Trying to quit artifact addiction? Welcome to our digital detox series! This series focuses on how to stop digital and screen addictions. Findall our posts about digital addictions. Today, let’s talk about how to quit the artifact addiction.

- What’s the artifact addiction?
- Addiction to artifact, a “real” addiction?
- What’s considered artifact addiction?
- How much artifact is too much?
- Some video games addiction facts & statistics
- Symptoms & Causes of the artifact addiction
- Why is artifact so addictive?
- Possible causes of artifact dependency
- Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of artifact addiction
- Problems, impacts & bad effects of artifact
- Some benefits of artifact
- Health problems
- Impact on brain & mental health
- Impact on relationships
- How to stop & quit your artifact addiction
- Main steps and solutions to break the artifact addiction
- Best artifact blocker apps & functionalities
- Where to seek extra help?
- Conclusion
- To Go Further
- How to help someone with artifact addiction
- Best books about video games addiction
- Research about video games addiction
What is the artifact addiction?
About artifact
An artifact is a human-made object, often of historical or cultural significance, such as tools, pottery, or art, which provides insight into past societies and their practices.
Addiction to artifact, a “real” addiction?
Officially an addiction?
First, let’s have a look at the DSM-5,the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Does it include artifact addiction?
Artifact addiction is not listed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5.. The DSM-5 is a comprehensive classification of mental disorders published by the American Psychiatric Association, and it includes specific criteria for diagnosing a wide range of mental health conditions. While the DSM-5 covers various substance-related and addictive disorders, such as those related to alcohol, drugs, and gambling, it does not specifically include a category for addiction to artifacts or objects.
If “artifact addiction” refers to a compulsive behavior related to collecting or hoarding objects, it might be more closely related to hoarding disorder, which is recognized in the DSM-5. Hoarding disorder involves persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, regardless of their actual value, due to a perceived need to save them and distress associated with discarding them. However, this is not the same as an addiction.
For any concerns about behavioral or mental health issues, it’s important to consult a qualified mental health professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
So what does “artifact addiction” mean?
Artifact Addiction isn’t a widely recognized term in psychology, but it can be understood by breaking down the words. An “artifact” typically refers to any object made by humans, especially one of historical or cultural interest. When combined with “addiction,” it suggests a strong, possibly compulsive, attachment to collecting or interacting with artifacts.
Here are a few ways to interpret Artifact Addiction:
- 1. Collecting Obsession: Some people have a deep passion for collecting items like antiques, vintage gadgets, or artwork. This passion can become so consuming that it affects their daily life and finances.
- 2. Digital Artifacts: In the digital world, artifacts can refer to data remnants or digital collectibles like NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). An addiction here might involve excessive time and resources spent on acquiring and managing digital items.
- 3. Technological Dependence: Sometimes, “artifact” can relate to technology itself. An addiction might involve excessive use of gadgets, software, or being overly dependent on technological tools.
- 4. Cultural or Historical Fixation: Being overly fixated on history or culture to the point where it interferes with personal growth or relationships.
If you or someone you know feels overwhelmed by an obsession with collecting or interacting with artifacts, it might be helpful to seek support from a mental health professional. Finding a balance can ensure that hobbies and interests remain enjoyable and healthy parts of life.
What is considered artifact addiction?
Diagnosing an addiction to artifacts, like any form of behavioral addiction, involves evaluating various psychological, behavioral, and emotional factors. While “artifact addiction” is not a formally recognized disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-
- 5., it can be understood in a similar framework to other behavioral addictions. Here are some criteria that might be considered when evaluating such an addiction:
- 1. Preoccupation with Artifacts: The individual spends an excessive amount of time thinking about, acquiring, or interacting with artifacts. This preoccupation often interferes with daily responsibilities and activities.
- 2. Loss of Control: The person finds it difficult to control or reduce their engagement with artifacts despite attempts to do so. They may repeatedly try to cut back on their activities related to artifacts without success.
- 3. Tolerance: Over time, the individual may require more artifacts or more time spent with artifacts to achieve the same level of satisfaction or excitement as before.
- 4. Withdrawal Symptoms: When unable to engage with artifacts, the person may experience symptoms of withdrawal, such as irritability, anxiety, or depression.
- 5. Neglect of Other Activities: The individual may neglect social, occupational, or recreational activities in favor of spending time with artifacts. This can lead to isolation and a decrease in overall life satisfaction.
- 6. Negative Consequences: Continued engagement with artifacts despite knowing the negative consequences, such as financial strain, relationship problems, or health issues.
- 7. Escapism: Using artifacts as a way to escape from problems or to relieve feelings of helplessness, guilt, anxiety, or depression.
- 8. Deception: The person may lie to family members, friends, or therapists to conceal the extent of their involvement with artifacts.
- 9. Risky Behavior: Engaging in risky or illegal activities to obtain or interact with artifacts, such as theft or spending beyond one’s means.
- 10. Emotional Attachment: Developing an emotional attachment to artifacts that goes beyond mere appreciation, often attributing personal significance or identity to them.
It’s important to note that diagnosing any form of addiction should be done by a qualified mental health professional. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation and determine the best course of action for treatment. If you or someone you know is struggling with this type of addiction, seeking professional help is a crucial step.
How much artifact is too much?
The amount of time spent on an artifact, whether it be a digital project, a piece of art, or any other creation, can vary greatly depending on the context and purpose of the work. However, there are several factors to consider when determining if too much time is being spent:
- 1. Project Scope and Deadlines: If the time spent exceeds the original scope or deadlines, it may indicate inefficiencies or scope creep. It’s important to regularly assess progress against initial plans and adjust as necessary.
- 2. Value and Impact: Consider whether additional time spent is adding significant value or just minor improvements. Diminishing returns can occur when extra effort does not proportionally increase the quality or impact of the artifact.
- 3. Resource Allocation: Evaluate if the time investment is justified given the available resources. Spending too much time on one artifact might detract from other important projects or responsibilities.
- 4. Personal Well-being: Excessive time spent on a project can lead to burnout, stress, and decreased productivity. It’s crucial to maintain a healthy work-life balance and take breaks to ensure sustained creativity and efficiency.
- 5. Feedback and Iteration: If possible, seek feedback early and often. This can help identify when an artifact is “good enough” and prevent over-polishing. Iterative processes can be more effective than striving for perfection in one go.
- 6. Opportunity Cost: Consider what other projects or opportunities might be missed due to the time spent on a single artifact. Prioritizing tasks and projects can help ensure that time is used effectively across multiple endeavors.
Ultimately, determining how much time is too much depends on the specific goals, resources, and context of the artifact. Regular evaluation and reflection can help ensure that time is being used efficiently and effectively.
Some video games addiction facts & statistics

Video game addiction, often referred to as gaming disorder, has been a topic of increasing concern among researchers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers. While the landscape of video game addiction is complex and multifaceted, several key statistics and findings have emerged over recent years:
- 1. Prevalence:
– The World Health Organization (WHO) included “gaming disorder” in its International Classification of Diseases (ICD-
- 11. in 2019, highlighting its growing recognition as a mental health issue.
– Estimates of the prevalence of gaming disorder vary widely. Research suggests that approximately 1% to 10% of gamers may exhibit behaviors consistent with gaming addiction, depending on the criteria used and the population studied.
- 2. Demographics:
– Gaming addiction is more commonly reported among males than females, with young males being particularly susceptible.
– Adolescents and young adults are the most affected age groups, with many studies focusing on individuals aged 12 to 24.
- 3. Associated Factors:
– Psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, and ADHD have been linked to a higher risk of developing gaming addiction.
– Social factors, including peer pressure and a lack of social support, can also contribute to excessive gaming behaviors.
- 4. Impact on Life:
– Individuals with gaming addiction may experience negative consequences in various aspects of life, including academic performance, social relationships, and physical health.
– Excessive gaming can lead to sleep disturbances, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor dietary habits, increasing the risk of obesity and related health issues.
- 5. Economic Impact:
– The gaming industry is a multi-billion-dollar market, and while it provides entertainment and economic benefits, the costs associated with gaming addiction, such as healthcare expenses and lost productivity, are significant.
- 6. Treatment and Intervention:
– Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most common treatment approaches for gaming addiction.
– Some countries, like South Korea and China, have implemented policies to limit gaming time among youth to combat addiction.
- 7. Research and Controversy:
– The classification of gaming disorder remains controversial, with some experts arguing that it pathologizes normal gaming behavior.
– Ongoing research aims to better understand the neurobiological and psychological mechanisms underlying gaming addiction.
- 8. Global Perspectives:
– Different countries report varying prevalence rates, influenced by cultural attitudes towards gaming and the availability of gaming platforms.
– In Asia, particularly in countries like China and South Korea, gaming addiction is recognized as a significant public health issue, leading to the implementation of specific interventions and regulations.
As the gaming industry continues to evolve, ongoing research is essential to better understand the nuances of gaming addiction and develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Is the artifact addiction widespread?
“Artifact” can refer to different things depending on the context, but it is commonly associated with a digital card game developed by Valve Corporation, released in
- 2018. If you’re asking about addiction to this game, it’s important to clarify a few points:
- 1. Popularity and Player Base: When “Artifact” was first released, it received attention due to Valve’s reputation and the involvement of Richard Garfield, the creator of “Magic: The Gathering.” However, the game struggled to maintain a large player base over time. Various factors, such as its complex mechanics, monetization model, and competition from other games, contributed to a decline in popularity.
- 2. Addiction in Gaming: Video game addiction is a recognized issue, affecting a small percentage of gamers. It is characterized by excessive gaming that interferes with daily life. However, given “Artifact’s” relatively small player base, it is unlikely that there is a significant number of people addicted to this specific game.
- 3. Game Redesign and Relaunch: Valve attempted to revitalize “Artifact” by redesigning the game, known as “Artifact 2.0” or “Artifact Foundry,” but eventually decided to stop development in2021. The game was made free to play, but it did not regain significant traction.
If you’re referring to another context or a different “Artifact,” please provide more details for a more accurate response.
Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of artifact addiction
Why is artifact so addictive?
Hey there! You asked, “Why is artifact so addictive?” Let’s dive into it in a simple and friendly way.
### What Makes Artifacts Addictive?
- 1. Collecting Satisfaction:
Humans love collecting things. Whether it’s stamps, coins, or in games, artifacts serve as milestones of your progress. Each new artifact you obtain gives a sense of achievement and encourages you to keep going.
- 2. Progress and Rewards:
Artifacts often act as rewards for completing tasks or challenges. This reward system triggers your brain to release dopamine, the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, making you want to pursue more rewards.
- 3. Personalization:
In many games or hobbies, artifacts allow you to customize your experience. Whether it’s decorating your virtual space or enhancing your character’s abilities, personalization makes the experience more engaging.
- 4. Social Recognition:
Showing off your collection of artifacts can boost your social status among peers. Whether online or offline, having rare or unique artifacts can make you feel proud and admired.
- 5. Curiosity and Discovery:
Artifacts often come with stories or hidden features. The desire to uncover these mysteries keeps you intrigued and continuously engaged in the pursuit.
- 6. Habit Formation:
Regularly seeking out artifacts can become a habit. The routine of searching, collecting, and managing artifacts becomes something you look forward to, integrating smoothly into your daily life.
### In a Nutshell
Artifacts tap into our natural desires for achievement, personalization, social recognition, and curiosity. Whether you’re collecting digital items in a game or real-world treasures, these elements combine to make the pursuit highly addictive and enjoyable.
Hope that helps explain why artifacts can be so captivating! If you have more questions, feel free to ask. 😊
Possible causes of artifact dependency
Artifact addiction, while not a formally recognized condition like substance addiction, refers to an intense obsession or compulsion to collect and possess artifacts, often historical or cultural items. This behavior can be driven by several factors:
- 1. Historical Fascination: Many individuals are deeply interested in history and culture. This fascination can lead to a desire to own a piece of history, resulting in the collection of artifacts.
- 2. Emotional Connection: Artifacts can hold significant emotional value. They may remind individuals of personal experiences, family heritage, or cultural identity, creating a strong emotional bond.
- 3. Status and Prestige: Owning rare or valuable artifacts can be seen as a status symbol. Collectors may seek artifacts to enhance their social standing or to gain admiration from peers.
- 4. Investment Potential: Some individuals view artifacts as investment opportunities. The potential for financial gain can drive the acquisition of artifacts, especially those that are rare or likely to appreciate in value.
- 5. Cognitive Bias: The endowment effect, a cognitive bias where people ascribe more value to things merely because they own them, can contribute to artifact addiction. This can lead to an irrational attachment to artifacts.
- 6. Nostalgia and Sentimentality: Artifacts can evoke feelings of nostalgia, transporting individuals to a different time or place. This sentimental value can fuel the desire to collect and preserve artifacts.
- 7. Psychological Needs: For some, collecting artifacts may fulfill psychological needs such as control, order, or identity. The process of collecting can provide a sense of purpose or accomplishment.
- 8. Cultural and Societal Influences: Societal norms and cultural influences can play a role. In some cultures, collecting artifacts is a respected and encouraged activity, which can reinforce the behavior.
- 9. Escapism: Collecting artifacts can serve as a form of escapism, providing a distraction from everyday life or personal issues. It offers a way to immerse oneself in a different world.
- 10. Compulsive Behavior: In some cases, artifact addiction may be linked to compulsive behavior patterns, similar to other forms of hoarding or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
While collecting artifacts can be a rewarding and educational hobby, it is important for individuals to maintain a healthy balance and be mindful of the ethical implications, such as the provenance and legality of the artifacts they acquire.
Signs & Symptoms of artifact addiction
Now let’s see if you have the artifact addiction problem.
Collecting artifacts can be a fascinating hobby, connecting you to history and cultures from around the world. However, like any passion, it can sometimes become an obsession. Here are seven signs that you might be an artifact addict:
- 1. Your Home Resembles a Museum:
If your living space is filled with display cases, shelves, and walls adorned with artifacts, and you find yourself constantly rearranging and adding to your collection, it might be a sign of addiction. Your home becomes a curated gallery, with each piece having its own story and significance.
- 2. You Spend Excessive Time and Money:
When you start prioritizing buying artifacts over essential expenses or find yourself spending hours scouring auctions, antique shops, and online marketplaces, it could indicate an addiction. The thrill of acquiring a new piece often outweighs financial prudence.
- 3. You Have Extensive Knowledge:
An artifact addict often becomes an expert in their field of interest. You might know the history, origin, and cultural significance of each piece in your collection, and you can spend hours discussing these details with anyone willing to listen.
- 4. You Experience Withdrawal Symptoms:
If you feel anxious or restless when you’re unable to add to your collection, or if you constantly think about your next acquisition, it might be a sign of addiction. The need for the next “fix” can be overwhelming.
- 5. Your Social Life Revolves Around Artifacts:
When most of your social interactions involve fellow collectors, attending artifact-related events, or visiting museums, it may indicate that your passion has taken over your social life. Conversations and friendships often center around your shared interest in artifacts.
- 6. You Neglect Other Hobbies and Responsibilities:
An artifact addiction can lead to neglecting other interests or responsibilities. You might find yourself skipping social events, missing deadlines, or ignoring other hobbies in favor of spending time with your collection.
- 7. You Feel a Deep Emotional Attachment:
If you experience a strong emotional connection to your artifacts, treating them almost like family members, it could be a sign of addiction. Letting go of any piece, even for a good reason, might feel like an emotional loss.
While collecting artifacts can be a rewarding and educational pursuit, it’s important to maintain a healthy balance. If you recognize these signs in yourself, it might be worth reflecting on your relationship with your collection and considering ways to ensure it remains a fulfilling and enjoyable hobby.
Try our digital habit & screen addiction test:
Problems, impacts & bad effects of artifact: should you quit?

What are some benefits of artifact
Artifacts, in the context of cultural history, archaeology, and technology, hold significant value for various reasons. Here are some of the pros and advantages of artifacts:
### Cultural and Historical Significance
- 1. Historical Insight: Artifacts provide tangible evidence of past societies, offering insights into their daily lives, social structures, and cultural practices. They help historians and archaeologists reconstruct historical events and understand the evolution of human civilization.
- 2. Cultural Preservation: Artifacts serve as a means of preserving cultural heritage. They embody the traditions, beliefs, and artistic expressions of different cultures, allowing future generations to appreciate and learn from them.
- 3. Educational Value: Artifacts are invaluable educational tools. Museums and educational institutions use them to teach history, anthropology, and art, making learning more engaging and interactive.
### Archaeological Importance
- 4. Chronological Framework: Artifacts help establish chronological frameworks for archaeological sites. By analyzing the materials, styles, and technologies used, archaeologists can date sites and understand the sequence of historical developments.
- 5. Technological Evolution: Artifacts reveal the technological advancements of past societies. They showcase the evolution of tools, materials, and craftsmanship, highlighting human ingenuity and adaptation.
- 6. Cultural Exchange: Artifacts often indicate trade and cultural exchange between societies. By studying the origins and distribution of artifacts, researchers can trace the movement of goods and ideas across regions.
### Technological Artifacts
- 7. Innovation and Inspiration: In the realm of technology, artifacts such as prototypes, models, and early versions of devices serve as sources of inspiration and innovation. They provide insights into the development process and can inspire future technological advancements.
- 8. Documentation of Progress: Technological artifacts document the progress of human innovation. They showcase the milestones achieved in various fields, from computing and engineering to medicine and communication.
### Social and Economic Impact
- 9. Tourism and Economy: Artifacts attract tourists and researchers, contributing to the local economy. Museums and cultural sites that house significant artifacts often become major tourist attractions.
- 10. Cultural Identity and Pride: Artifacts are symbols of cultural identity and pride. They connect people to their heritage, fostering a sense of belonging and continuity.
### Aesthetic and Artistic Value
- 11. Artistic Expression: Many artifacts are works of art, showcasing the creativity and artistic skills of their creators. They contribute to the appreciation of art across different cultures and time periods.
- 12. Inspiration for Artists: Contemporary artists often draw inspiration from historical artifacts, incorporating traditional styles and techniques into modern art forms.
In summary, artifacts are invaluable resources that offer a window into the past, enrich our understanding of human history, and inspire future generations. Whether in the context of cultural heritage or technological development, artifacts play a crucial role in preserving and advancing human knowledge.But on the other hand, what are some artifact addiction problems that addicts suffer from?
General health problems
Artifacts, in the context of health, can refer to various things depending on the field. Generally, artifacts are human-made objects or disturbances that can affect health data or health outcomes. Here are some ways artifacts can impact health:
- 1. Medical Imaging Artifacts:
– Definition: In medical imaging, artifacts are distortions or errors in images that can obscure or mimic pathology.
– Effects: These can lead to misdiagnosis or unnecessary additional testing. For example, metal implants can cause artifacts in MRI scans, making it difficult to interpret the images accurately.
- 2. Electrocardiogram (ECG) Artifacts:
– Definition: Artifacts in ECGs are extraneous signals that can interfere with the accurate reading of heart rhythms.
– Effects: They can lead to misinterpretation of heart conditions, potentially resulting in incorrect treatment. Common causes include patient movement, poor electrode contact, or electrical interference.
- 3. Data Artifacts in Research:
– Definition: In research, artifacts refer to data anomalies that arise from the research process itself rather than the phenomenon being studied.
– Effects: These can skew study results, leading to false conclusions. Ensuring rigorous data collection and analysis methods can help minimize these artifacts.
- 4. Cultural Artifacts and Health:
– Definition: Cultural artifacts include objects, practices, or beliefs that are part of a society’s culture.
– Effects: These can influence health behaviors and perceptions. For instance, traditional health practices or dietary habits can impact physical and mental health, both positively and negatively.
- 5. Digital Health Artifacts:
– Definition: In digital health, artifacts can refer to inaccuracies or noise in data collected by health monitoring devices.
– Effects: These can affect the reliability of health tracking, leading to incorrect health assessments or interventions. Ensuring device accuracy and proper usage can mitigate these effects.
- 6. Environmental Artifacts:
– Definition: These are unintended byproducts of human activity that can impact health, such as pollution or noise.
– Effects: Long-term exposure can lead to chronic health conditions like respiratory diseases or stress-related disorders.
To mitigate the negative effects of artifacts on health, it is crucial to employ accurate diagnostic techniques, maintain rigorous research standards, and promote awareness of cultural and environmental influences on health. Understanding and addressing these artifacts can lead to better health outcomes and more accurate data interpretation.
artifact and sleep disorders
Artifacts themselves do not directly create sleep disorders or sleep problems. However, certain artifacts, particularly those related to technology and modern living, can contribute to conditions that may affect sleep quality. Here are a few ways in which artifacts might influence sleep:
- 1. Electronic Devices: The use of electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers before bedtime can interfere with sleep. The blue light emitted by these screens can suppress the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep-wake cycles, making it harder to fall asleep.
- 2. Noise Pollution: Artifacts like televisions, radios, and other electronic devices can contribute to noise pollution, which can disrupt sleep. Even low levels of noise can prevent deep, restful sleep or cause frequent awakenings.
- 3. Temperature Control: Modern heating and cooling systems can sometimes be set at inappropriate temperatures for sleep, either too hot or too cold, which can disrupt sleep patterns.
- 4. Lighting: Artificial lighting, especially bright or poorly timed light exposure, can affect circadian rhythms. Exposure to artificial light late in the evening can delay sleep onset and reduce overall sleep quality.
- 5. Stress and Anxiety: The constant connectivity enabled by modern technology can lead to increased stress and anxiety, which are known contributors to sleep disorders such as insomnia.
- 6. Sedentary Lifestyle: The convenience of modern artifacts can lead to a more sedentary lifestyle, which is associated with poorer sleep quality. Regular physical activity is important for maintaining healthy sleep patterns.
- 7. Caffeine and Stimulants: Artifacts like coffee makers and energy drinks can facilitate the consumption of caffeine and other stimulants, which can interfere with the ability to fall asleep or stay asleep.
While artifacts themselves are not the root cause of sleep disorders, their use and the lifestyle changes they bring can significantly impact sleep health. To mitigate these effects, it is recommended to establish good sleep hygiene practices, such as limiting screen time before bed, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and maintaining a regular sleep schedule.
artifact affecting your brain & mental health: bad for brain and mental health?
Some effects of artifact on your brain
Hey there!
Let’s dive into how certain artifacts—those extra bits and pieces in our environment, especially from technology—can impact our brains. While technology brings us amazing benefits, some artifacts can have unintended negative effects. Here are a few to watch out for:
###
- 1. Digital Overload
Constant exposure to screens and digital devices can lead to:
– Reduced Attention Span: Multitasking with multiple apps can make it harder to focus on one task for long.
– Mental Fatigue: Endless notifications and information can tire your brain, making it harder to think clearly.
###
- 2. Sleep Disruption
Artifacts like smartphones and tablets emit blue light, which can:
– Interfere with Sleep Patterns: Blue light suppresses melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep, making it harder to fall asleep.
– Impact Memory and Learning: Poor sleep affects how well your brain consolidates memories and learns new information.
###
- 3. Increased Stress and Anxiety
Constant connectivity can lead to:
– Information Overload: Too much information can overwhelm your brain, increasing stress levels.
– Social Pressure: Seeing others’ highlights on social media can create feelings of inadequacy or anxiety.
###
- 4. Reduced Physical Activity
Spending excessive time on gadgets can result in:
– Sedentary Lifestyle: Less movement can affect brain health, as physical activity is important for cognitive function.
– Poor Posture: Extended device use can lead to discomfort and even chronic pain, distracting your brain from tasks.
###
- 5. Cognitive Impairment
Dependence on technology might:
– Weaken Memory: Relying on devices to remember information can reduce your brain’s ability to retain and recall facts.
– Diminish Problem-Solving Skills: Easy access to answers can limit opportunities to develop critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
###
- 6. Sensory Overstimulation
Artifacts like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) can:
– Overwhelm the Senses: Too much sensory input can make it hard for your brain to process information efficiently.
– Cause Disorientation: Intense or poorly designed virtual environments can confuse the brain, leading to headaches or dizziness.
### How to Balance It Out
– Take Regular Breaks: Step away from screens to give your brain a rest.
– Set Boundaries: Limit device usage, especially before bedtime.
– Stay Active: Incorporate physical activity into your daily routine to boost brain health.
– Mindfulness Practices: Activities like meditation can help reduce stress and improve focus.
Remember, while artifacts and technology are integral to modern life, being mindful of their impact on our brains can help us use them in healthier, more balanced ways. Stay smart and take care of your amazing brain!
Some effects of artifact on your mental health
Artifacts, in the context of mental health, can refer to various elements or influences that negatively impact psychological well-being. These can include digital artifacts, such as social media, or physical artifacts, such as clutter in one’s environment. Here are some ways these artifacts can adversely affect mental health:
- 1. Digital Overload: Constant exposure to digital artifacts, such as notifications, emails, and social media updates, can lead to information overload. This can increase stress levels, reduce attention spans, and contribute to anxiety and depression.
- 2. Social Media Comparison: Artifacts from social media, including curated images and posts, can lead to unhealthy comparisons. This can result in feelings of inadequacy, low self-esteem, and body image issues, as individuals compare their lives to the seemingly perfect lives of others.
- 3. Clutter and Disorganization: Physical artifacts, such as clutter in living or working spaces, can create a chaotic environment. This can lead to feelings of being overwhelmed, increased stress, and difficulty concentrating, which can negatively affect mental health.
- 4. Cultural Artifacts: Exposure to cultural artifacts, such as media portrayals and stereotypes, can perpetuate unrealistic standards and expectations. This can contribute to identity issues, cultural dissonance, and feelings of alienation or marginalization.
- 5. Technological Dependence: Reliance on technological artifacts, such as smartphones and computers, can lead to reduced face-to-face interactions. This can result in social isolation, loneliness, and a decrease in the quality of interpersonal relationships.
- 6. Sleep Disruption: The use of digital artifacts, particularly before bedtime, can interfere with sleep patterns. The blue light emitted by screens can disrupt circadian rhythms, leading to insomnia and other sleep disorders, which can exacerbate mental health issues.
- 7. Cognitive Overload: The constant influx of information from digital artifacts can lead to cognitive overload. This can impair decision-making abilities, reduce productivity, and increase feelings of frustration and mental fatigue.
- 8. Privacy Concerns: The digital artifacts of surveillance and data collection can lead to privacy concerns and a sense of being constantly monitored. This can increase anxiety and lead to trust issues.
To mitigate these negative effects, it’s important to establish boundaries with technology, maintain organized and clutter-free environments, and cultivate a balanced lifestyle that includes offline activities and social interactions. Prioritizing mental health through mindfulness, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can also help counteract the adverse impacts of various artifacts.
Does artifact cause stress and anxiety?
Artifacts, in the context of cultural or historical objects, are generally not direct causes of stress or anxiety. However, there are circumstances where artifacts might contribute to these feelings indirectly:
- 1. Emotional Impact: Some artifacts, particularly those with historical significance or personal meaning, can evoke strong emotional responses. For instance, artifacts from traumatic events, such as war memorabilia or items from a tragic historical event, can trigger anxiety or stress in individuals who have a personal connection to those events.
- 2. Cultural Sensitivity: Artifacts that are culturally significant can sometimes be a source of stress or anxiety if they are displayed or handled insensitively. This can be particularly true for indigenous artifacts or those belonging to marginalized communities. The mishandling or misrepresentation of such artifacts can lead to distress among community members.
- 3. Conservation and Preservation: For those working in museums or in the field of conservation, the responsibility of preserving artifacts can be a source of stress. Ensuring that artifacts are protected from damage, theft, or decay requires meticulous care and can be a significant source of pressure.
- 4. Academic Pressure: Researchers or students studying artifacts may experience stress related to academic performance, deadlines, or the pressure to publish findings. The need to interpret and understand artifacts accurately can also contribute to anxiety.
- 5. Legal and Ethical Concerns: Issues surrounding the ownership, provenance, and repatriation of artifacts can be contentious and stressful. Legal battles over the rightful ownership of artifacts can create anxiety for individuals and institutions involved.
- 6. Personal Interpretation: For some individuals, artifacts might symbolize personal or collective histories that are painful or unresolved, leading to stress or anxiety when confronted with these items.
While artifacts themselves are not inherently stress-inducing, the contexts in which they are encountered and the personal or cultural significance they hold can lead to stress or anxiety for some individuals.
Can artifact addiction lead to sadness and depression?

Artifact addiction, while not a formally recognized psychological condition, can be understood as an excessive preoccupation or obsession with collecting, acquiring, or interacting with artifacts—be they historical items, collectibles, or digital assets like NFTs. This kind of addiction can potentially lead to sadness and depression, much like other forms of addiction. Here are several ways this could happen:
- 1. Emotional Dependence: Individuals may develop an emotional reliance on acquiring artifacts to experience happiness or fulfillment. When they are unable to obtain new items, they may feel a void, leading to sadness or depressive symptoms.
- 2. Financial Strain: The pursuit of artifacts can become financially burdensome, especially if individuals spend beyond their means. This financial stress can contribute to anxiety and depression, as the individual struggles with debt or financial insecurity.
- 3. Social Isolation: Those with artifact addiction might prioritize their collection over social interactions, leading to isolation. A lack of social support and interaction is a well-known risk factor for depression.
- 4. Neglect of Responsibilities: An intense focus on collecting artifacts might lead individuals to neglect personal, professional, or familial responsibilities. This neglect can result in guilt, shame, or conflict, which are common precursors to depression.
- 5. Unrealistic Expectations: The anticipation of acquiring a new artifact can create unrealistic expectations about the happiness it will bring. When reality falls short, individuals may experience disappointment, contributing to feelings of sadness.
- 6. Identity and Self-Worth Issues: Some individuals may tie their self-worth to their collection. If their collection is incomplete or not as impressive as they desire, it can lead to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem, both of which are linked to depression.
- 7. Loss of Control: Recognizing a loss of control over one’s collecting habits can lead to feelings of helplessness and despair, which are closely associated with depression.
While the concept of artifact addiction is not widely studied, the patterns observed in other behavioral addictions suggest that similar psychological and emotional challenges could arise. It’s important for individuals who feel their collecting habits are negatively affecting their mental health to seek support from mental health professionals. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can help address underlying issues and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Dopamine and artifact
The relationship between dopamine and artifacts is an intriguing topic that spans various fields, including neuroscience, psychology, and even art and technology. Let’s explore how these two seemingly disparate concepts intersect.
### Dopamine: The Neurotransmitter of Reward
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in the brain’s reward system. It is often associated with feelings of pleasure and satisfaction. When you experience something enjoyable, such as eating your favorite food, listening to music, or achieving a goal, dopamine is released in the brain, reinforcing the behavior and encouraging repetition. This mechanism is essential for survival, as it motivates individuals to seek out activities that are beneficial for their well-being.
### Artifacts: Human-Made Objects
Artifacts are objects made or modified by humans, often carrying cultural, historical, or personal significance. They range from ancient tools and artworks to modern technological devices. Artifacts serve as tangible representations of human creativity, innovation, and cultural evolution.
### The Intersection of Dopamine and Artifacts
- 1. Art and Aesthetic Experience: Artifacts, particularly in the form of art, can stimulate the release of dopamine. Engaging with art—whether through creation or appreciation—can trigger emotional responses and pleasure, similar to other rewarding experiences. This is why people often feel a sense of joy or fulfillment when viewing or creating art.
- 2. Technological Artifacts and Dopamine: Modern technological artifacts, such as smartphones and video games, are designed to engage users and often stimulate dopamine release. Features like notifications, social media interactions, and game rewards are crafted to keep users engaged by tapping into the brain’s reward system.
- 3. Cultural and Historical Significance: Artifacts that hold cultural or historical importance can also evoke emotional responses, including pride, nostalgia, or curiosity. These emotions can be linked to dopamine release, as they contribute to the rewarding experience of learning about one’s heritage or history.
- 4. Consumerism and Material Artifacts: The acquisition of material artifacts, such as new gadgets or fashion items, can also trigger dopamine release. The anticipation and act of purchasing can be rewarding, which is why shopping can sometimes become addictive for some individuals.
### Conclusion
The interplay between dopamine and artifacts highlights the complex ways in which human-made objects can influence our brains and behaviors. Whether through the appreciation of art, the engagement with technology, or the acquisition of material goods, artifacts have the power to affect our emotional and psychological states by interacting with the brain’s reward system. Understanding this relationship can provide insights into human motivation, creativity, and the societal impact of artifacts.
artifact effects on focus, productivity, attention span, academic performance…
Absolutely, artifacts can significantly impact your focus, productivity, attention span, and academic performance. Let’s break it down:
###
- 1. Focus
Cluttered Environment: Having too many items (artifacts) on your workspace can create visual distractions, making it harder to concentrate on the task at hand.
Positive Artifacts: Items like a motivational quote or a plant can enhance your focus by creating a more pleasant and personalized workspace.
###
- 2. Productivity
Distractions: Unnecessary artifacts such as gadgets, personal items, or unrelated books can interrupt your workflow, reducing overall productivity.
Organized Space: Minimizing clutter and keeping only essential items can streamline your tasks and boost efficiency.
###
- 3. Attention Span
Overstimulation: Excessive artifacts can overwhelm your senses, making it difficult to maintain attention for extended periods.
Simplified Environment: A tidy and minimalistic setup helps sustain your attention by reducing potential interruptions.
###
- 4. Academic Performance
Study Efficiency: A well-organized study area with appropriate artifacts (like planners, stationery, and educational materials) can enhance learning and retention.
Stress Reduction: Personal artifacts that make you feel comfortable can lower stress levels, improving your ability to perform academically.
### Tips to Manage Artifacts Effectively:
– Declutter Regularly: Remove items that aren’t necessary for your current tasks.
– Personalize Mindfully: Choose a few meaningful artifacts that inspire or motivate you without causing distractions.
– Organize Strategically: Keep tools and materials you use frequently within easy reach to maintain a smooth workflow.
By being mindful of the artifacts in your environment, you can create a space that supports your focus, boosts your productivity, maintains your attention span, and ultimately enhances your academic performance.
A word about ADHD and artifact
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Individuals with ADHD may interact differently with various artifacts, which can include objects, tools, or technologies, due to their unique cognitive and behavioral profiles. Here are some ways in which people with ADHD might interact differently with artifacts:
- 1. Technology and Gadgets: People with ADHD often find technology both a helpful tool and a source of distraction. They may be drawn to interactive and engaging digital interfaces, such as video games or apps, which can hold their attention more effectively than static or less stimulating artifacts. However, they may also struggle with time management when using these technologies, leading to prolonged use or difficulty in switching tasks.
- 2. Organizational Tools: Artifacts designed for organization, such as planners, calendars, or task management apps, can be particularly beneficial for individuals with ADHD. These tools can help them manage time, prioritize tasks, and remember important information. However, the effectiveness of these tools often depends on their ease of use and the individual’s commitment to consistently using them.
- 3. Educational Materials: In educational settings, individuals with ADHD may benefit from artifacts that incorporate multimedia elements, interactive components, or hands-on activities. Traditional textbooks or lectures may not hold their attention as effectively. Artifacts that allow for active participation or movement can be particularly engaging.
- 4. Physical Environment: The physical arrangement of artifacts in a space can significantly impact individuals with ADHD. Cluttered or visually overstimulating environments may be distracting, while organized and minimalistic spaces can help reduce distractions and improve focus.
- 5. Creative Tools: Many people with ADHD have strong creative abilities and may interact with artistic artifacts, such as musical instruments, drawing tools, or crafting materials, in unique ways. These tools can provide an outlet for self-expression and help improve focus through engaging and enjoyable activities.
- 6. Assistive Technologies: There are specific artifacts designed to assist individuals with ADHD, such as fidget tools, noise-canceling headphones, or specialized software that aids in concentration and task management. These tools can help mitigate some of the challenges associated with ADHD by providing sensory input or reducing environmental distractions.
- 7. Social Interaction: Artifacts that facilitate social interaction, such as social media platforms or communication devices, can be both beneficial and challenging. They offer opportunities for connection and engagement but can also contribute to distraction and impulsive behavior if not managed carefully.
Overall, the interaction between individuals with ADHD and various artifacts is highly individualized. What works well for one person may not be as effective for another, highlighting the importance of personalized approaches and flexibility in choosing and using artifacts. Understanding these interactions can lead to better support and accommodations for individuals with ADHD in various settings.
Affecting your relationships
artifact and self-esteem
### How Artifacts Affect Self-Esteem
Artifacts—personal items that hold special meaning to us—can have a surprising impact on our self-esteem. Whether it’s a cherished piece of jewelry, a favorite book, or a memorable photograph, these objects play a unique role in shaping how we feel about ourselves. Here’s how:
####
- 1. Connection to Identity
Artifacts often represent who we are or who we aspire to be. Wearing a necklace passed down through generations, for example, can reinforce a sense of heritage and continuity. This connection to your roots or personal values can boost your confidence and self-worth.
####
- 2. Reminder of Achievements
Having items that remind you of your accomplishments—like a trophy, certificate, or even a signed autograph—can reinforce your belief in your abilities. These artifacts serve as tangible proof of your successes, helping you feel more capable and proud of yourself.
####
- 3. Emotional Support
Certain artifacts offer comfort during tough times. A favorite blanket, a soothing scented candle, or a photo of loved ones can provide emotional support and reassurance. This sense of security can improve your overall mood and self-esteem.
####
- 4. Inspiration and Motivation
Artifacts can inspire you to pursue your goals. A vision board, inspirational quotes, or items related to your passions can keep you motivated. Seeing these items regularly reminds you of your aspirations, encouraging you to stay positive and driven.
####
- 5. Social Connection
Sharing artifacts with others can strengthen social bonds. Displaying items that tell your story can help others understand and appreciate you, fostering a sense of belonging and acceptance. Feeling connected to a community boosts your self-esteem by reinforcing that you matter to others.
####
- 6. Self-Expression
Artifacts allow you to express your personality and creativity. Decorating your space with items that reflect your tastes and interests showcases your uniqueness. This self-expression affirms your identity, making you feel more confident and self-assured.
### Tips to Use Artifacts to Boost Self-Esteem
– Choose Meaningful Items: Surround yourself with artifacts that truly resonate with you and reflect your values.
– Rotate Your Collection: Regularly updating your artifacts can keep your environment fresh and inspiring.
– Display Them Proudly: Make your artifacts visible to remind yourself of their significance throughout the day.
– Share Their Stories: Talking about your artifacts with others can deepen your appreciation and strengthen relationships.
### Conclusion
Artifacts are more than just objects; they are extensions of ourselves. By carefully selecting and cherishing meaningful items, you can enhance your self-esteem, find motivation, and strengthen your sense of identity. Embrace the power of artifacts to create a supportive and uplifting environment that celebrates who you are.
artifact addiction leads to isolation and loneliness?
.jpg)
Artifact addiction, while not a widely recognized or clinically defined condition, can be understood as an intense preoccupation or obsession with collecting, preserving, or interacting with artifacts. These artifacts could range from historical objects, collectibles, or even digital artifacts like NFTs. While the concept of addiction in this context is not extensively studied, parallels can be drawn from other forms of behavioral addictions, such as gaming or shopping, to explore potential impacts on social behavior and mental health.
### Potential Pathways to Isolation and Loneliness
- 1. Time Consumption:
– Obsessive Behavior: Individuals may spend excessive amounts of time searching for, acquiring, and maintaining their collections. This can lead to neglect of social relationships and responsibilities.
– Prioritization: The prioritization of artifact-related activities over social interactions can result in reduced opportunities for social engagement.
- 2. Financial Strain:
– Resource Allocation: Significant financial resources may be diverted to support the addiction, potentially leading to financial stress. This stress can cause strain in relationships, particularly if family or partners are affected by the financial decisions.
– Debt and Isolation: Financial difficulties can lead to isolation as individuals may withdraw from social situations to avoid discussing their financial issues.
- 3. Emotional Attachment:
– Emotional Substitution: Artifacts may become substitutes for emotional fulfillment typically gained from human interactions, leading to a preference for solitude.
– Loss of Interest: Over time, individuals may lose interest in social activities that do not involve their artifacts, leading to a narrowing of their social circle.
- 4. Social Disconnect:
– Niche Interests: The specialized nature of artifact collecting can make it challenging to find others with similar interests, potentially leading to feelings of isolation.
– Perceived Judgment: Individuals may fear judgment or lack of understanding from others regarding their intense interest in artifacts, leading to withdrawal from social interactions.
- 5. Mental Health Impacts:
– Anxiety and Depression: The pressures of maintaining a collection, coupled with potential financial and social consequences, can contribute to anxiety and depression, exacerbating feelings of loneliness.
– Identity and Self-Worth: For some, their identity and self-worth may become tied to their collection, leading to emotional distress if they perceive their collection as inadequate.
### Mitigating Isolation and Loneliness
- 1. Community Engagement:
– Joining clubs or online forums related to artifact collecting can provide social interaction and a sense of community.
- 2. Balanced Lifestyle:
– Efforts should be made to balance artifact-related activities with other social and recreational activities.
- 3. Professional Support:
– Seeking support from mental health professionals can help address underlying issues and develop healthier relationships with artifact collecting.
- 4. Open Communication:
– Discussing interests with friends and family can foster understanding and support, reducing feelings of isolation.
In conclusion, while artifact addiction is not a formally recognized condition, the behaviors associated with intense preoccupation with artifacts can potentially lead to isolation and loneliness. Recognizing the signs and taking proactive steps to maintain social connections and mental well-being is crucial.
Effects of artifact on your relationships
Artifacts, in the context of relationships, refer to objects or items that hold significance and meaning, such as photographs, gifts, or heirlooms. These artifacts can have both positive and negative effects on relationships. Here’s a closer look at both sides:
### Positive Effects
- 1. Strengthening Bonds:
– Shared Memories: Artifacts like photographs or souvenirs from trips can evoke shared memories, reinforcing the bond between individuals by reminding them of the good times they’ve experienced together.
– Sentimental Value: Gifts exchanged between partners, such as jewelry or personalized items, can serve as constant reminders of love and commitment, fostering a deeper emotional connection.
- 2. Facilitating Communication:
– Conversation Starters: Artifacts can serve as excellent conversation starters, allowing individuals to share stories and experiences, thereby enhancing understanding and empathy within the relationship.
– Cultural Exchange: Artifacts from different cultures or backgrounds can promote learning and appreciation, enriching the relationship through cultural exchange and understanding.
- 3. Providing Comfort and Support:
– Emotional Anchors: During challenging times, certain artifacts can provide comfort and a sense of stability, reminding individuals of their partner’s support and love.
– Legacy and Continuity: Heirlooms or family artifacts can provide a sense of continuity and belonging, helping partners feel connected to each other’s histories and families.
### Negative Effects
- 1. Triggering Negative Emotions:
– Painful Memories: Some artifacts may be associated with negative or painful memories, such as reminders of past arguments or losses, which can cause distress and strain the relationship.
– Comparison and Jealousy: Artifacts from previous relationships, like old love letters or gifts, might trigger feelings of jealousy or insecurity, leading to tension between partners.
- 2. Creating Misunderstandings:
– Misinterpretation: The significance of an artifact might be misunderstood or undervalued by one partner, leading to feelings of neglect or lack of appreciation.
– Cultural Misunderstandings: Artifacts from different cultural backgrounds might be misinterpreted, potentially causing offense or misunderstanding if not properly communicated.
- 3. Causing Clutter and Stress:
– Physical Space: An overabundance of artifacts, especially if they are not mutually appreciated, can lead to clutter, creating stress and conflict over living space and organization.
– Emotional Burden: Holding onto too many artifacts for sentimental reasons can become an emotional burden, making it difficult for individuals to move forward or let go of the past.
In conclusion, artifacts play a significant role in relationships by serving as symbols of shared experiences and emotions. While they can enhance bonds and facilitate communication, they can also introduce challenges if not managed thoughtfully. The key is to recognize the impact of these artifacts and address any issues they may present, ensuring they contribute positively to the relationship.
How To Stop & Quit Your artifact Addiction
Finally, you think you are addicted to artifact and you are wondering how to quit it? How to break and overcome your cravings for artifact?
Here are the best solutions, steps, supports, resources, and help you can get to treat your artifact addiction.
Main steps and solutions to break the artifact addiction
Artifact addiction, often associated with the compulsive collection or hoarding of items, can be challenging to overcome. While the term “artifact addiction” is not widely recognized in clinical settings, it can be akin to hoarding disorder or compulsive collecting. Here are some general steps that might help individuals address and overcome this behavior:
- 1. Acknowledgment and Acceptance:
– Recognize the problem: Understand that the behavior is affecting your life negatively.
– Accept the need for change: Be open to seeking help and making lifestyle adjustments.
- 2. Seek Professional Help:
– Therapy: Engage with a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, who specializes in hoarding or compulsive behaviors.
– Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This is particularly effective in addressing the underlying thoughts and behaviors associated with addiction.
- 3. Develop a Plan:
– Set realistic goals: Break down the process into manageable steps, such as decluttering one room at a time.
– Create a schedule: Allocate specific times for organizing and decluttering.
- 4. Organize and Declutter:
– Sort items: Categorize items into keep, donate, sell, or discard.
– Prioritize: Focus on items that hold genuine value or necessity.
- 5. Build a Support System:
– Involve family and friends: They can provide encouragement and practical help.
– Join support groups: Connect with others who have similar experiences for mutual support.
- 6. Develop New Habits:
– Mindfulness: Practice being present and aware of your actions and decisions.
– Limit acquisitions: Set rules for acquiring new items, such as a one-in-one-out policy.
- 7. Address Underlying Issues:
– Emotional triggers: Identify and work through emotional triggers that lead to compulsive collecting.
– Stress management: Develop healthy coping mechanisms for stress and anxiety.
- 8. Monitor Progress:
– Keep a journal: Document your journey, noting successes and areas for improvement.
– Regular check-ins: Schedule follow-up sessions with a therapist to assess progress and adjust strategies as needed.
- 9. Celebrate Successes:
– Acknowledge achievements: Reward yourself for reaching milestones, reinforcing positive behavior.
- 10. Maintain Long-term Strategies:
– Continuous evaluation: Regularly assess your relationship with items and adjust strategies to prevent relapse.
– Stay engaged: Keep participating in therapy or support groups to maintain progress.
Overcoming artifact addiction is a gradual process that requires commitment, patience, and support. Professional guidance is crucial in addressing the psychological aspects of the behavior, while practical steps can help manage the physical aspects.Actually, that’s what most documentation out there is about… However, quitting a digital addiction can be a bit trickier than that.
So our team, after testing many ways, designed a bulletproof way to overcome them. Here are some clear and practical steps that are very powerful to quit a digital addiction, including artifact:
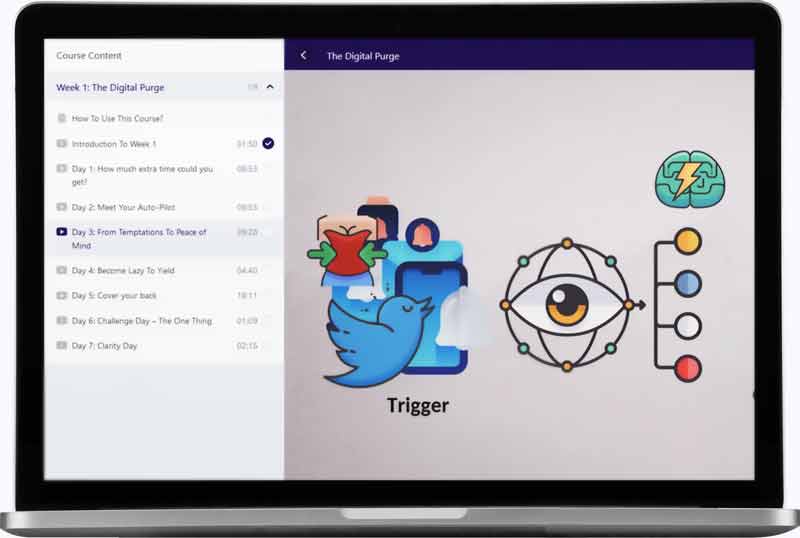
1. Purge temptations: Get rid of artifact
First, cleaning your life from temptations is much easier than resisting them. Disable or delete your artifact accounts, change the password and hide it somewhere you can’t access easily, keep your phone / computer far away… Out of sight, out of mind.
Here is a video from our course The Digital Purge. on how to add resistance to your temptations, so you become so lazy to engage with them that you give them up:
2. Spot & Reveal your emotional triggers
Second, there are some reasons, often hidden ones, that your brain and your heart love so much artifact. Those reasons act as triggers to pull your cravings. Rather than chasing the addiction, it’s a more efficient strategy to look at the feelings driving you toward it. That way you can cure and heal the feeling. You’ll feel better, and the cravings will magically disappear. Just get away.
3. Rewire to life

An addiction FOMO (fear of missing out) can be huge and really painful to resist, especially if it was here for a long time. However, learning to live with it is necessary to build a life full of peace and joy. Strategies to fight FOMO and rewire to life include meditation, nature activities, social interaction, intellectual and creative projects, meaningful adventures… basically anything that fills your soul.
4. How to not relapse and fully recover from artifact?
Finally, it’s important to acknowledge that quitting may take days, weeks, months, or even years. Getting over and quitting artifact forever can be difficult. You may relapse a few times, but the most important thing is that you keep engaging less and less with artifact. Each day you resist it is a day weakening your brain connections with artifact. From your patience and discipline will arise incredible mind strength, hope, and wisdom.

Best artifact blocker apps & functionalities
Additionally, you can increase your chance of withdrawal by limiting or blocking access to artifact using these apps.
They will help you filter, reduce, or block artifact:
In today’s digital age, video games can be both entertaining and addictive. For parents, educators, or individuals looking to manage screen time, finding effective tools to limit or block access to video games is crucial. Here are five of the best apps designed to help manage and control video game usage:
- 1. Qustodio
– Overview: Qustodio is a comprehensive parental control app that offers a wide range of features to manage and monitor digital activity.
– Features: It allows you to set time limits for specific apps and games, block inappropriate content, and monitor online activity. The app also provides detailed reports on usage.
– Platforms: Available on Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Kindle.
- 2. Net Nanny
– Overview: Known for its robust internet filtering capabilities, Net Nanny also offers tools to manage video game usage.
– Features: It includes features like app blocking, screen time management, and real-time alerts. Parents can set schedules for when games can be played and receive notifications when limits are reached.
– Platforms: Compatible with Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Kindle Fire.
- 3. FamilyTime
– Overview: FamilyTime is a versatile parental control app designed to help families manage screen time and ensure safe online experiences.
– Features: The app allows parents to block or limit access to specific games and apps, set daily screen time limits, and track device usage. It also offers location tracking and geofencing features.
– Platforms: Available on Android and iOS.
- 4. FamiSafe
– Overview: FamiSafe offers an intuitive interface and a variety of features to help manage children’s digital habits.
– Features: Users can block or restrict access to specific apps and games, set screen time limits, and receive reports on app usage. The appCheck our full video games addiction tool list (ranked):
Where to seek extra help?
Do you need some support and help to stop, overcome, and recover from your artifact addiction? If you or someone you know is struggling with artifact addiction, there are a few places to seek help.
The Ultimate Rewiring Program For artifact Addicts
Our course The Digital Purge. This course has already helped many digital addicts to rewire to what matters.
Is there a “treatment” to cure video games addiction?
Absolutely, there are effective treatments to help overcome video game addiction! If you or someone you know is struggling, here are some approaches that can make a big difference:
###
- 1. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a popular method that helps individuals understand and change the thoughts and behaviors contributing to their gaming habits. By identifying triggers and developing healthier coping strategies, CBT can reduce the urge to play excessively.
###
- 2. Setting Boundaries
Creating a structured schedule can help manage gaming time. Setting specific limits on when and how long you play can prevent gaming from interfering with daily responsibilities and relationships.
###
- 3. Engaging in Alternative Activities
Finding other hobbies or activities that are enjoyable can replace the time spent on video games. Whether it’s sports, reading, or learning a new skill, diversifying your interests can reduce the reliance on gaming for satisfaction.
###
- 4. Support Groups
Connecting with others who are facing similar challenges can provide encouragement and accountability. Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences and strategies for overcoming addiction.
###
- 5. Mindfulness and Stress Management
Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can help manage stress and reduce the impulse to turn to video games for relief.
###
- 6. Professional Help
Sometimes, seeking help from a mental health professional is the best step. Therapists can offer personalized guidance and support tailored to your specific situation.
###
- 7. Parental Involvement (for Younger Gamers)
For younger individuals, parental support is crucial. Setting rules around gaming, monitoring game content, and encouraging other activities can help mitigate addiction risks.
Remember, overcoming video game addiction is entirely possible with the right strategies and support. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for assistance. Taking the first step towards change is a brave and positive move!
Does video games therapy exist?
Yes, therapy to address video game addiction does exist. As video games have become an integral part of modern entertainment, concerns about excessive gaming and its impact on individuals’ lives have grown. Video game addiction, often referred to as gaming disorder, is characterized by impaired control over gaming, increasing priority given to gaming over other activities, and continuation or escalation of gaming despite negative consequences.
Various therapeutic approaches are used to help individuals struggling with video game addiction:
- 1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This is one of the most common forms of therapy for gaming addiction. CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with excessive gaming. It also focuses on developing healthier coping mechanisms and improving time management skills.
- 2. Motivational Interviewing (MI): This approach involves working with individuals to enhance their motivation to change their gaming habits. It helps them explore and resolve ambivalence about reducing gaming time.
- 3. Family Therapy: Since gaming addiction can affect family dynamics, family therapy can be beneficial. It addresses communication issues, sets boundaries, and helps family members support the individual in their recovery process.
- 4. Group Therapy: Group sessions provide a supportive environment where individuals can share their experiences and learn from others facing similar challenges. It can also help reduce feelings of isolation.
- 5. Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques: These techniques can help individuals manage stress and anxiety, which may contribute to excessive gaming. Practices like meditation and yoga can promote relaxation and self-awareness.
- 6. Digital Detox Programs: Some treatment centers offer structured programs that include a period of abstinence from digital devices, combined with therapy and activities that promote healthy lifestyle changes.
- 7. Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to address underlying mental health issues such as depression or anxiety, which can contribute to gaming addiction.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of treatment can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the addiction. Seeking help from a mental health professional who specializes in gaming addiction can provide a tailored approach to recovery.
Additionally, as research in this area continues to evolve, new strategies and interventions may emerge to better address this issue.
Where to find support groups if you are addicted to artifact?
If you or someone you know is struggling with video game addiction, finding the right support group can be an essential step towards recovery. Here are some places where you can find support groups for video game addicts:
- 1. Online Support Groups:
– OLGA (Online Gamers Anonymous): This is a well-known online community that offers support for individuals struggling with gaming addiction. They provide forums, chat rooms, and resources for both addicts and their families.
– Reddit: Subreddits like r/StopGaming offer a community of individuals who share experiences and strategies for overcoming gaming addiction.
- 2. Local Support Groups:
– Therapists and Counselors: Many therapists specialize in addiction and can recommend local support groups or create one-on-one therapy plans.
– Community Centers: Check with local community centers or libraries, which may host support groups or have information on local meetings.
- 3. 12-Step Programs:
– Some areas have adapted 12-step programs similar to those used for alcohol and drug addiction to address video game addiction.
- 4. Mental Health Organizations:
– Organizations like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) or Mental Health America may offer resources or support groups for behavioral addictions, including gaming.
- 5. Healthcare Providers:
– Speak with a primary care doctor or mental health professional who may have recommendations for local support groups or treatment programs.
- 6. Educational Institutions:
– Schools and universities often have counseling services that can provide support or direct students to appropriate resources.
- 7. Social Media Groups:
– Platforms like Facebook have groups dedicated to supporting individuals with gaming addiction, where members can share experiences and advice.
When seeking support, it’s important to find a group or resource that feels comfortable and supportive. Each person’s journey with addiction is unique, so it may take some time to find the right fit.
But other artifact addiction solutions exist
If you or someone you know is struggling with an addiction to collecting artifacts, it’s important to seek professional help. Here are some individuals and professionals you can consider reaching out to:
- 1. Therapist or Counselor: A licensed therapist or counselor who specializes in addiction can provide personalized strategies and coping mechanisms to address the underlying issues related to artifact addiction.
- 2. Psychologist: A psychologist can help in understanding the behavioral and emotional aspects of addiction and work on developing healthier habits.
- 3. Psychiatrist: If there are underlying mental health issues contributing to the addiction, a psychiatrist can offer a comprehensive evaluation and, if necessary, prescribe medication to help manage symptoms.
- 4. Art or Cultural Heritage Consultant: These professionals can provide guidance on the ethical and legal aspects of collecting artifacts, helping to shift the focus from compulsive collecting to more responsible and informed practices.
- 5. Life Coach: A life coach can assist in setting goals and developing a balanced lifestyle that reduces the reliance on collecting artifacts as a primary source of fulfillment.
- 6. Legal Advisor: If the addiction has led to legal issues, such as the acquisition of artifacts that may not have been obtained legally, consulting with a legal advisor can help navigate these challenges.
- 7. Art Historian or Curator: Engaging with professionals who have a deep understanding of artifacts can help redirect the passion into educational or volunteer opportunities that satisfy the interest in a more constructive manner.
- 8. Financial Advisor: If the addiction has financial implications, a financial advisor can help in creating a plan to manage and recover from any financial strain caused by the addiction.
These professionals can provide support tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of the individual, helping to address both the addiction and any related issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, overcoming artifact addiction is a journey that requires self-awareness, commitment, and support. By recognizing the impact of this addiction on our lives, we can begin to take proactive steps towards change. Whether it’s through digital detoxes, setting boundaries, or seeking professional help, there are numerous strategies to regain control and foster a healthier relationship with technology. It’s important to remember that while artifacts like smartphones and social media platforms are integral to modern life, they should enhance rather than dominate our existence. By prioritizing real-world connections and experiences, we can create a balanced lifestyle that nurtures both our mental well-being and personal growth. Ultimately, overcoming artifact addiction is not about eliminating technology from our lives but about using it mindfully and intentionally to enrich our daily experiences.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.Here is the trailer:
To Go Further
Take our 4-min test
How to help someone with artifact addiction?
Helping someone with artifact addiction, or any form of compulsive collecting behavior, involves a compassionate and structured approach. Here are some steps to consider:
- 1. Understand the Addiction: Educate yourself about artifact addiction. This involves understanding why the person feels compelled to collect artifacts and how it affects their life. Recognize that this behavior might be linked to deeper psychological issues such as anxiety, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- 2. Open Communication: Approach the individual with empathy and without judgment. Initiate a conversation to express your concerns and willingness to help. Make sure to listen actively to their perspective and feelings about their collecting habits.
- 3. Encourage Professional Help: Suggest seeking help from a mental health professional who specializes in addiction or compulsive behaviors. Therapy options such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be effective in addressing the underlying issues and developing healthier coping mechanisms.
- 4. Set Boundaries: If the addiction is impacting your relationship or living situation, set clear and respectful boundaries. Explain how their behavior affects you and what changes are necessary for a healthier dynamic.
- 5. Support Groups: Encourage participation in support groups where individuals can share experiences and strategies for managing their addiction. Groups like Hoarders Anonymous or other addiction support networks can provide a sense of community and understanding.
- 6. Assist in Organization: Help them organize and assess their collection. This might involve cataloging items, discussing the significance of each piece, and determining which items are truly valuable or necessary.
- 7. Promote Alternative Activities: Encourage engagement in alternative hobbies or activities that can fulfill the emotional needs met by collecting artifacts. This might include art, sports, or volunteering, which can provide a sense of purpose and satisfaction.
- 8. Monitor Progress: Regularly check in on their progress and offer ongoing support. Celebrate small victories and improvements to encourage continued efforts.
- 9. Be Patient: Recovery from addiction is a gradual process.
Best books about video games addiction
Video game addiction is a topic that has garnered increasing attention as gaming becomes more integrated into daily life. Several authors have explored this subject, offering insights into its psychological, social, and personal impacts. Here are five noteworthy books that delve into video game addiction:
- 1. “Irresistible: The Rise of Addictive Technology and the Business of Keeping Us Hooked” by Adam Alter
This book examines the broader scope of addictive technologies, including video games. Alter explores how game designers use psychological principles to keep players engaged, often leading to addictive behaviors. He provides a comprehensive look at the impact of these technologies on our lives and suggests ways to mitigate their addictive nature.
- 2. “Game Addiction: The Untold Stories of Game Addicts” by Neils Clark and P. Shavaun Scott
Clark and Scott delve into the personal stories of individuals affected by video game addiction. The book combines these narratives with scientific research to provide a balanced view of the issue. It discusses the psychological mechanisms behind gaming addiction and offers practical advice for those struggling with it.
- 3. “Unplugged: My Journey into the Dark World of Video Game Addiction” by Ryan Van Cleave
This memoir offers a personal account of the author’s battle with video game addiction. Van Cleave shares his experiences of how gaming took over his life, affecting his relationships and career. His story is both a cautionary tale and a source of hope for those seeking to overcome similar challenges.
- 4. “Video Game Addiction: The Essential Guide for Parents and Gamers” by Alexis Leon
Aimed at both parents and gamers, this book provides an overview of video game addiction and its effects. Leon offers practical strategies for managing gaming habits and fostering a healthy balance between gaming and other life activities. It’s a valuable resource for anyone looking to understand and address gaming addiction.
- 5. “Reset: Gaming and the Psychology of Video Game Addiction” by Michael R.
Research about video games addiction
Video game addiction, often referred to as gaming disorder, has been the subject of numerous studies as researchers seek to understand its prevalence, causes, and effects. Below are summaries of several official studies that have contributed significantly to the field:
1. Gentile et al. (2011. – “Pathological Video Game Use Among Youths: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study”:
– Published In: Pediatrics
– Summary: This study tracked over 3,000 children in Singapore over two years to assess the prevalence and impact of pathological gaming. It found that approximately 9% of gamers were classified as pathological, exhibiting behaviors similar to other addictive disorders. The study highlighted that pathological gaming was associated with increased depression, anxiety, social phobias, and lower academic performance.
2. Weinstein et al. (2017. – “Internet Gaming Disorder: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature”:
– Published In: Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment
– Summary: This systematic review analyzed existing literature on Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) to understand its characteristics and impact. The study emphasized the need for standardized diagnostic criteria and found that IGD was associated with various psychological issues, including depression and anxiety. The review also discussed the neurobiological underpinnings of gaming addiction, suggesting similarities with other addictive behaviors.
3. Przybylski et al. (2017. – “Motivational, Emotional, and Behavioral Correlates of Fear of Missing Out”:
– Published In: Computers in Human Behavior
– Summary: While not exclusively focused on gaming addiction, this study explored the concept of “Fear of Missing Out” (FoMO) and its relationship with online behaviors, including gaming. The research found that FoMO could drive excessive gaming as individuals seek to remain connected and engaged with online communities. This behavioral pattern can contribute to gaming addiction, highlighting the social aspects of the disorder.
4. Király et al. (2018. – “Ten-Item Internet Gaming Disorder Test (IGDT-10.: Measurement Invariance and Cross-Cultural Validation Across Seven Language-Based Samples”:
– Published In: Psychology of Addictive Behaviors
– Summary: This study focused on the development and validation of the IGDT-10, a tool designed to assess Internet Gaming Disorder across different cultures. The research involved participants from multiple countries and languages, confirming the tool’s reliability and validity. The study underscored the importance of a standardized assessment for better understanding and diagnosing gaming addiction globally.
5. King et al. (2019. – “Clinical Interventions for Technology-Based Problems: Excessive Internet and Video Game Use”:
– Published In: Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy
– Summary: This study reviewed various clinical interventions aimed at addressing excessive gaming and internet use. It highlighted cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) as an effective treatment for gaming disorder, alongside other therapeutic approaches. The research provided insights into the challenges of treating gaming addiction and emphasized the need for tailored interventions based on individual needs.
These studies collectively contribute to a deeper understanding of video game addiction, its psychological and social implications, and potential treatment strategies. They also highlight the importance of continued research to refine diagnostic criteria and develop effective interventions.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.
The impact of video games on our society
Video game addiction has emerged as a significant concern in modern society, affecting individuals across various age groups and demographics. As video games have evolved from simple pixelated screens to immersive, complex virtual worlds, their influence has grown exponentially, leading to both positive and negative societal impacts. While gaming can offer cognitive benefits and foster social connections, excessive and compulsive gaming can lead to addiction, with profound implications for individuals and society at large.
### Psychological and Health Impacts
One of the most immediate effects of video game addiction is on mental health. Individuals who are addicted to gaming often experience increased levels of anxiety, depression, and stress. The immersive nature of games can lead to a detachment from reality, where players find it difficult to balance their virtual achievements with real-world responsibilities. This detachment can exacerbate feelings of isolation and loneliness, particularly if gaming becomes a substitute for real-world social interactions.
Physically, prolonged gaming sessions can lead to a sedentary lifestyle, contributing to obesity, poor posture, and repetitive strain injuries. Sleep deprivation is another common issue, as individuals may sacrifice rest to continue gaming, leading to fatigue and impaired cognitive function.
### Social Consequences
On a social level, video game addiction can strain relationships with family and friends. Individuals may prioritize gaming over spending time with loved ones, leading to conflicts and misunderstandings. The isolation that often accompanies addiction can further erode social skills, making it challenging for individuals to engage in face-to-face interactions.
Moreover, the online communities within games can sometimes propagate toxic behaviors, such as cyberbullying and harassment. These negative interactions can have a lasting impact on individuals, particularly younger players who may be more impressionable.
### Economic Impact
The economic implications of video game addiction are multifaceted. On one hand, the gaming industry is a significant economic driver, generating billions in revenue and creating numerous jobs. However, addiction can lead to decreased productivity in the workplace or academic settings, as individuals may neglect responsibilities in favor of gaming. This can result in job loss or poor academic performance, which has broader economic repercussions.
### Educational Challenges
For students, video game addiction can interfere with educational attainment. The time and energy devoted to gaming can detract from homework, study, and other academic pursuits. This distraction can lead to a decline in academic performance, which may have long-term consequences for future career opportunities.
### Addressing the Issue
Addressing video game addiction requires a multifaceted approach. Education and awareness are crucial in helping individuals recognize the signs of addiction and understand its potential impacts. Parents, educators, and mental health professionals play a vital role in monitoring gaming habits and encouraging healthy gaming practices.
Regulation and policy can also help mitigate the effects of gaming addiction. Some countries have implemented measures such as gaming curfews for minors and restrictions on in-game purchases to prevent excessive gaming. Game developers can contribute by designing games that encourage breaks and promote balanced gaming habits.
### Conclusion
While video games are an integral part of modern entertainment and culture, the potential for addiction poses significant challenges for individuals and society. By fostering awareness and promoting responsible gaming, society can harness the benefits of video games while minimizing their negative impacts. Balancing the virtual with the real world is essential to ensuring that gaming remains a healthy and enjoyable activity.
To go further, please check our course The Digital Purge.