly taxing.
- 2. Shorter Break Durations: While frequent breaks are beneficial, the duration may need to be shorter. Extended breaks can sometimes lead to difficulty in transitioning back to tasks, as re-engaging can be challenging.
- 3. Active Breaks: People with ADHD often benefit from active breaks that involve physical movement. Activities such as stretching, walking, or even brief exercises can help reset their focus and energy levels.
- 4. Structured Breaks: Having a clear plan or structure for breaks can be helpful. Unstructured time might lead to distractions or difficulty returning to tasks. Setting a timer or having a specific activity planned can provide the necessary boundaries.
- 5. Mindfulness and Relaxation: Incorporating mindfulness or relaxation techniques during breaks can be beneficial. Practices such as deep breathing, meditation, or even listening to calming music can help manage stress and improve focus.
- 6. Avoiding Overstimulation: During breaks, it’s important to avoid activities that might lead to overstimulation, such as excessive screen time or engaging in highly stimulating environments, which can make it harder to return to the task at hand.
- 7. Social Interaction: For some individuals with ADHD, social interaction during breaks can be energizing and refreshing. However, for others, it might be distracting, so it’s important to tailor break activities to individual preferences.
- 8. Transition Strategies: Transitioning back to work after a break can be challenging. Strategies such as setting a clear end time for breaks, using alarms, or having a small task to ease back into work can be effective.
Understanding these unique needs can help individuals with ADHD manage their time and energy more effectively, leading to improved productivity and well-being. It’s important to note that ADHD affects individuals differently, so strategies should be personalized to fit each individual’s specific needs and preferences.
Affecting your relationships
break and self-esteem
## How a Breakup Can Affect Your Self-Esteem
Going through a breakup is never easy. Whether it was mutual or unexpected, ending a relationship can leave you feeling a whirlwind of emotions. One of the areas that often take a hit during this time is your self-esteem. Let’s explore how a breakup can impact how you feel about yourself and what you can do to bounce back.
###
- 1. Feelings of Rejection
When a relationship ends, it’s natural to feel rejected. You might start questioning why it happened and if there’s something wrong with you. This feeling of not being wanted can lower your self-esteem, making you doubt your value in future relationships.
###
- 2. Doubting Your Worth
A breakup can lead you to question your worthiness of love and companionship. You might think, “Am we not good enough?” or “What did we do wrong?” These thoughts can chip away at your confidence and make you feel less deserving of happiness.
###
- 3. Loss of Confidence
Being in a relationship often involves relying on someone else’s support and reassurance. When it’s gone, you might feel uncertain about making decisions or handling situations on your own. This loss of confidence can make you feel vulnerable and insecure.
###
- 4. Negative Self-Talk
During heartache, it’s easy to fall into the trap of negative self-talk. You might criticize yourself more harshly, focusing on your flaws instead of your strengths. Phrases like “We can’t do anything right” or “We’m always going to be alone” can become a harmful habit.
###
- 5. Changes in Self-Identity
Relationships often become a significant part of our identity. After a breakup, you might struggle to figure out who you are without your partner. This confusion can lead to feelings of lost direction and a weakened sense of self-worth.
###
- 6. Time to Heal and Rebuild
While a breakup can shake your self-esteem, it also offers an opportunity to grow and rebuild. Taking time for self-care, surrounding yourself with supportive friends and family, and engaging in activities you love can help restore your confidence and sense of self.
### Moving Forward
Remember, it’s okay to feel down after a breakup. Healing takes time, and it’s important to be gentle with yourself during this period. Focus on your strengths, celebrate small victories, and gradually, your self-esteem will recover. You are worthy of love and happiness, both from others and from yourself.
break addiction leads to isolation and loneliness?
.jpg)
Breaking an addiction is a challenging and often isolating journey. While the ultimate goal is to achieve a healthier, addiction-free life, the process can sometimes lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness. Here are several reasons why this can happen:
- 1. Loss of Social Circles: Many individuals struggling with addiction find themselves surrounded by others who share similar habits. When they decide to break free from addiction, they may need to distance themselves from these social circles to avoid triggers and temptations. This can lead to a sense of isolation as they lose contact with people they once spent a significant amount of time with.
- 2. Stigma and Judgment: Despite growing awareness and understanding of addiction as a mental health issue, stigma still exists. Individuals in recovery might feel judged or misunderstood by others, leading them to withdraw and isolate themselves to avoid negative perceptions.
- 3. Emotional Vulnerability: The process of overcoming addiction often involves confronting deep-seated emotional issues and vulnerabilities. This can be an intensely personal journey, and some may choose to isolate themselves as they work through these emotions, fearing that others might not understand or support them.
- 4. Fear of Relapse: The fear of relapse can be a constant companion for those in recovery. This fear might lead individuals to avoid social situations or environments where they feel vulnerable to falling back into old habits, further contributing to feelings of loneliness.
- 5. Lack of Support: Not everyone has access to a strong support system. Without friends, family, or professional support, individuals may feel alone in their journey, increasing the sense of isolation.
- 6. Identity Crisis: Addiction can become a significant part of an individual’s identity. Breaking free from it might lead to an identity crisis, where individuals struggle to redefine themselves without the addiction. This can be a lonely process as they navigate their new sense of self.
To combat these feelings of isolation and loneliness, it’s crucial for individuals in recovery to seek out supportive communities, whether through support groups, therapy, or new social circles that encourage healthy habits. Building a strong support network can provide the encouragement and understanding needed to successfully navigate the challenges of recovery.
Additionally, engaging in activities that promote well-being, such as exercise, hobbies, or volunteering, can help individuals connect with others and reduce feelings of loneliness.
Effects of break on your relationships
Taking a break in a relationship can be a complex decision, and its effects can vary significantly depending on the circumstances and how both parties handle the situation. Here are some potential positive and negative effects of taking a break in a relationship:
### Positive Effects
- 1. Personal Growth:
– A break can provide individuals with the time and space needed for self-reflection and personal growth. This can lead to a better understanding of one’s own needs, desires, and goals, which can ultimately strengthen the relationship if both parties choose to reunite.
- 2. Clarity and Perspective:
– Time apart can offer clarity about the relationship’s dynamics and whether it truly meets the needs of both individuals. It can help partners assess their feelings and the relationship’s future objectively.
- 3. Reduced Tension:
– A temporary separation can alleviate immediate stress and tension, allowing both partners to cool down and address issues more calmly and rationally when they reconvene.
- 4. Rekindling Appreciation:
– Absence can make the heart grow fonder. Time apart might lead to a renewed appreciation for each other and the relationship, highlighting the positive aspects that may have been taken for granted.
- 5. Improved Communication:
– A break can serve as a reset button, encouraging partners to communicate more effectively and openly about their needs and expectations when they come back together.
### Negative Effects
- 1. Emotional Distress:
– Taking a break can cause significant emotional distress, including feelings of uncertainty, anxiety, and loneliness. This can be particularly challenging if one partner is more invested in the relationship than the other.
- 2. Miscommunication:
– If the terms of the break are not clearly defined, it can lead to misunderstandings and miscommunication about the status of the relationship and what is permissible during the break.
- 3. Drifting Apart:
– Time apart can sometimes lead to partners growing apart rather than closer. Without regular interaction, emotional connections may weaken, making it difficult to rekindle the relationship.
- 4. Jealousy and Insecurity:
– The uncertainty of a break can lead to feelings of jealousy and insecurity, especially if one partner is concerned about the other meeting someone new or losing interest.
- 5. Potential for Permanent Separation:
– A break might highlight irreconcilable differences, leading to the realization that the relationship is not salvageable. This can result in a permanent separation, which might not have been the initial intention.
### Conclusion
Taking a break in a relationship is a decision that should be approached with careful consideration and clear communication. It’s important for both partners to discuss and agree on the terms of the break, including its duration and boundaries. Whether a break leads to a stronger relationship or a permanent separation depends largely on the individuals involved and their commitment to addressing the underlying issues.
How To Stop & Quit Your break Addiction
Finally, you think you are addicted to break and you are wondering how to quit it? How to break and overcome your cravings for break?
Here are the best solutions, steps, supports, resources, and help you can get to treat your break addiction.
Main steps and solutions to break the break addiction
Breaking an addiction is a challenging journey that requires commitment, support, and a structured approach. Here are the main steps to consider when attempting to overcome an addiction:
- 1. Acknowledgment and Acceptance:
– Recognize that you have an addiction and understand the impact it has on your life. Acceptance is the first step towards change.
- 2. Seek Professional Help:
– Consult with healthcare professionals who specialize in addiction. This may include doctors, therapists, or counselors who can provide guidance and support.
- 3. Set Clear Goals:
– Define specific, achievable goals for overcoming your addiction. These goals should be realistic and measurable to help track progress.
- 4. Develop a Support System:
– Surround yourself with supportive friends, family, or support groups. Sharing your journey with others can provide encouragement and accountability.
- 5. Identify Triggers:
– Understand the situations, emotions, or environments that trigger your addictive behavior. Developing awareness of these triggers is crucial for avoiding them.
- 6. Create a Plan:
– Develop a structured plan to replace addictive behaviors with healthier alternatives. This may involve new hobbies, exercise, or other positive activities.
- 7. Consider Behavioral Therapy:
– Engage in cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or other therapeutic approaches that focus on changing thought patterns and behaviors related to addiction.
- 8. Explore Medication Options:
– In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage withdrawal symptoms or reduce cravings. Consult with a healthcare provider for advice.
- 9. Practice Mindfulness and Stress Management:
– Incorporate mindfulness practices, such as meditation or yoga, to manage stress and maintain focus on recovery.
- 10. Monitor Progress and Adjust:
– Regularly assess your progress and be open to adjusting your strategies as needed. Celebrate small victories to maintain motivation.
- 11. Prepare for Relapse:
– Understand that relapse can be part of the recovery process. Have a plan in place to address setbacks and continue moving forward.
- 12. Commit to Long-term Recovery:
– Recovery is an ongoing process. Continue to engage in supportive activities and seek help when needed to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Breaking an addiction is a personal journey that varies for each individual. It’s important to approach it with patience and persistence, utilizing available resources and support systems to achieve lasting change.Actually, that’s what most documentation out there is about… However, quitting a digital addiction can be a bit trickier than that.
So our team, after testing many ways, designed a bulletproof way to overcome them. Here are some clear and practical steps that are very powerful to quit a digital addiction, including break:
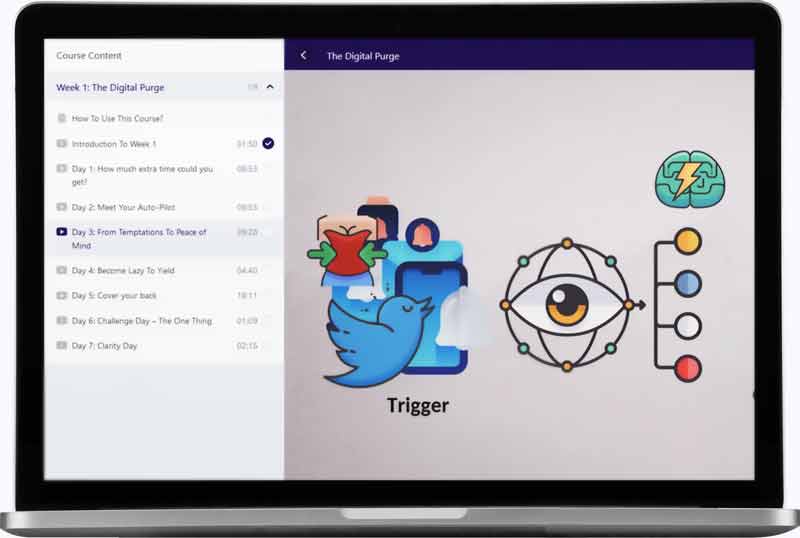
1. Purge temptations: Get rid of break
First, cleaning your life from temptations is much easier than resisting them. Disable or delete your break accounts, change the password and hide it somewhere you can’t access easily, keep your phone / computer far away… Out of sight, out of mind.
Here is a video from our course The Digital Purge. on how to add resistance to your temptations, so you become so lazy to engage with them that you give them up:
2. Spot & Reveal your emotional triggers
Second, there are some reasons, often hidden ones, that your brain and your heart love so much break. Those reasons act as triggers to pull your cravings. Rather than chasing the addiction, it’s a more efficient strategy to look at the feelings driving you toward it. That way you can cure and heal the feeling. You’ll feel better, and the cravings will magically disappear. Just get away.
3. Rewire to life

An addiction FOMO (fear of missing out) can be huge and really painful to resist, especially if it was here for a long time. However, learning to live with it is necessary to build a life full of peace and joy. Strategies to fight FOMO and rewire to life include meditation, nature activities, social interaction, intellectual and creative projects, meaningful adventures… basically anything that fills your soul.
4. How to not relapse and fully recover from break?
Finally, it’s important to acknowledge that quitting may take days, weeks, months, or even years. Getting over and quitting break forever can be difficult. You may relapse a few times, but the most important thing is that you keep engaging less and less with break. Each day you resist it is a day weakening your brain connections with break. From your patience and discipline will arise incredible mind strength, hope, and wisdom.

Best break blocker apps & functionalities
Additionally, you can increase your chance of withdrawal by limiting or blocking access to break using these apps.
They will help you filter, reduce, or block break:
In today’s digital age, maintaining focus and productivity can be challenging due to the myriad of distractions available at our fingertips. Whether it’s social media, games, or other non-work-related apps, these distractions can significantly impact your ability to concentrate on tasks. Fortunately, there are several apps designed to help limit or block access to these distractions, thereby enhancing productivity. Here are five of the best apps for this purpose:
- 1. Freedom
Freedom is a popular app that helps users block distracting websites and apps across all devices. It allows you to create custom blocklists and schedule sessions to ensure you stay focused during work hours. One of its standout features is the ability to block the entire internet if necessary, ensuring that you remain undistracted. Freedom is available on Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android.
- 2. Cold Turkey
Cold Turkey is a powerful app for blocking distractions on your computer. It offers a range of features, including the ability to block specific websites, applications, or even the entire internet. With its “Frozen Turkey” feature, you can lock yourself out of your computer for a set period, ensuring you can’t disable the app to access distractions. Cold Turkey is available for Windows and Mac.
- 3. Focus
@Will
Focus@Will takes a different approach by using music to enhance concentration. This app provides specially curated music tracks designed to improve focus and productivity. By listening to these tracks, users can enter a state of flow, reducing the likelihood of succumbing to distractions. It’s available on both desktop and mobile platforms.
- 4. StayFocusd
StayFocusd is a Google Chrome extension that helps users limit the amount of time spent on distracting websites. You can set time limits for specific sites, and once the limit is reached, the sites become inaccessible for the rest of the day. It’s a simple yet effective tool for those who primarily work within the Chrome browser.
- 5. RescueTime
RescueTimeCheck our full work and productivity addiction tool list (ranked):
Where to seek extra help?
Do you need some support and help to stop, overcome, and recover from your break addiction? If you or someone you know is struggling with break addiction, there are a few places to seek help.
The Ultimate Rewiring Program For break Addicts
Our course The Digital Purge. This course has already helped many digital addicts to rewire to what matters.
Is there a “treatment” to cure work and productivity addiction?
Absolutely, there are effective ways to address work and productivity addiction! If you find yourself constantly working, struggling to take breaks, or feeling anxious when not being productive, you’re not alone. Here are some treatments and strategies that can help:
###
- 1. Therapy and Counseling
– Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This helps you identify and change negative thought patterns related to work.
– Talk Therapy: Speaking with a counselor can provide support and strategies to manage your work habits.
###
- 2. Setting Boundaries
– Define Work Hours: Stick to specific times for work and leisure to create a healthy balance.
– Learn to Say No: It’s okay to decline extra tasks if they overwhelm you.
###
- 3. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
– Meditation: Incorporate mindfulness practices to reduce stress and increase self-awareness.
– Deep Breathing: Simple exercises can help calm your mind during hectic days.
###
- 4. Developing Hobbies and Interests
– Explore New Activities: Engage in activities outside of work to diversify your interests and reduce dependency on productivity.
– Reconnect with Passions: Rediscover what you love doing that isn’t related to your job.
###
- 5. Time Management Skills
– Prioritize Tasks: Focus on what’s most important and delegate when possible.
– Take Breaks: Regular short breaks can boost overall productivity and prevent burnout.
###
- 6. Support Systems
– Join Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide encouragement and accountability.
– Lean on Friends and Family: Share your feelings with loved ones who can offer support.
###
- 7. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
– Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can reduce stress and improve mood.
– Balanced Diet and Sleep: Proper nutrition and adequate rest are crucial for mental well-being.
Remember, overcoming work and productivity addiction is a journey, and it’s okay to seek help along the way. Consulting a mental health professional can provide personalized strategies and support to help you achieve a healthier work-life balance.
Does work and productivity therapy exist?
Yes, therapy for work and productivity addiction does exist, and it can be quite effective in helping individuals regain balance in their lives. Work addiction, often referred to as workaholism, is characterized by an excessive and compulsive need to work, which can lead to neglect of personal relationships, health, and overall well-being. Here are some therapeutic approaches that can be used to address work and productivity addiction:
- 1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a common approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. For work addiction, CBT can help individuals recognize the underlying beliefs driving their work habits, such as the need for approval or fear of failure, and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- 2. Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques: Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals become more aware of their work habits and stress levels. These techniques can aid in reducing anxiety and improving focus on the present moment, rather than being consumed by work-related thoughts.
- 3. Psychodynamic Therapy: This approach explores the unconscious motivations and emotional conflicts that may contribute to work addiction. By understanding these deeper issues, individuals can work towards resolving them and reducing their compulsive work behaviors.
- 4. Family Therapy: Work addiction often affects not just the individual, but also their family and close relationships. Family therapy can help improve communication, set healthy boundaries, and rebuild relationships that may have been strained by excessive work habits.
- 5. Coaching and Goal Setting: Working with a coach or therapist to set realistic and balanced goals can help individuals prioritize their time and energy more effectively. This approach encourages a healthier work-life balance and helps prevent burnout.
- 6. Support Groups: Joining a support group, such as Workaholics Anonymous, can provide individuals with a community of peers who understand their struggles and can offer support and accountability.
- 7. Lifestyle Changes: Therapists may also work with individuals to make lifestyle changes, such as incorporating regular exercise, hobbies, and social activities, to create a more balanced and fulfilling life outside of work.
It’s important for individuals struggling with work addiction to seek help from a qualified mental health professional who can tailor a treatment plan to their specific needs. Addressing work addiction can lead to improved mental and physical health, better relationships, and a more satisfying and balanced life.
Where to find support groups if you are addicted to break?
Finding support groups for work and productivity addicts can be a crucial step in addressing the challenges associated with workaholism and productivity obsession. Here are some avenues to explore:
- 1. Online Support Groups and Forums:
– Websites like Reddit have communities such as r/stopworking and r/productivity where individuals share experiences and advice.
– Platforms like Meetup often host virtual and in-person groups focused on work-life balance and productivity management.
- 2. Professional Organizations:
– The American Psychological Association (APA) and similar organizations in other countries may have resources or directories for support groups related to work addiction.
- 3. Therapy and Counseling Services:
– Many therapists specialize in work-life balance issues and may offer group therapy sessions. Websites like Psychology Today have directories to find professionals who may offer such groups.
– Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) often provide resources or referrals to support groups for work-related stress and addiction.
- 4. Community Centers and Nonprofits:
– Local community centers or nonprofit organizations sometimes host support groups focused on mental health and work-life balance.
- 5. Books and Online Courses:
– Authors and educators who specialize in work addiction often have associated online communities or courses that include support group elements.
- 6. Social Media Groups:
– Platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn have groups dedicated to work-life balance and overcoming work addiction, where members can share insights and support.
- 7. Workplace Initiatives:
– Some companies have internal support groups or wellness programs aimed at promoting a healthier work-life balance.
When seeking support, it’s important to find a group or community that feels comfortable and aligns with your specific needs and preferences.
But other break addiction solutions exist
If you’re seeking help to break an addiction and prefer not to engage with support groups, there are several other resources and professionals you can turn to for assistance:
- 1. Mental Health Professionals: Psychologists, psychiatrists, and counselors who specialize in addiction can provide one-on-one therapy and develop personalized treatment plans.
- 2. Medical Doctors: Primary care physicians can offer initial advice and may refer you to specialists in addiction medicine. They can also help manage any physical health issues related to addiction.
- 3. Addiction Specialists: These are healthcare providers with specific training in addiction treatment. They can offer comprehensive care, including medication-assisted treatment if necessary.
- 4. Therapists: Licensed therapists, such as cognitive-behavioral therapists, can help address the underlying psychological issues contributing to addiction.
- 5. Rehabilitation Centers: These facilities offer structured programs that include medical care, therapy, and other resources to help individuals overcome addiction.
- 6. Social Workers: They can provide support and connect you with community resources, including housing, employment, and healthcare services.
- 7. Holistic Practitioners: Some individuals find benefit in alternative therapies such as acupuncture, meditation, or yoga, which can be supportive in managing cravings and stress.
- 8. Online Resources: There are numerous online platforms and apps that offer educational materials, self-help tools, and virtual therapy sessions.
- 9. Family and Friends: Trusted loved ones can provide emotional support and encouragement throughout the recovery process.
It’s important to find a combination of resources and support systems that work best for you. Seeking professional help is a crucial step in addressing addiction effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, overcoming break addiction is a journey that requires self-awareness, commitment, and a supportive environment. It’s essential to recognize the patterns and triggers that lead to excessive breaks and address the underlying causes. By setting clear goals, establishing a structured routine, and utilizing tools and techniques to stay focused, individuals can regain control over their time and productivity.
Additionally, seeking support from friends, family, or professionals can provide the encouragement and accountability needed to make lasting changes. Remember, breaking free from this cycle is not about eliminating breaks altogether but rather finding a healthy balance that enhances both personal well-being and professional success. As you embark on this path, be patient with yourself and celebrate small victories along the way, knowing that each step brings you closer to a more fulfilling and productive life.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.Here is the trailer:
To Go Further
Take our 4-min test
How to help someone with break addiction?
Helping someone break an addiction can be a challenging but rewarding process. It requires patience, understanding, and a supportive approach. Here are several steps you can take to assist someone in overcoming addiction:
- 1. Educate Yourself: Learn about the specific addiction they are facing. Understanding the nature of the addiction, its effects, and the recovery process will help you provide informed support.
- 2. Communicate Openly: Approach the person with empathy and without judgment. Encourage open and honest communication, allowing them to express their feelings and struggles without fear of criticism.
- 3. Encourage Professional Help: Suggest seeking help from addiction specialists, therapists, or counselors. Professional treatment is often crucial in overcoming addiction and can include therapy, medication, or support groups.
- 4. Support Healthy Habits: Encourage the person to engage in healthy activities such as exercise, hobbies, or mindfulness practices. These can provide positive outlets and help reduce cravings.
- 5. Set Boundaries: While offering support, it’s important to set clear boundaries to protect your own well-being. Avoid enabling behaviors that may inadvertently support the addiction.
- 6. Be Patient and Persistent: Recovery is often a long and non-linear process. Be prepared for setbacks and continue to offer support and encouragement throughout their journey.
- 7. Promote Support Groups: Encourage participation in support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA), where they can connect with others who understand their struggles.
- 8. Celebrate Progress: Acknowledge and celebrate small victories and milestones in their recovery journey. Positive reinforcement can boost their motivation to continue.
- 9. Take Care of Yourself: Supporting someone with an addiction can be emotionally taxing. Ensure you are also taking care of your own mental and physical health.
- 10. Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with new treatment methods and resources that might benefit the person you are supporting.
Remember, while you can provide support and encouragement, the
Best books about work and productivity addiction
Exploring the themes of work and productivity addiction can offer valuable insights into how these issues impact our lives and society. Here are five notable books that delve into these topics, providing a mix of personal narratives, psychological analysis, and practical advice:
- 1. “Deep Work: Rules for Focused Success in a Distracted World” by Cal Newport
– Cal Newport’s “Deep Work” explores the importance of focused, undistracted work in an increasingly noisy world. While not directly about addiction, it addresses the cultural shift towards constant connectivity and multitasking, offering strategies to cultivate deep concentration and productivity. Newport emphasizes the value of deep work in achieving meaningful accomplishments and highlights the dangers of shallow work habits.
- 2. “Rest: Why You Get More Done When You Work Less” by Alex Soojung-Kim Pang
– Alex Soojung-Kim Pang’s “Rest” challenges the notion that longer hours equate to greater productivity. The book argues for the importance of rest and downtime in enhancing creativity and efficiency. By examining historical figures and scientific research, Pang demonstrates how deliberate rest can lead to more sustainable work habits and prevent burnout, a common consequence of work addiction.
- 3. “Do Nothing: How to Break Away from Overworking, Overdoing, and Underliving” by Celeste Headlee
– Celeste Headlee’s “Do Nothing” offers a critique of the modern obsession with busyness and productivity. Through historical analysis and personal anecdotes, Headlee explores how societal pressures have led to overworking and undervaluing leisure. The book provides practical advice for reclaiming time, setting boundaries, and finding fulfillment beyond constant productivity.
- 4. “The Joy of Missing Out: Live More by Doing Less” by Tonya Dalton
– Tonya Dalton’s “The Joy of Missing Out” focuses on the empowerment that comes from intentionally choosing what not to do. Dalton encourages readers to prioritize what truly matters and to let go of the pressure to do
Research about work and productivity addiction
Work and productivity addiction, often referred to as “workaholism,” is a phenomenon that has garnered increasing attention in recent years. Below are summaries of three to five official studies that explore various aspects of work and productivity addiction:
1. Study on Workaholism and Health Outcomes (2016.:
Conducted by researchers at the University of Bergen, this study examined the health outcomes associated with workaholism. The researchers developed the Bergen Work Addiction Scale to identify workaholics and assess their health. The study found that workaholism is significantly associated with higher levels of stress, sleep problems, and burnout. The scale has been widely used in subsequent research to measure work addiction.
2. The Impact of Workaholism on Family Life (2018.:
A study published in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology explored how workaholism affects family dynamics. The researchers found that individuals who are addicted to work often experience conflicts at home, leading to strained relationships and reduced family satisfaction. The study highlighted the importance of work-life balance and the need for interventions to address workaholic behaviors.
3. Neurobiological Perspectives on Work Addiction (2020.:
This study, published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology, investigated the neurobiological underpinnings of work addiction. The researchers used neuroimaging techniques to explore brain activity in individuals identified as workaholics. They discovered that workaholism shares similarities with other behavioral addictions, such as gambling, in terms of brain activity patterns. This study provided insights into the potential for developing targeted treatments for work addiction.
4. Workaholism and Job Performance (2019.:
Conducted by researchers at the University of Georgia, this study examined the relationship between workaholism and job performance. Contrary to the common belief that workaholics are highly productive, the study found that excessive work can lead to decreased efficiency and lower job performance over time. The researchers suggested that sustainable productivity requires a balanced approach to work.
5. Cross-Cultural Examination of Workaholism (2021.:
Published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, this study explored workaholism across different cultures. The researchers surveyed employees from various countries to understand cultural influences on work addiction. They found significant cultural variations in the prevalence and perception of workaholism, indicating that societal norms and values play a crucial role in shaping work-related behaviors.
These studies collectively highlight the complexity of work and productivity addiction, emphasizing its impact on health, family life, and job performance. They also underscore the need for a nuanced understanding of cultural factors and the potential for developing effective interventions.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.
The impact of work and productivity on our society
In today’s fast-paced world, the pressure to achieve and excel has intensified, leading to a phenomenon known as work and productivity addiction. This addiction, characterized by an overwhelming compulsion to work excessively and a constant drive to be productive, has far-reaching implications on both individuals and society as a whole.
### Individual Impacts
- 1. Mental Health Issues: Work and productivity addiction can lead to severe mental health problems, including anxiety, depression, and burnout. The relentless pursuit of productivity often results in chronic stress, which can exacerbate these conditions.
- 2. Physical Health Consequences: The physical toll of excessive work is significant. Long hours and insufficient rest can lead to fatigue, sleep disorders, and a weakened immune system. Moreover, sedentary work habits contribute to lifestyle diseases such as obesity and cardiovascular issues.
- 3. Strained Relationships: Individuals addicted to work often prioritize their jobs over personal relationships, leading to isolation and strained family dynamics. The lack of work-life balance can result in a disconnect from loved ones, causing emotional distress and relationship breakdowns.
- 4. Decreased Job Satisfaction: Ironically, the pursuit of constant productivity can lead to decreased job satisfaction. When work becomes an obsession, individuals may lose sight of their passion and purpose, leading to a sense of emptiness and dissatisfaction.
### Societal Impacts
- 1. Cultural Shift: Society increasingly values productivity and success, often equating them with personal worth. This cultural shift places immense pressure on individuals to perform, perpetuating the cycle of work addiction.
- 2. Economic Implications: While initially, high productivity levels may boost economic output, the long-term effects can be detrimental. Burnout and health issues lead to increased absenteeism and decreased efficiency, ultimately affecting economic productivity.
- 3. Impact on Innovation: A culture focused solely on productivity can stifle creativity and innovation. When individuals are pressured to constantly produce, there is little room for experimentation and creative thinking, which are essential for innovation.
- 4. Social Inequality: Work addiction often exacerbates social inequality. Those who cannot keep up with the relentless pace, whether due to personal choice or circumstances, may find themselves marginalized or undervalued in the workforce.
### Addressing the Issue
To mitigate the impact of work and productivity addiction, a multi-faceted approach is necessary:
– Promoting Work-Life Balance: Employers can play a crucial role by encouraging flexible work arrangements and emphasizing the importance of work-life balance. Policies that support mental health and well-being can help reduce the pressure to overwork.
– Redefining Success: Society needs to redefine success beyond productivity metrics. Valuing creativity, emotional intelligence, and personal fulfillment can help shift the focus from constant productivity to holistic well-being.
– Raising Awareness: Education and awareness campaigns can highlight the dangers of work addiction and promote healthier work habits. Encouraging open discussions about mental health in the workplace can also reduce stigma and support those struggling with addiction.
– Individual Responsibility: On a personal level, individuals should be encouraged to set boundaries, prioritize self-care, and seek help if they find themselves unable to disconnect from work.
In conclusion, while productivity is essential for progress, an addiction to work can have detrimental effects on both individuals and society. By fostering a culture that values balance and well-being, we can create a healthier, more sustainable approach to work and productivity.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.